Abstract
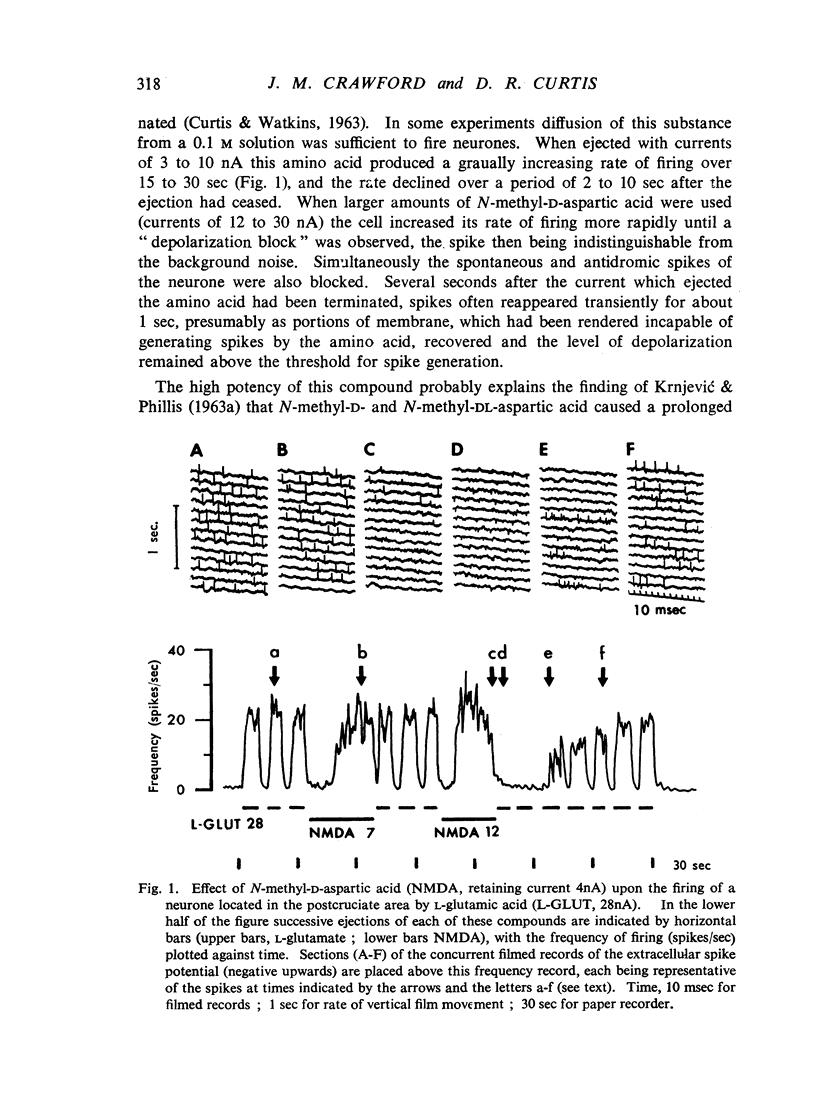
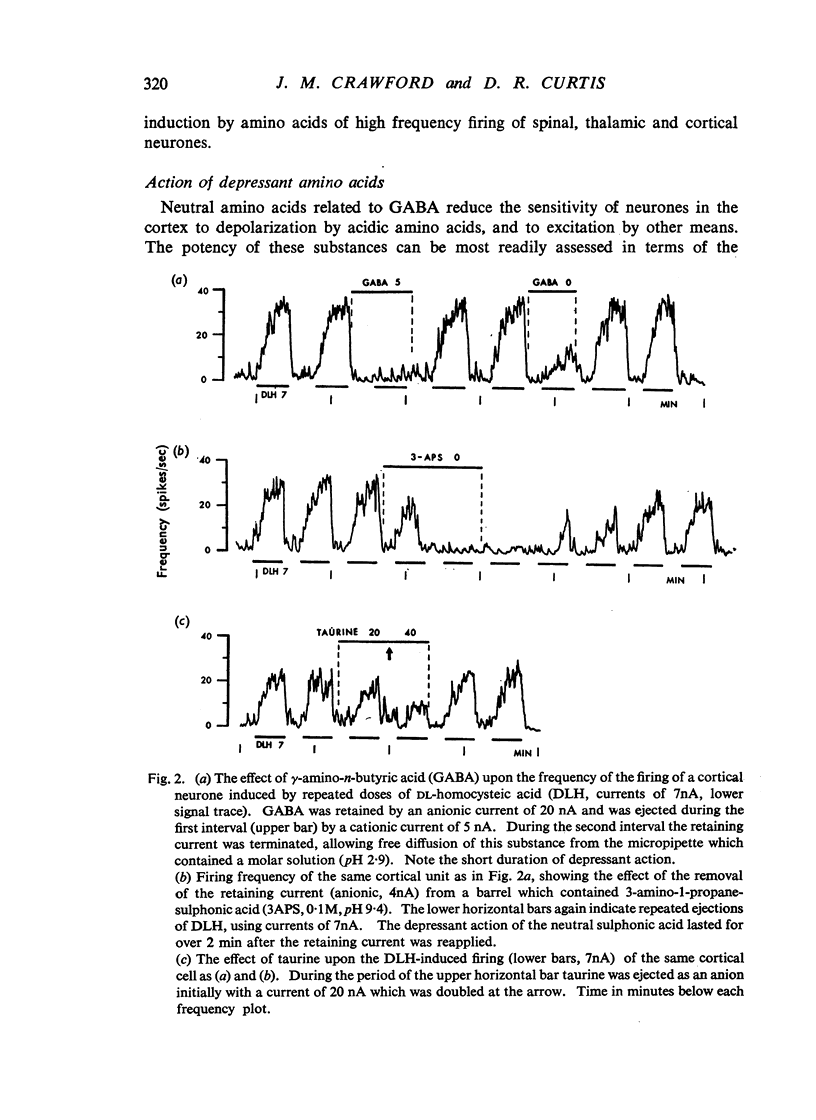
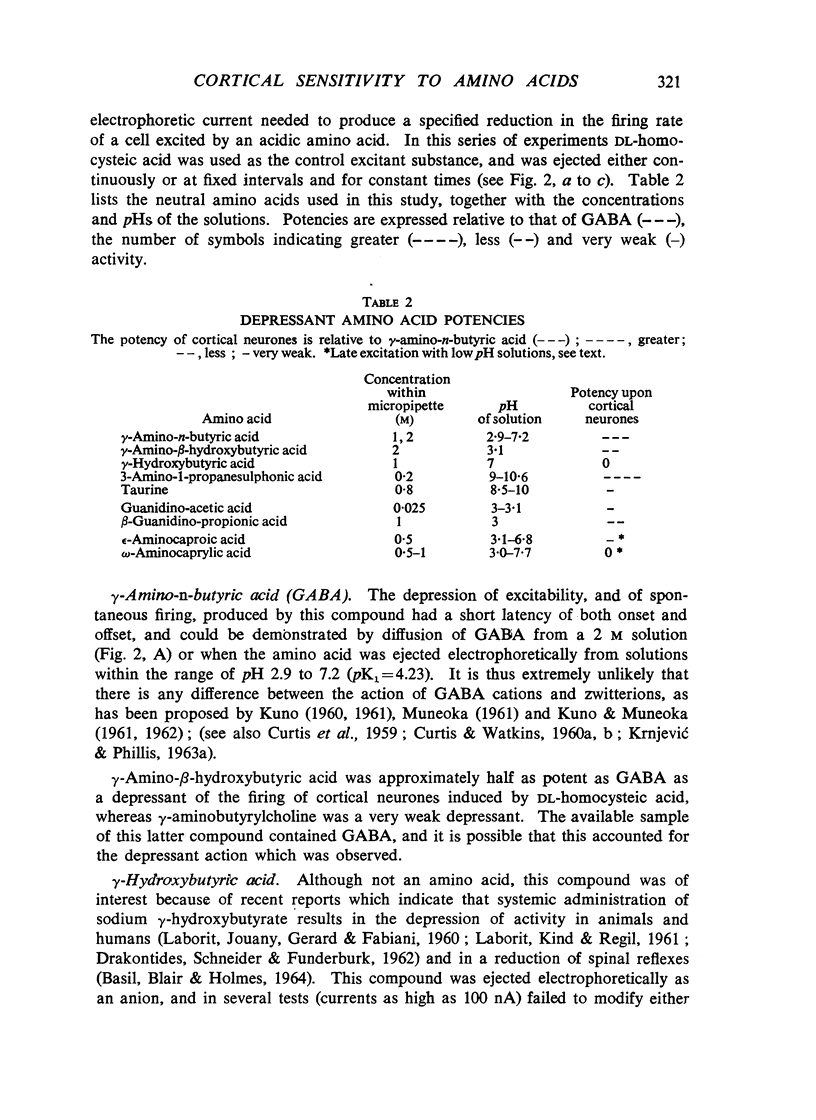
Amino acids related to L-glutamic and γ-amino-n-butyric acid have been administered electrophoretically, and by pressure ejection, into the extraneuronal environment of single neurones in the pericruciate cortex of cats anaesthetized with allobarbitone or allobarbitone-urethane. Acidic amino acids related to glutamic acid, particularly N-methyl-D-aspartic acid, excited cortical neurones. Neutral amino acids related to γ-amino-n-butyric acid, particularly 3-amino-1-propanesulphonic acid, depressed cortical neurones. Some of the depressants blocked the antidromic invasion of Betz cells by pyramidal volleys. There are no essential differences between the sensitivities of cortical and spinal neurones towards locally administered amino acids. A transmitter function of such amino acids within the mammalian central nervous system is considered unlikely.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P., CURTIS D. R. THE EXCITATION OF THALAMIC NEURONES BY ACETYLCHOLINE. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 May-Jun;61:85–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb02945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN P., CURTIS D. R. THE PHARMACOLOGY OF THE SYNAPTIC AND ACETYLCHOLINE-INDUCED EXCITATION OF VENTROBASAL THALAMIC NEURONES. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 May-Jun;61:100–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb02946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BASIL B., BLAIR A. M., HOLMES S. W. THE ACTION OF SODIUM 4-HYDROXYBUTYRATE ON SPINAL REFLEXES. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:318–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BINDMAN L. J., LIPPOLD O. C., REDFEARN J. W. The nonselective blocking action of gamma-amino-butyric acid on the sensory cerebral cortex of the rat. J Physiol. 1962 Jun;162:105–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. M., CURTIS D. R., VOORHOEVE P. E., WILSON V. J. EXCITATION OF CEREBELLAR NEURONES BY ACETYLCHOLINE. Nature. 1963 Nov 9;200:579–580. doi: 10.1038/200579b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. M. THE EFFECT UPON MICE OF INTRAVENTRICULAR INJECTION OF EXCITANT AND DEPRESSANT AMINO ACIDS. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Dec;12:1443–1444. