Abstract
1. Prostaglandin-like material has been found in superfusates of cerebral cortex in unanaesthetized encéphale isolé cat preparations.
2. The material was assayed on the isolated rat uterus and identified by thin-layer chromatography.
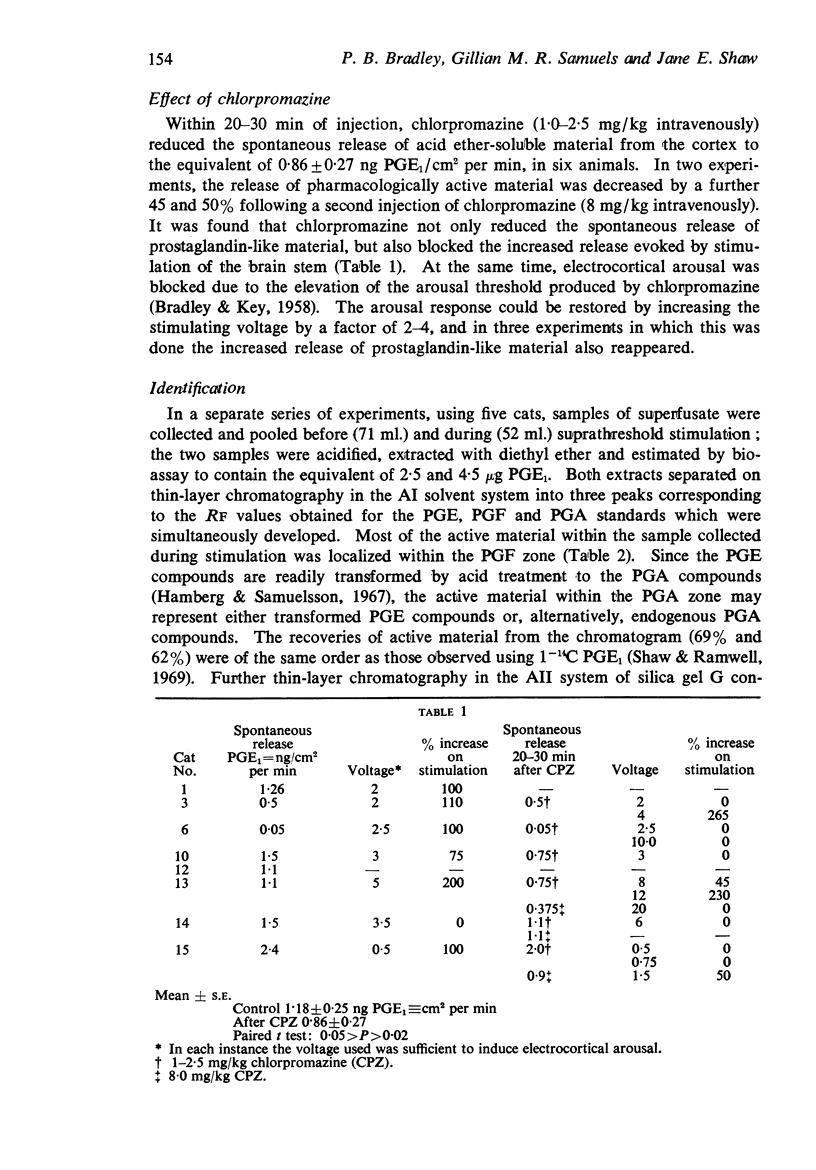
3. The level of spontaneous release of prostaglandin-like material was greater than that which had been found in anaesthetized preparations and it increased further with electrical stimulation of the reticular formation which induced electrocortical arousal.
4. Chlorpromazine (1·0-8·0 mg/kg) not only depressed the spontaneous release but blocked the increase evoked by stimulation concomitantly with blocking electrocortical arousal. Increasing the stimulating voltage to restore the arousal response also restored the evoked release of prostaglandins.
5. Most of the prostaglandin-like material released spontaneously was represented by E type compounds, but the increase with stimulation was mainly of F compounds.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avanzino G. L., Bradley P. B., Wolstencroft J. H. Actions of prostaglandins E1, E2, and F2-alpha on brain stem neurones. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 May;27(1):157–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., ELKES J. A technique for recording the electrical activity of the brain in the conscious animal. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1953 Aug;5(3):451–456. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(53)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., ELKES J. The effects of some drugs on the electrical activity of the brain. Brain. 1957 Mar;80(1):77–117. doi: 10.1093/brain/80.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., KEY B. J. The effect of drugs on arousal responses produced by electrical stimulation of the reticular formation of the brain. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1958 Feb;10(1):97–110. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(58)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Carlson L. A., Weeks J. R. The prostaglandins: a family of biologically active lipids. Pharmacol Rev. 1968 Mar;20(1):1–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCEANI F., WOLFE L. S. PROSTAGLANDINS IN BRAIN AND THE RELEASE OF PROSTAGLANDIN-LIKE COMPOUNDS FROM THE CAT CEREBELLAR CORTEX. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1965 May;43:445–450. doi: 10.1139/y65-045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duda P., Horton E. W., McPherson A. The effects of prostaglandins E1, F1-alpha and F2-alpha on monosynaptic reflexes. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):151–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Myers R. D. Appearance of 5-hydroxytryptamine and an unidentified pharmacologically active lipid acid in effluent from perfused cerebral ventricles. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):837–855. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN K., SAMUELSSON B. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS: XIX. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PROSTAGLANDINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:117–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORTON E. W. ACTIONS OF PROSTAGLANDINS E1, E2 AND E3 ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Feb;22:189–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes S. W., Horton E. W. The identification of four prostaglandins in dog brain and their regional distribution in the central nervous system. J Physiol. 1968 Apr;195(3):731–741. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. W., Main I. H. Further observations on the central nervous actions of prostaglandins F2a and E1. With an addendum on the effects of prostglandins E1 and F2a on systemic arterial blood pressure in chicks. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Aug;30(3):568–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02163.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. W., Main I. H. Identification of prostaglandins in central nervous tissues of the cat and chicken. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Aug;30(3):582–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka K., Ramwell P. W., Jessup S. Prostaglandins: localization in subcellular particles of rat cerebral cortex. Science. 1967 Sep 8;157(3793):1187–1189. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3793.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Tebecis A. K. Prostaglandins and toad spinal cord responses. Nature. 1968 Mar 16;217(5133):1076–1077. doi: 10.1038/2171076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E., Jessup R. Spontaneous and evoked release of prostaglandins from frog spinal cord. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):998–1004. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E. Spontaneous and evoked release of prostaglandins from cerebral cortex of anesthetized cats. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):125–134. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMUELSSON B. IDENTIFICATION OF A SMOOTH MUSCLE-STIMULATING FACTOR IN BOVINE BRAIN. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 20;84:218–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. E., Ramwell P. W. Release of a substance P polypeptide from the cerebral cortex. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):262–267. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. E., Ramwell P. W. Release of prostaglandin from rat epididymal fat pad on nervous and hormonal stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1498–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


