Abstract
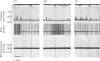
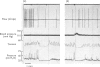
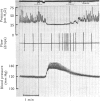
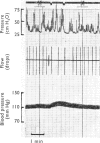
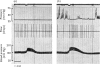
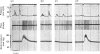
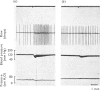
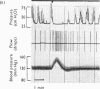
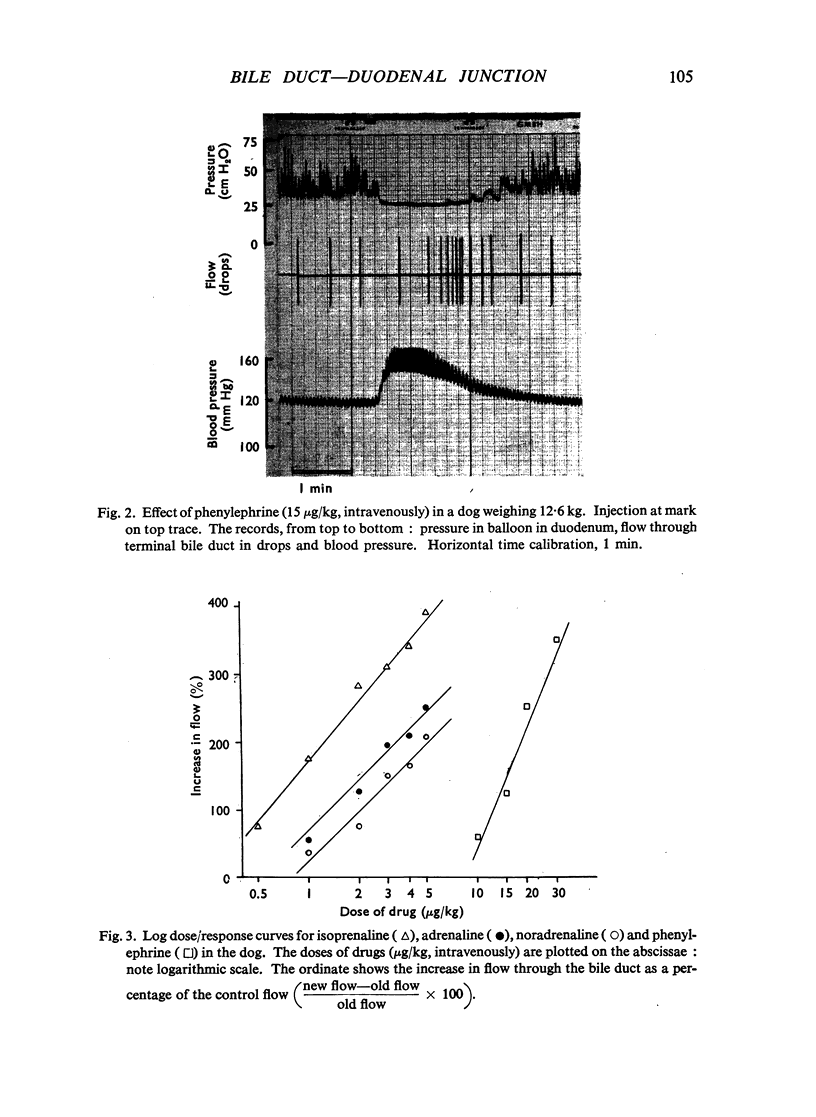
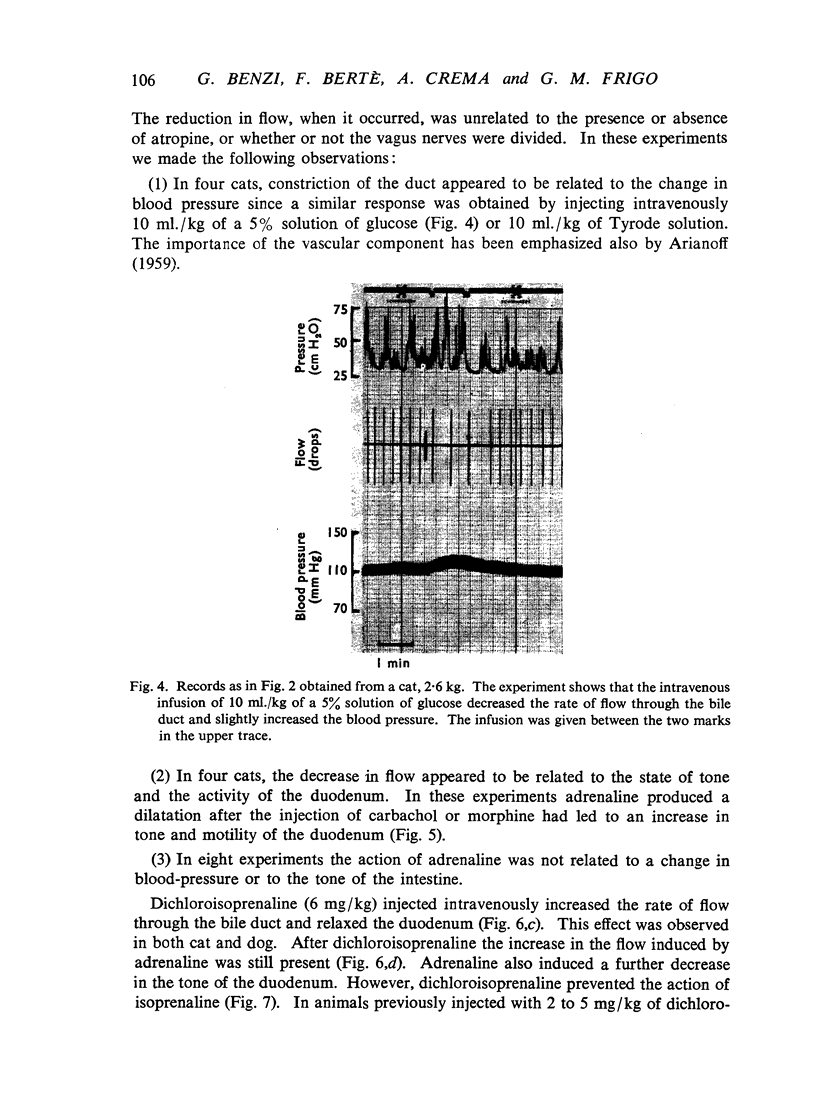
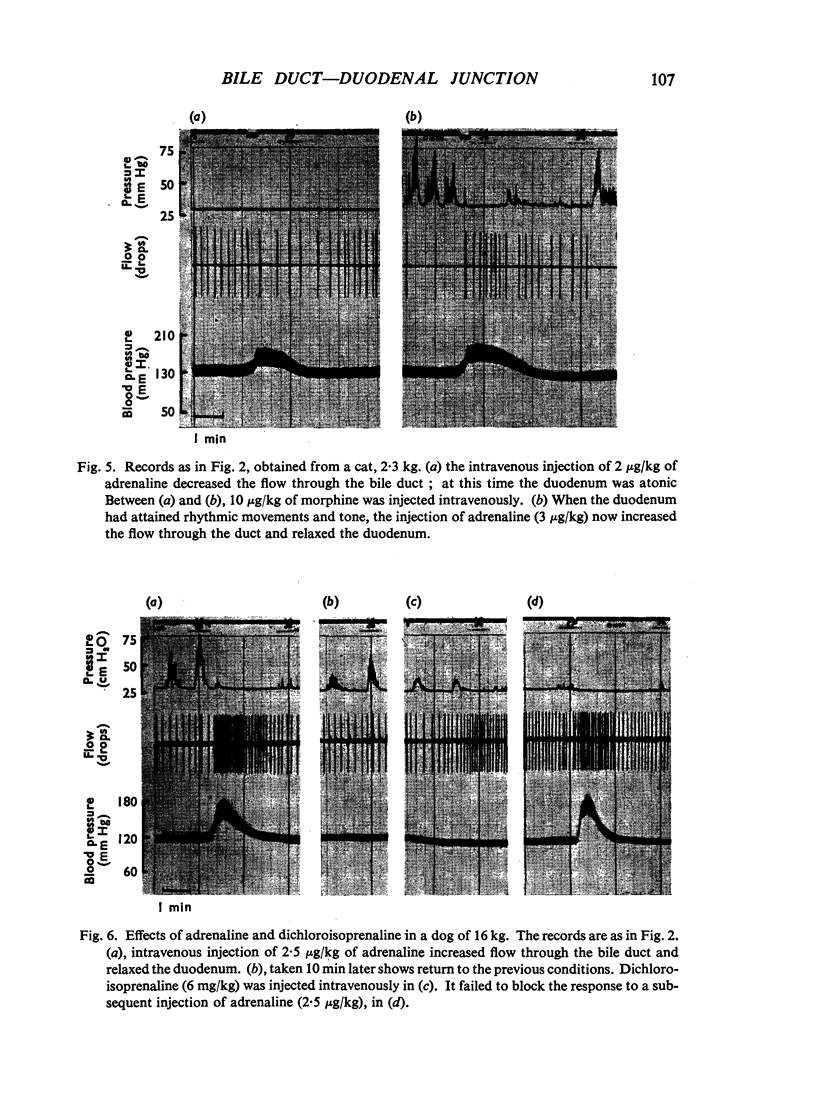
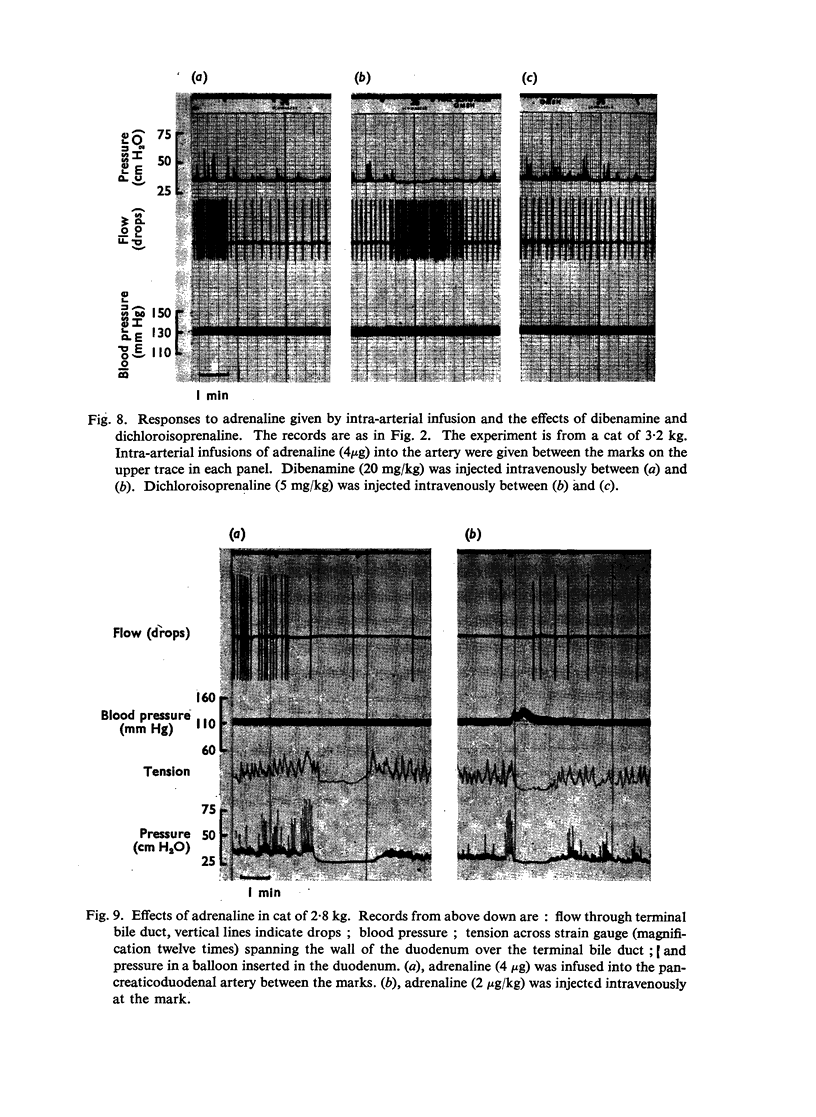
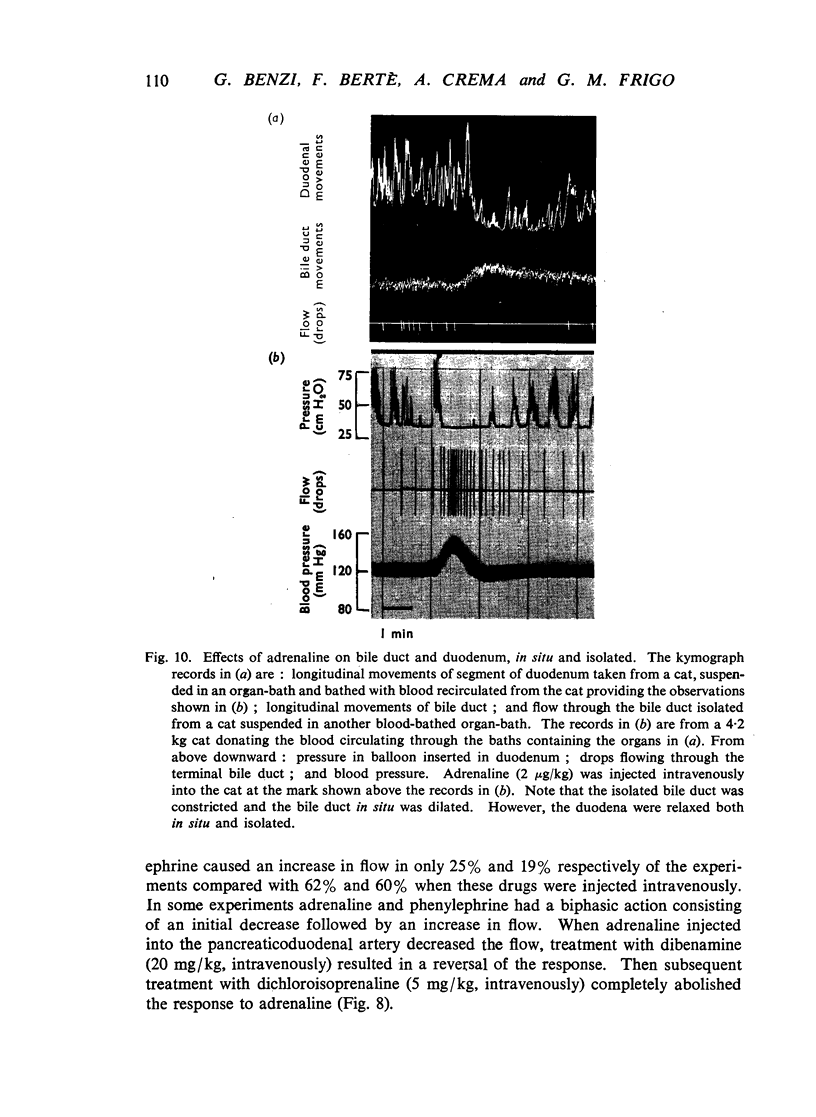
The actions of adrenaline, noradrenaline, phenylephrine and isoprenaline have been examined on flow through the terminal bile duct and on the tone of the duodenum in the vicinity of the terminal bile duct. These drugs were injected intravenously, or intra-arterially into the blood supply of the junction of the bile duct and duodenum. The effects of the antagonistic drugs, dibenamine and dichloroisoprenaline, were also tested. Isoprenaline always relaxed the duodenum and increased the flow through the bile duct. Adrenaline, noradrenaline and phenylephrine relaxed the duodenum, but had variable effects on