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., ANDERSEN P. Acetylcholine: a central transmitter? Nature. 1962 Sep 15;195:1105–1106. doi: 10.1038/1951105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., DAVIS R. Pharmacological studies upon neurones of the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Apr;18:217–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., ECCLES R. M. The excitation of Renshaw cells by pharmacological agents applied electrophoretically. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):435–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., KOIZUMI K. Chemical transmitter substances in brain stem of cat. J Neurophysiol. 1961 Jan;24:80–90. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. Cholinergic and non-cholinergic transmission in the mammalian spinal cord. J Physiol. 1961 Sep;158:296–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. The chemical excitation of spinal neurones by certain acidic amino acids. J Physiol. 1960 Mar;150:656–682. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. The depression of spinal neurones by gamma-amino-n-butyric acid and beta-alanine. J Physiol. 1959 Apr 23;146(1):185–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., WATKINS J. C. Acidic amino acids with strong excitatory actions on mammalian neurones. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:1–14. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., WATKINS J. C. Analogues of glutamic and gamma-amino-n-butyric acids having potent actions on mammalian neurones. Nature. 1961 Sep 2;191:1010–1011. doi: 10.1038/1911010a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., WATKINS J. C. The excitation and depression of spinal neurones by structurally related amino acids. J Neurochem. 1960 Sep;6:117–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1960.tb13458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRAKONTIDES A. B., SCHNEIDER J. A., FUNDERBURK W. H. Some effects of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate on the central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Mar;135:275–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIARMAN N. J., SCHMIDT K. F. Some neurochemical aspects of the depressant action of gamma-butyrolactone on the central nervous system. