Abstract
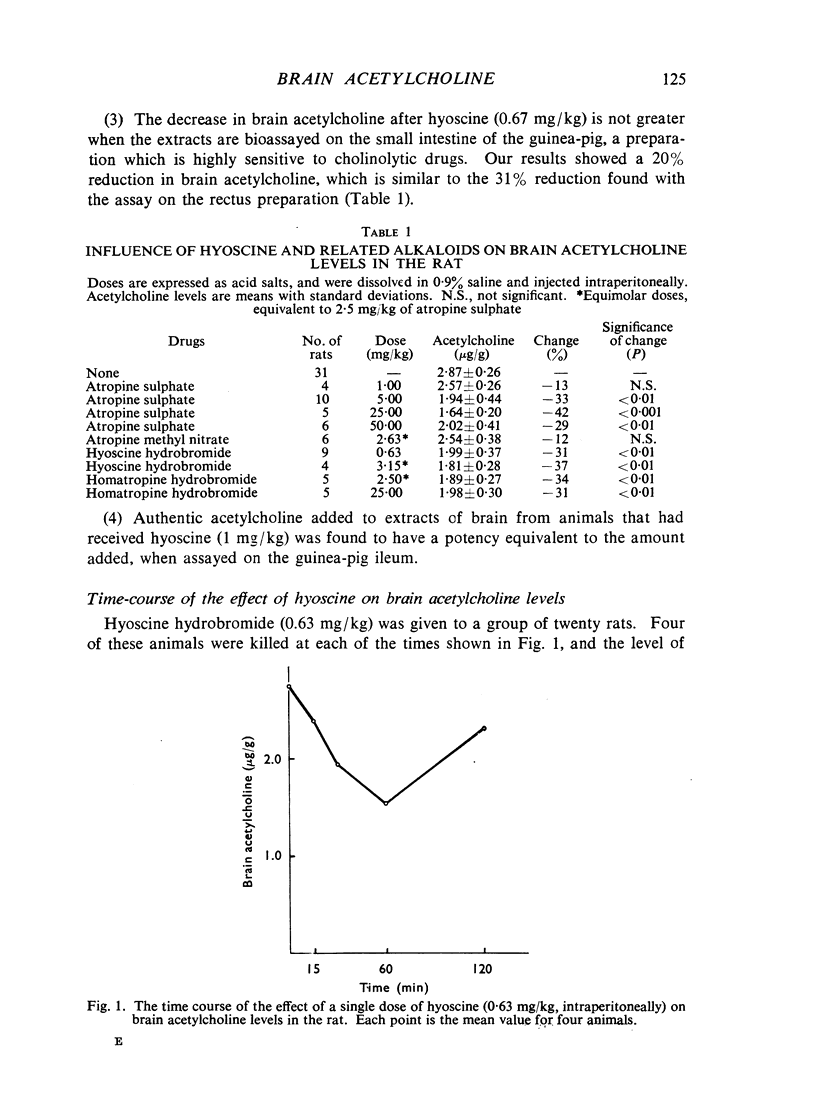
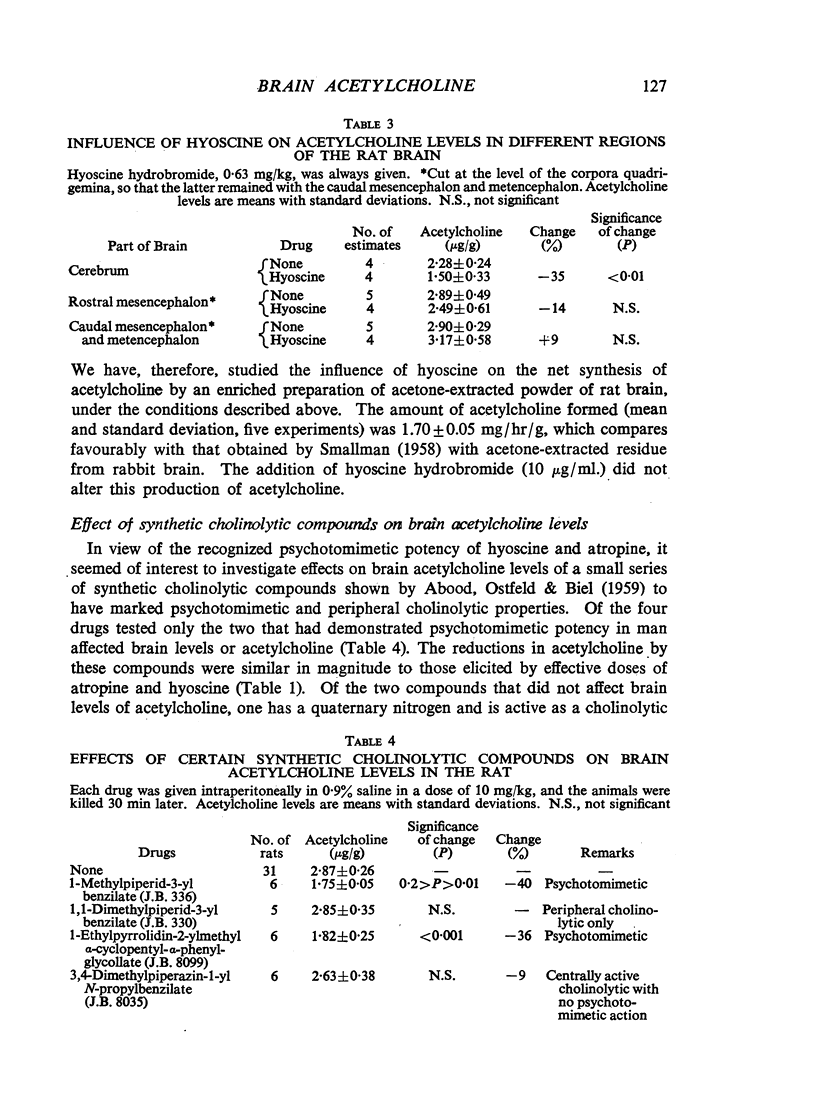
A number of centrally acting cholinolytic drugs reduced levels of cerebral acetylcholine in the rat. Among its naturally occurring analogues, hyoscine had the greatest potency, producing a decrease of 31% at a dose of 0.63 mg/kg. Atropine methyl nitrate, which acts as a cholinolytic drug in the periphery, had no effect on brain acetylcholine levels. The fall in acetylcholine produced by hyoscine was greatest after 60 min and disappeared at about 120 min. The animals tended to show a partial tolerance to this effect of hyoscine when the drug was administered repeatedly. The reduction in acetylcholine after hyoscine was restricted to the cerebral hemispheres, and did not appear in subcortical regions of the brain. Hyoscine had no influence on the net synthesis of acetylcholine by acetone-extracted powder of rat brain. In a series of four synthetic cholinolytic drugs, only the two with conspicuous psychotomimetic actions in man produced a decrease in brain acetylcholine comparable to that seen with hyoscine and related alkaloids.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABOOD L. G., OSTFELD A., BIEL J. H. Structure-activity relationships of 3-piperidyl benzilates with psychotogenic properties. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1959 Jun 1;120(2):186–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERRY J. F., STOTZ E. Acetylcholine and acetoin in brain during acetaldehyde intoxication. Q J Stud Alcohol. 1956 Jun;17(2):190–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSSLAND J., REDFERN P. H. CHROMATOGRAPHIC BEHAVIOUR OF ACETYLCHOLINE IN BRAIN EXTRACTS. Life Sci. 1963 Oct;10:711–716. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(63)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOMER F. R., SCHUELER F. W. Investigations of the amnesic properties of scopolamine and related compounds. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1960 Sep 1;127:449–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIARMAN N. J., PEPEU G. Drug-induced changes in brain acetylcholine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Oct;19:226–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEB C., MAGNI F., ROSSI G. F. [Study of the electroencephalographic effects of atropine in the cat]. