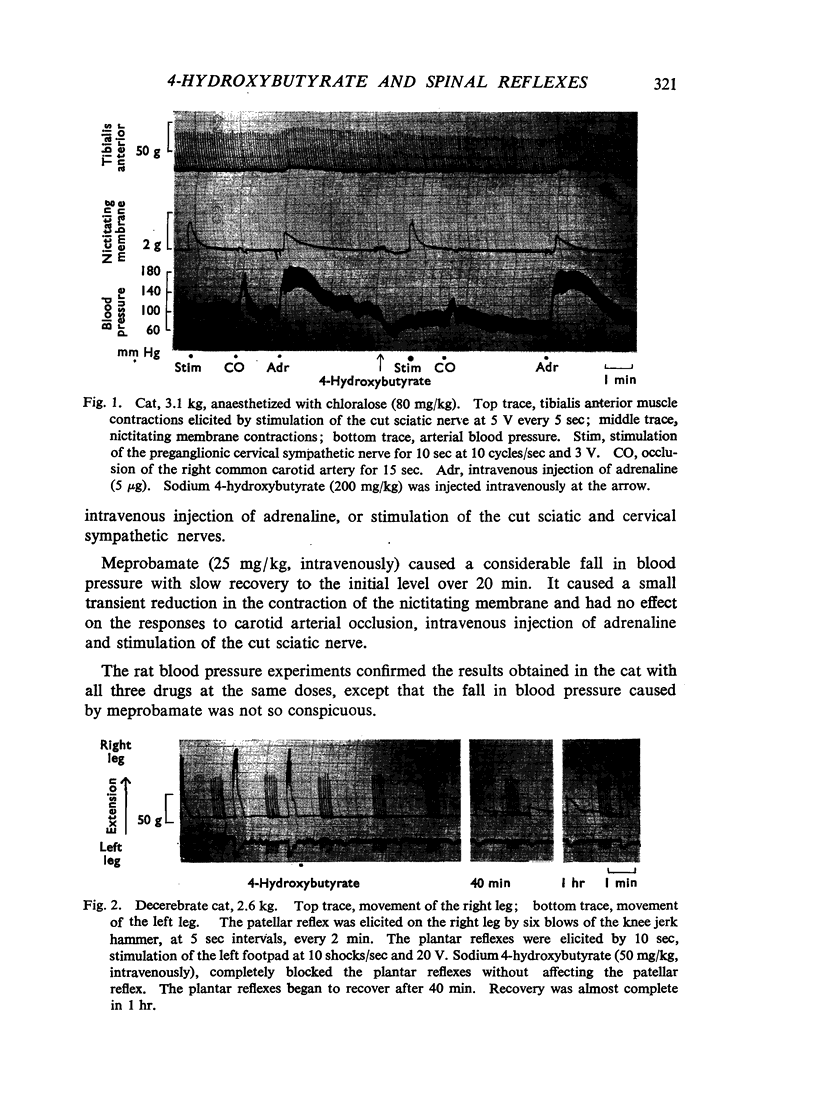
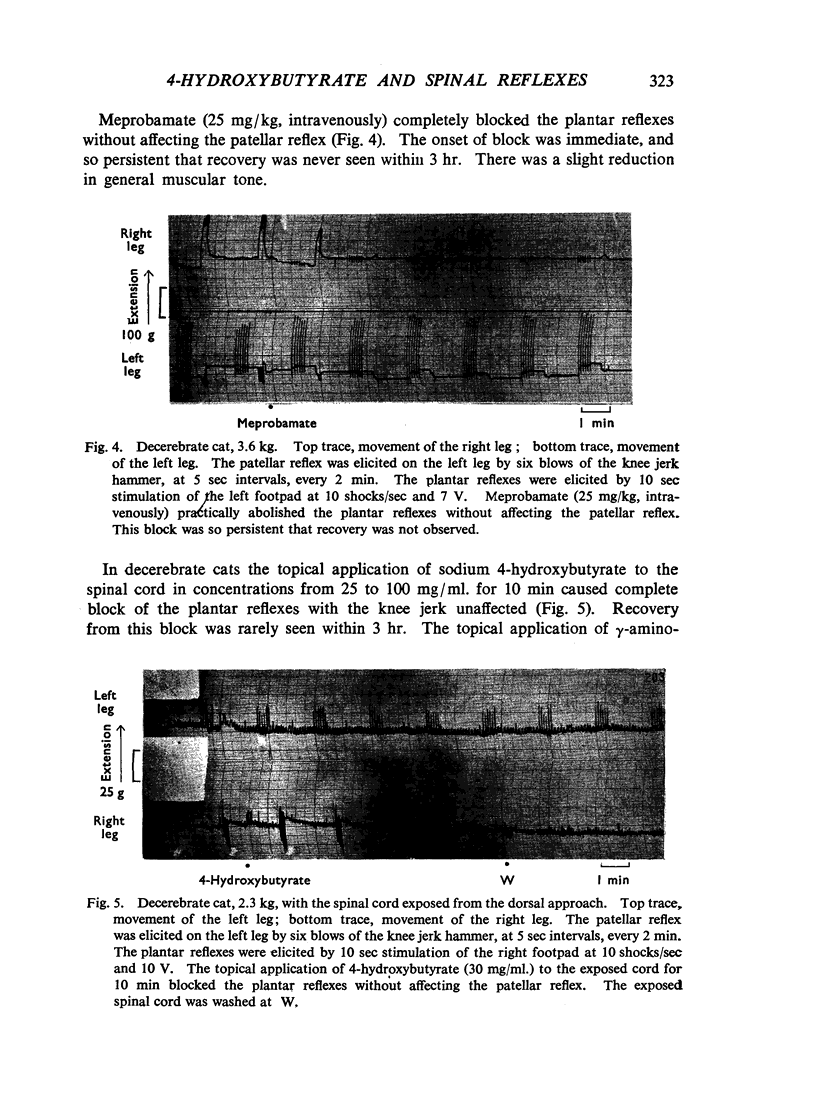
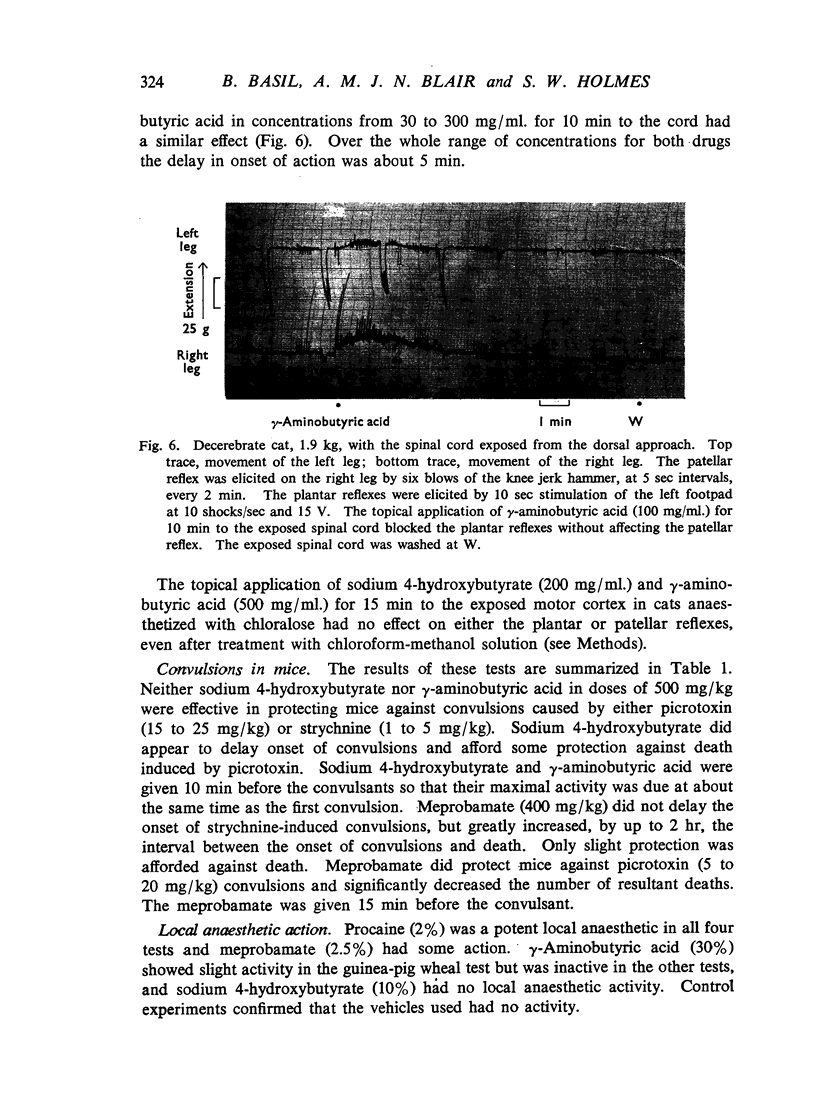
Abstract
The actions of sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate, γ-aminobutyric acid and meprobamate have been studied in unanaesthetized animals, in local anaesthetic tests, on isolated organ preparations, on convulsions induced by picrotoxin and strychnine, and on monosynaptic (patellar) and polysynaptic (plantar) reflexes of the spinal cord. Sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate induced a sleep-like state with three unusual features: the righting reflex was remarkably persistent, respiration was good throughout and recovery was abrupt. γ-Aminobutyric acid was inactive and meprobamate caused flaccid paralysis with loss of the righting reflex. None of the agents affected the responses of the rat diaphragm either to direct stimulation of the muscle or to indirect stimulation through the phrenic nerve. Only meprobamate reduced the responses of theguinea-pig isolated ileum preparation, showed local anaesthetic action and had an anticonvulsant action. All three compounds were capable, after intravenous or topical application, of blocking plantar reflexes in doses which did not affect the patellar reflex. The spinal animal responded in the same way, to the same dose of sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate, as the decerebrate preparation. Topical application to the motor cortex had no effect on spinal reflexes. We conclude that sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate acts preferentially on the internuncial neurones in the spinal cord but differs from meprobamate in its other actions. The similarity between the actions of sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate and of γ-aminobutyric acid provides furtherevidence in support of the hypothesis that sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate is involved in the γ-aminobutyric acid metabolic pathways.