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Jun;20:563–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDFEST H. An electrophysiological basis for neuropharmacology. Fed Proc. 1958 Dec;17(4):1006–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMRIN R. P., KAMRIN A. A. The effects of pyridoxine antagonists and other convulsive agents on amino acid concentrations of the mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1961 Feb;6:219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1961.tb13468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:296–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Actions of certain amines on cerebral cortical neurones. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Jun;20:471–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M., MUNEOKA A. Further studies on site of action of systemic omega-amino acids in the spinal cord. Jpn J Physiol. 1962 Aug 15;12:397–410. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.12.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M. Site of action of systemic gamma-aminobutyric acid in the spinal cord. Jpn J Physiol. 1961 Jun 15;11:304–318. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.11.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABORIT G., KIND A., DE LEON REGIL C. [220 cases of anesthesia in neurosurgery with sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate]. Presse Med. 1961 Jun 3;69:1216–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABORIT H., JOUANY J. M., GERARD J., FABIANI F. [Summary of an experimental and clinical study on a metabolic substrate with inhibitory central action: sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate]. Presse Med. 1960 Nov 12;68:1867–1869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEDINA M. A. The in vivo effects of hydrazines and vitamin B6 on the metabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 May;140:133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNEOKA A. Depression and facilitation of spinal reflexes by systemic omega-amino acids. Jpn J Physiol. 1961 Oct 15;11:555–563. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.11.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. G. Intracellular records from Betz cells in the cat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1956 Jan;41(1):58–69. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1956.sp001163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURPURA D. P., GIRADO M., GRUNDFEST H. Selective blockade of excitatory synapses in the cat brain by gamma-aminobutyric acid. Science. 