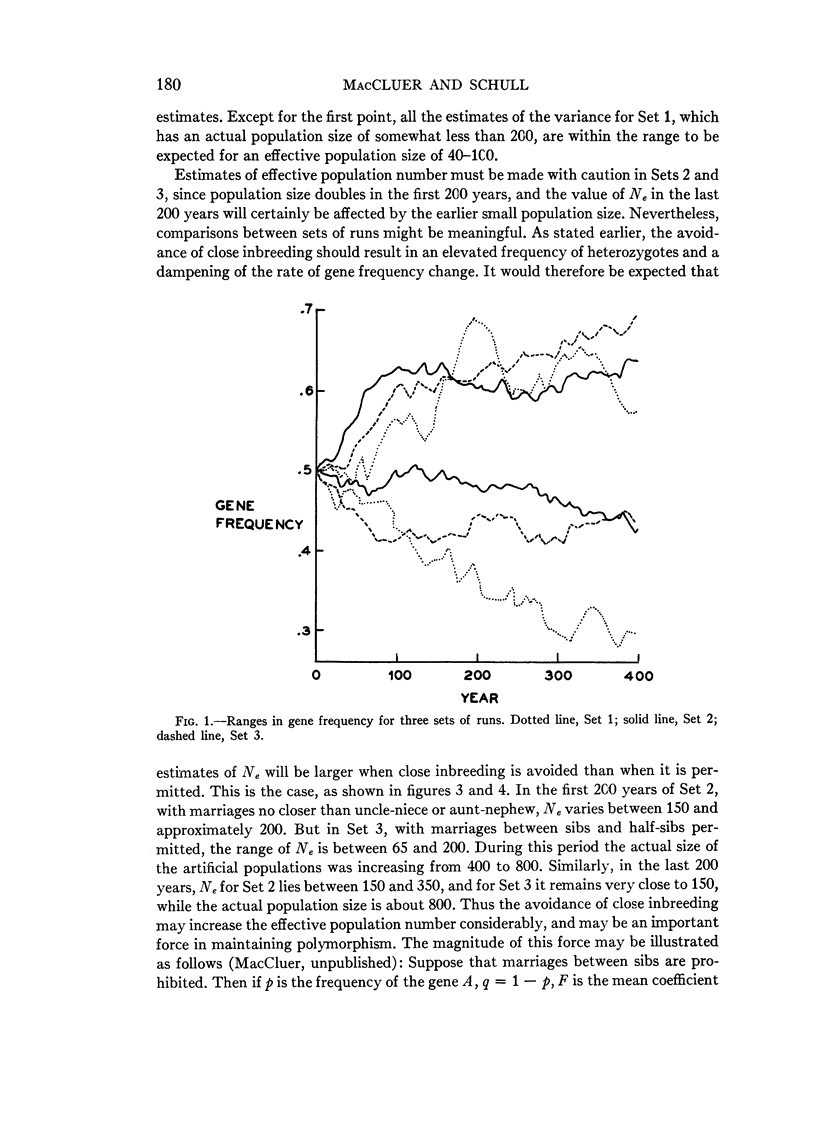
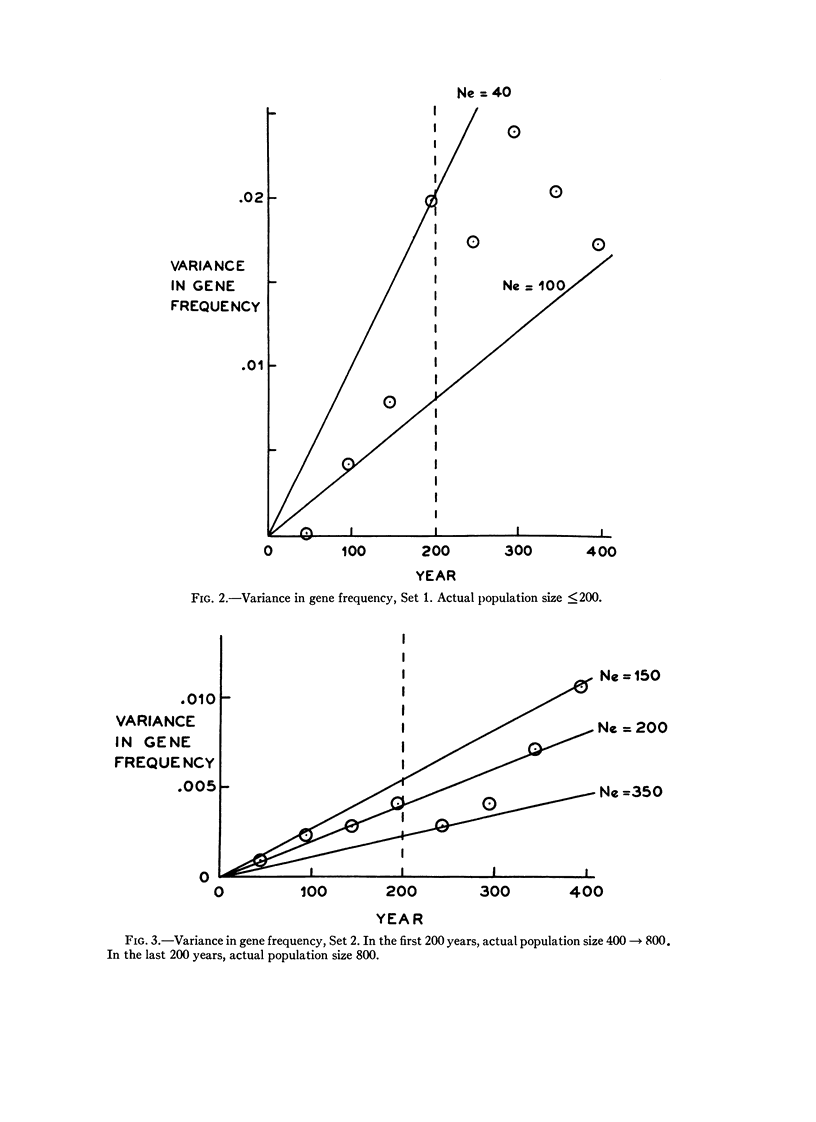
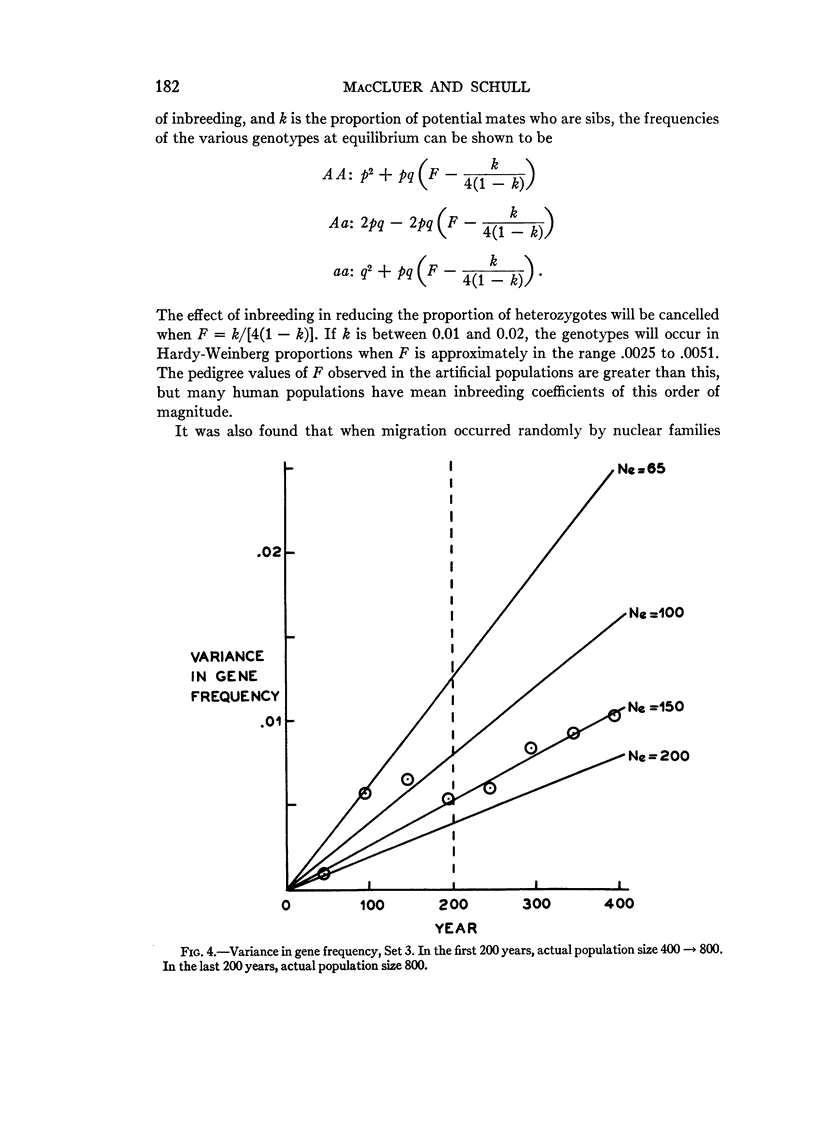
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- MacCluer J. W. Monte Carlo methods in human population genetics: a computer model incorporating age-specific birth and death rates. Am J Hum Genet. 1967 May;19(3 Pt 1):303–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCluer J. W., Schull W. J. Frequencies of consanguineous marriage and accumulation of inbreeding in an artifical population. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 Mar;22(2):160–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Imaizumi Y. Genetic structure of human populations. II. Differentiation of blood group gene frequencies among isolated populations. Heredity (Edinb) 1966 May;21(2):183–190. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1966.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schull W. J., Komatsu I., Nagano H., Yamamoto M. Hirado: temporal trends in inbreeding and fertility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):671–679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. Evolution in Mendelian Populations. Genetics. 1931 Mar;16(2):97–159. doi: 10.1093/genetics/16.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