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BESSMAN S. P., ROSSEN J., LAYNE E. C. Gamma-Aminobutyric acid-glutamic acid transamination in brain. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):385–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIANCHI C., FRANCESCHINI J. Experimental observations on Haffner's method for testing analgesic drugs. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1954 Sep;9(3):280–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb01681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKMAN J. A., Jr, BURSON S. L., Jr Multiple nature of inhibitory factor (factor I) from brain. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Mar;94(3):450–452. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANA M., BARON C., LABORIT H. [Radioprotective action of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate (preliminary notes)]. Agressologie. 1962 May-Jun;3:497–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT K. A., HOBBIGER F. gamma Aminobutyric acid; circulatory and respiratory effects in different species; re-investigation of the anti-strychnine action in mice. J Physiol. 1959 Apr 23;146(1):70–84. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HONOUR A. J., McLENNAN H. The effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid and other compounds on structure of the mammalian nervous system which are inhibited by Factor I. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:306–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOUANY J. M., GERARD J., LABORIT H. [Comparison of the hypnogenic and protective actions of the sodium salts of butyric and 4-hydroxybutyric acids against certain convulsant agents]. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1960;154:1206–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Iontophoretic studies of neurones in the mammalian cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:274–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABORIT H., BUCHARD F., LABORIT G., KIND A., WEBER B. [Use of sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate in anesthesia and resuscitation]. Agressologie. 1960 Nov;1:549–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARRAZZI A. S., HART E. R., RODRIGUEZ J. M. Action of blood-borne gamma-aminobutyric acid on central synapses. Science. 1958 Feb 7;127(3293):284–285. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3293.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLENNAN H. A comparison of some physiological properties of an inhibitory factor from brain (factor I) and of gamma-aminobutyric acid and related compounds. J Physiol. 1957 Nov 14;139(1):79–86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M. W., JAKOBY W. B. Enzymatic utilization of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Apr;235:954–960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURPURA D. P., GIRADO M., SMITH T. G., Jr, GOMEZ J. A. Effects of systemically administered omega-amino and guanidino acids on spontaneous and evoked cortical activity in regions of blood-brain barrier destruction. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1958 Nov;10(4):677–685. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(58)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]