1957 Jun 14;125(3259):1200–1202. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3259.1200-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURPURA D. P., GIRADO M., SMITH T. G., CALLAN D. A., GRUNDFEST H. Structure-activity determinants of pharmacological effects of amino acids and related compounds on central synapses. J Neurochem. 1959 Jan;3(3):238–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1959.tb12630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURPURA D. P. Nature of electrocortical potentials and synaptic organizations in cerebral and cerebellar cortex. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1959;1:47–163. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60314-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYALL R. W. Sub-cellular distribution of pharmacologically active substances in guinea pig brain. Nature. 1962 Nov 17;196:680–681. doi: 10.1038/196680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYALL R. W. THE SUBCELLULAR DISTRIBUTIONS OF ACETYLCHOLINE, SUBSTANCE P, 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE, GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID AND GLUTAMIC ACID IN BRAIN HOMOGENATES. J Neurochem. 1964 Mar;11:131–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb06124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HARREVELD A. Compounds in brain extracts causing spreading depression of cerebral cortical activity and contraction of crustacean muscle. J Neurochem. 1959 Feb;3(4):300–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1959.tb12636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERZEANO M., CALMA I. Unit activity in spindle bursts. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Sep;17(5):417–428. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.5.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATKINS J. C. THE SYNTHESIS OF SOME ACIDIC AMINO ACIDS POSSESSING NEUROPHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIVITY. J Med Pharm Chem. 1962 Nov;91:1187–1199. doi: 10.1021/jm01241a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINSTEIN H., ROBERTS E., KAKEFUDA T. Studies of subcellular distribution of gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamic decarboxylase in mouse brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 May;12:503–509. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


