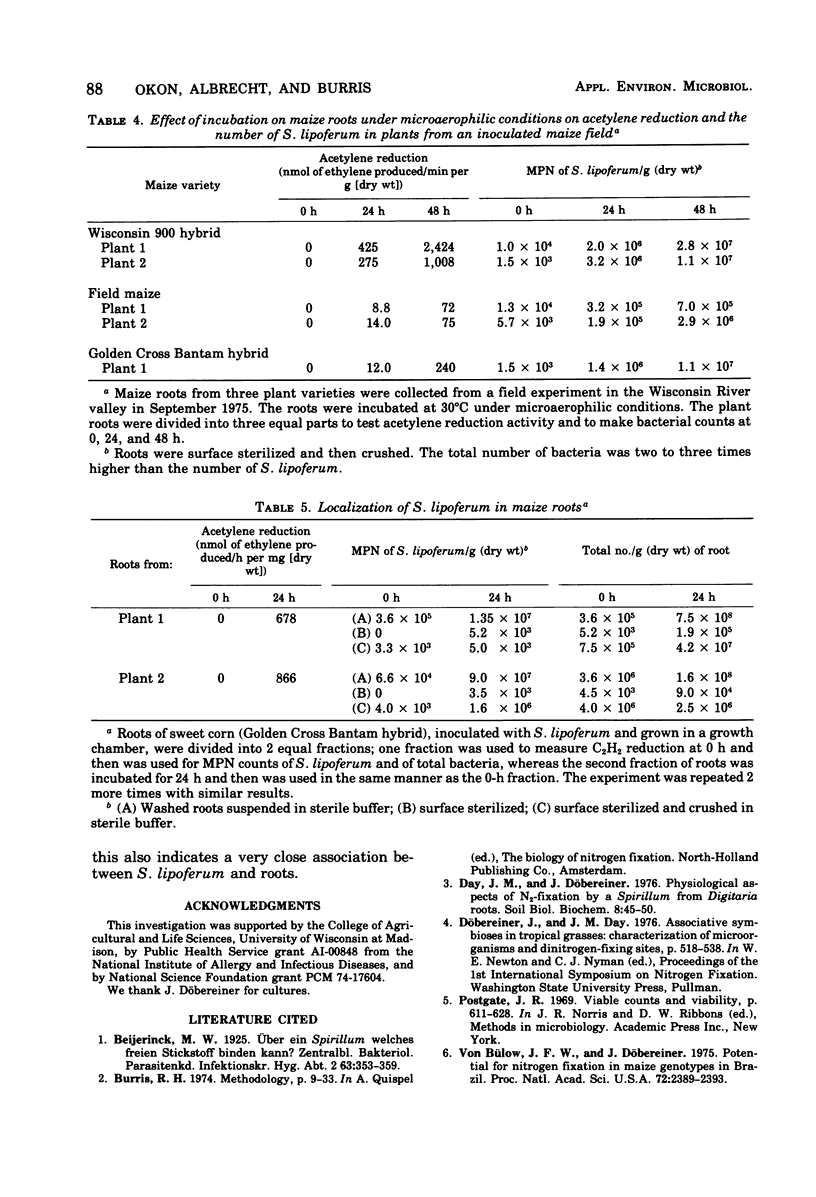
Abstract
Methods are described for growing Spirillum lipoferum in quantities sufficient to serve as inoculant in field trials of its associative N2-fixing ability with higher plants and as a source of cells for the preparation of nitrogenase, cytochromes, respiratory enzymes, etc. A heavy inoculum of S. lipoferum grown on NH4+ was transferred to a medium of minimal nitrogen content, and initial rapid growth at the expense of residual combined nitrogen was replaced later by slower growth on N2. Conversion to N2 fixation was prompt upon exhaustion of fixed nitrogen; growth on N2 was most rapid at a pO2 of 0.005 to 0.007 atm. Numbers of S. lipoferum can be estimated by diluting soil, crushed roots, or other material, and inoculating diluted samples into a stagnant semisolid medium. Development of a characteristic subsurface layer of organisms and demonstration the these organisms can reduce C2H2 are presumptive evidence that they are S. lipoferum. With most-probable-number tables the observations can be converted to numbers of S. lipoferum in the samples. The most-probable-number method indicated that numbers of S. lipoferum may increase 100-fold or more in roots of maize removed from the plant and incubated for 24 h at 30°C at a pO2 initially adjusted to 0.01 atm.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Plant R. The greatest happiness. J Med Ethics. 1975 Jul;1(2):104–106. doi: 10.1136/jme.1.2.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Bülow J. F., Döbereiner J. Potential for nitrogen fixation in maize genotypes in Brazil. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2389–2393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