the flow through the bile duct. It is concluded that adrenaline acts directly on the smooth muscle of the bile duct to contract it, but the influence of the neighbouring duodenal muscle may nevertheless result in an increase in flow through the duct.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CREMA A., BENZI G., BERTE F. The action of some natural substances on the terminal portion of the common bile duct isolated "in toto". Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1962 Jun 1;137:307–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMA A., BENZI G. [Behavior in vitro of Oddi's sphincter of animals]. Arch Fisiol. 1961 Sep 25;60:374–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMA A., BENZI G. [Pharmacological data on the isolated sphincter of Oddi]. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1960 Dec 31;129:264–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMA A., BERTE F. Action of sympathomimetic drugs on the isolated junction of the bile duct and duodenum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Apr;20:221–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERDMANN W. D., HENNE H. F. Uber spasmolytische Wirkungen am Sphincter Oddi. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1953;218(6):462–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOGLIATI A. E., CIOCATTO E., CATTANEO A. D., GIUDICE P. A. Les modifications du tonus des voies biliaires sous l'action de certains médicaments; recherches expérimentales de mamométrie biliaire. Arch Mal Appar Dig Mal Nutr. 1954 Apr;43(4):428–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANSER G., HERTTING G., RISSEL E., WEWALKA F. Untersuchungen über die Beeinflussbarkeit des Sphinkter Oddi. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1956 Mar 1;105(3-4):389–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORENZINI L., ELZENBAUM G. Dell'azione di alcuni farmaci sul dinamismo delle vie biliari extraepatiche e del problema dell'anestesia nell'esplorazione manometrica per operatoria di esse. G Ital Anestesiol. 1952 Apr;8(4):225–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALLOS A. J. An electrical caliper for continuous measurement of relative displacement. J Appl Physiol. 1962 Jan;17:131–134. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1962.17.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENGUY R. B., HALLENBECK G. A., BOLLMAN J. L., GRINDLAY J. H. Intraductal pressures and sphincteric resistance in canine pancreatic and biliary ducts after various stimuli. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1958 Mar;106(3):306–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PASECHNIK I. Kh. [Effect of noradrenalin on Oddi's sphincter tonus]. Farmakol Toksikol. 1959 Nov-Dec;22:519–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POILLEUX F., GOIDIN, NICHOLAIDIS Dystonies biliaires fonctionnelles. Role du pneumogastrique droit; étude expérimentale et déductions chirurgicales. Presse Med. 1952 Feb 13;60(10):196–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STALPORT J., NICOLAS E., DEMELENNE A., HORECZKI G. Sur la pharmacologie de la voie biliaire principale. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1959 Mar 1;119(1-2):142–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILLE G., HILFIKER H. [On the effect of drugs on the biliary system]. Arzneimittelforschung. 1962 May;12:461–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]