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1959 Sep 30;35:1168–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONGO V. G. Effects of scopolamine and atropine electroencephalographic and behavioral reactions due to hypothalamic stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 Feb;116(2):198–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LULLMANN H., FORSTER W., WESTERMANN E. Uber eine paradoxe Atropinwirkung an isolierten Organen und ihre statistische Erfassung. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1952;215(1-2):8–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. F. The spontaneous and evoked release of acetylcholine from the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Jan;165(1):98–116. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPEU G. EFFECT OF 'TREMORINE' AND SOME ANTI-PARKINSON'S DISEASE DRUGS ON ACETYLCHOLINE IN THE RAT'S BRAIN. Nature. 1963 Nov 30;200:895–895. doi: 10.1038/200895a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHTER D., CROSSLAND J. Variation in acetylcholine content of the brain with physiological state. Am J Physiol. 1949 Nov;159(2):247–255. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1949.159.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMALLMAN B. N., FISHER R. W. Effect of anticholinesterases on acetylcholine levels in insects. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Jun;36(6):575–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMALLMAN B. N. The choline acetylase activity of rabbit brain. J Neurochem. 1958;2(2-3):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZERB J. C. Nature of acetylcholine-like activity released from brain in vivo. Nature. 1963 Mar 9;197:1016–1017. doi: 10.1038/1971016a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE R. P., BOYAJY L. D. Neuropharmacological comparison of atropine, scopolamine, banactyzine, diphenhydramine and hydroxyzine. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1960 Sep 1;127:260–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


