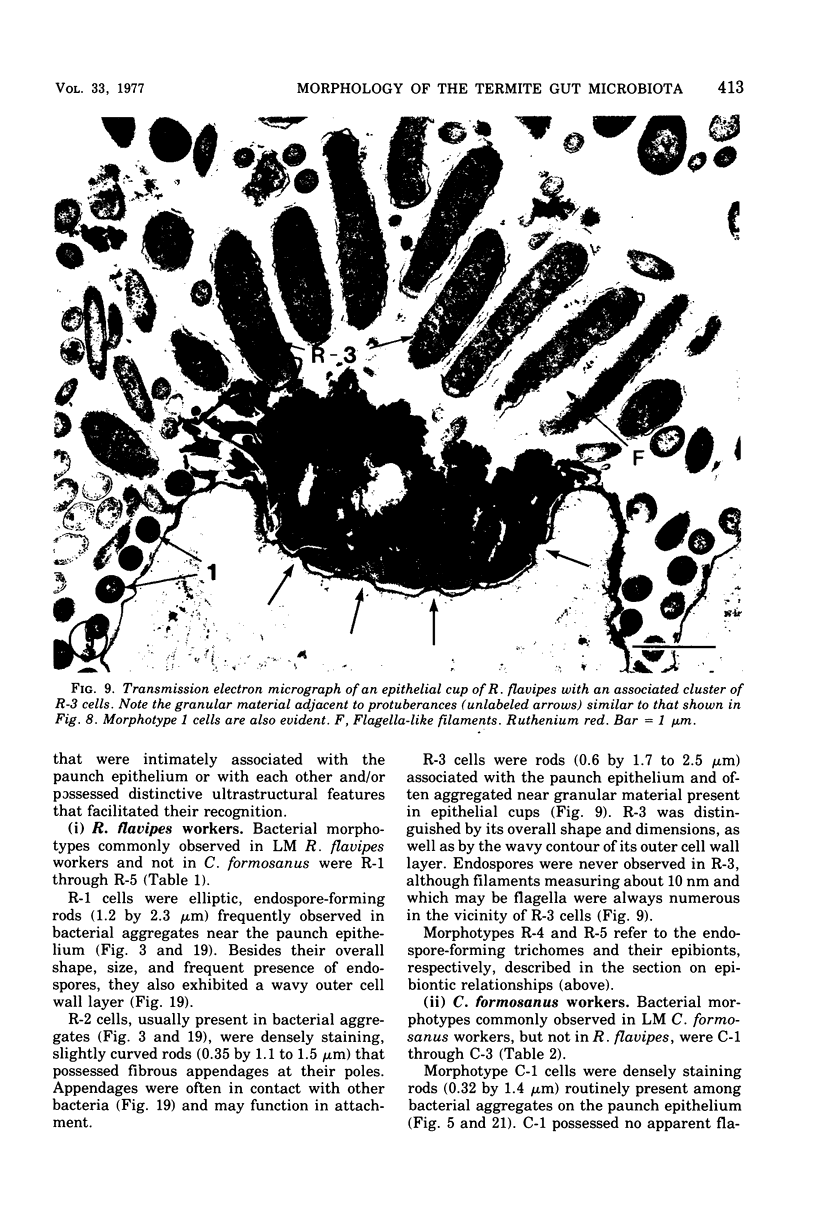
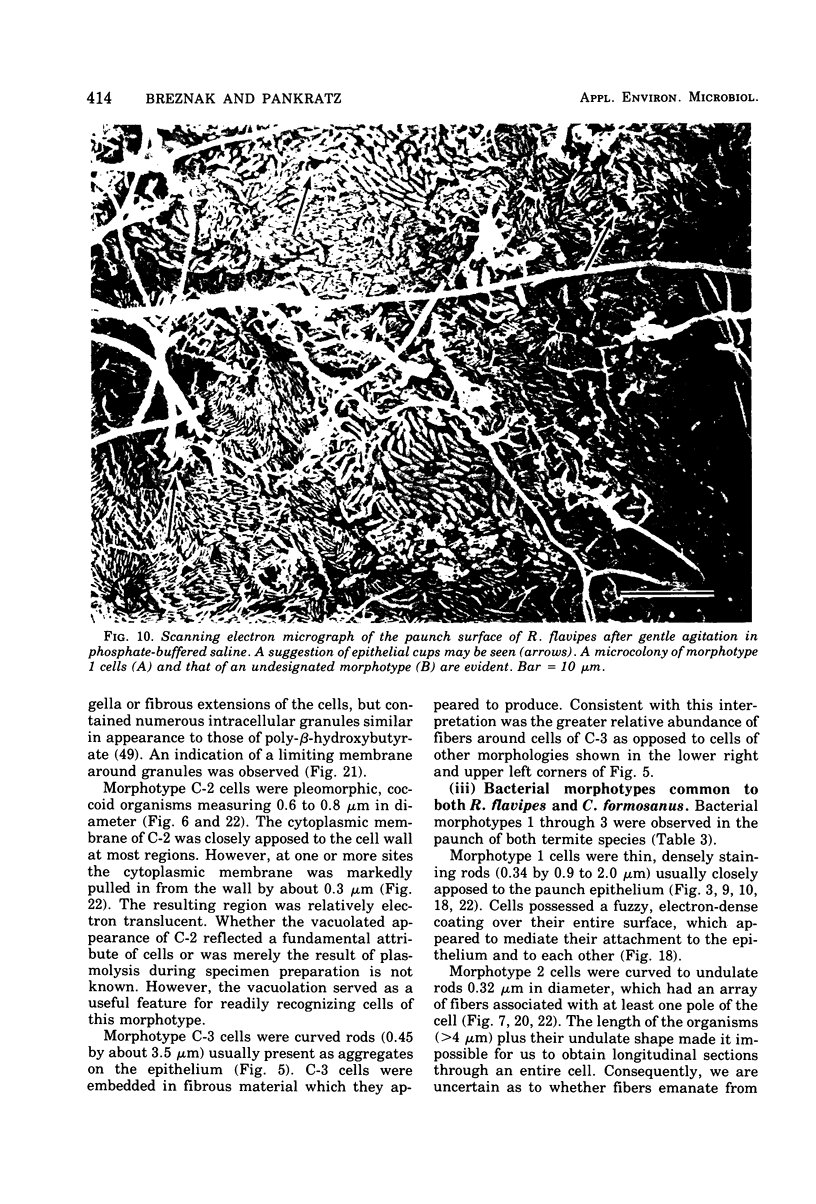
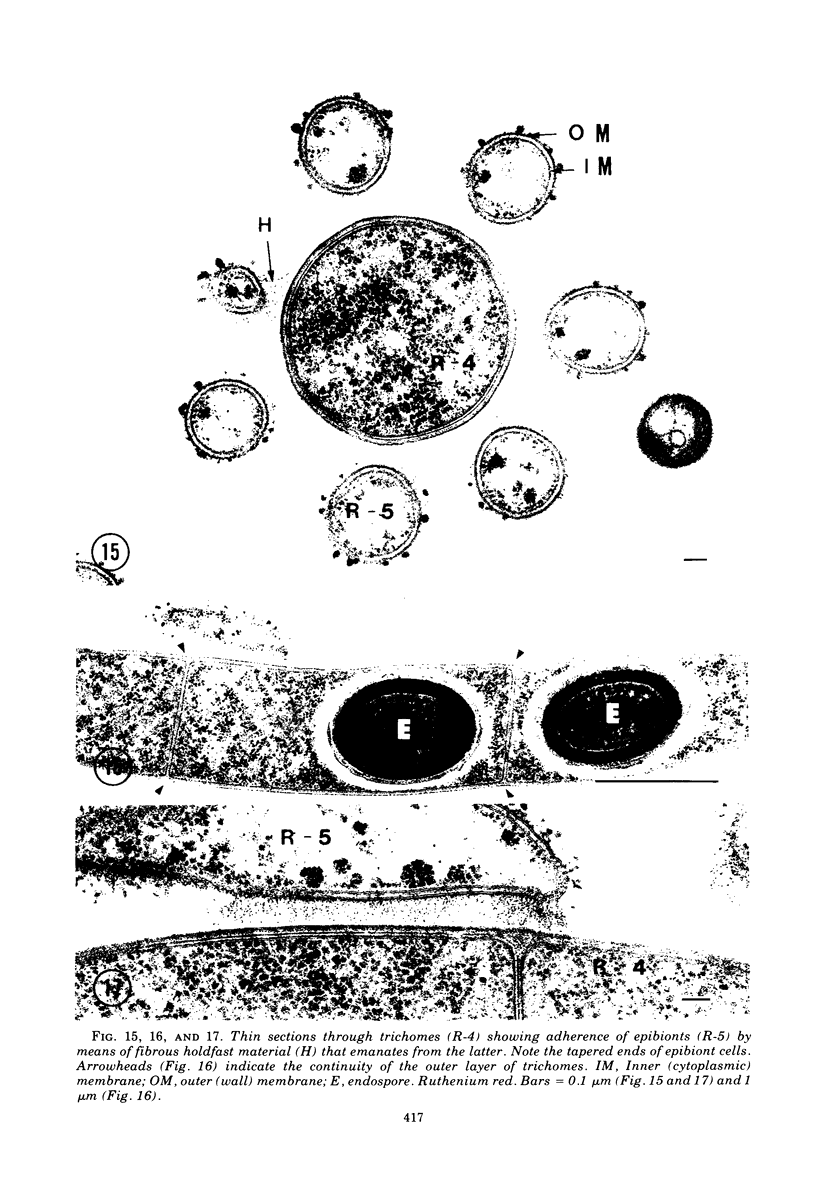
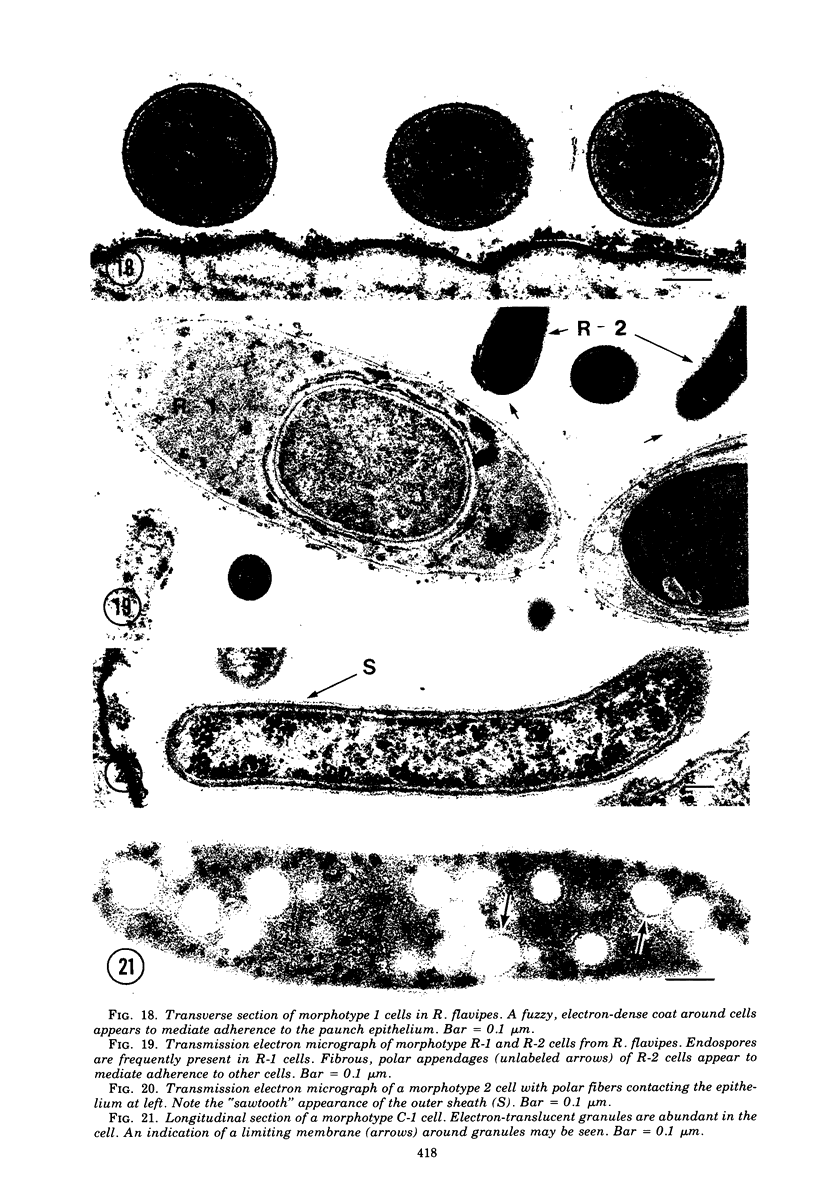
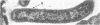Abstract
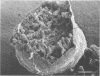
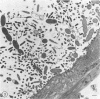
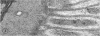
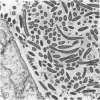
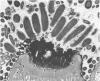
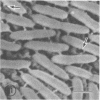
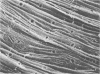
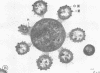
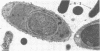
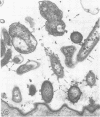
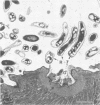
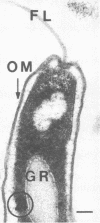
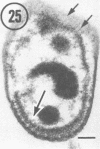
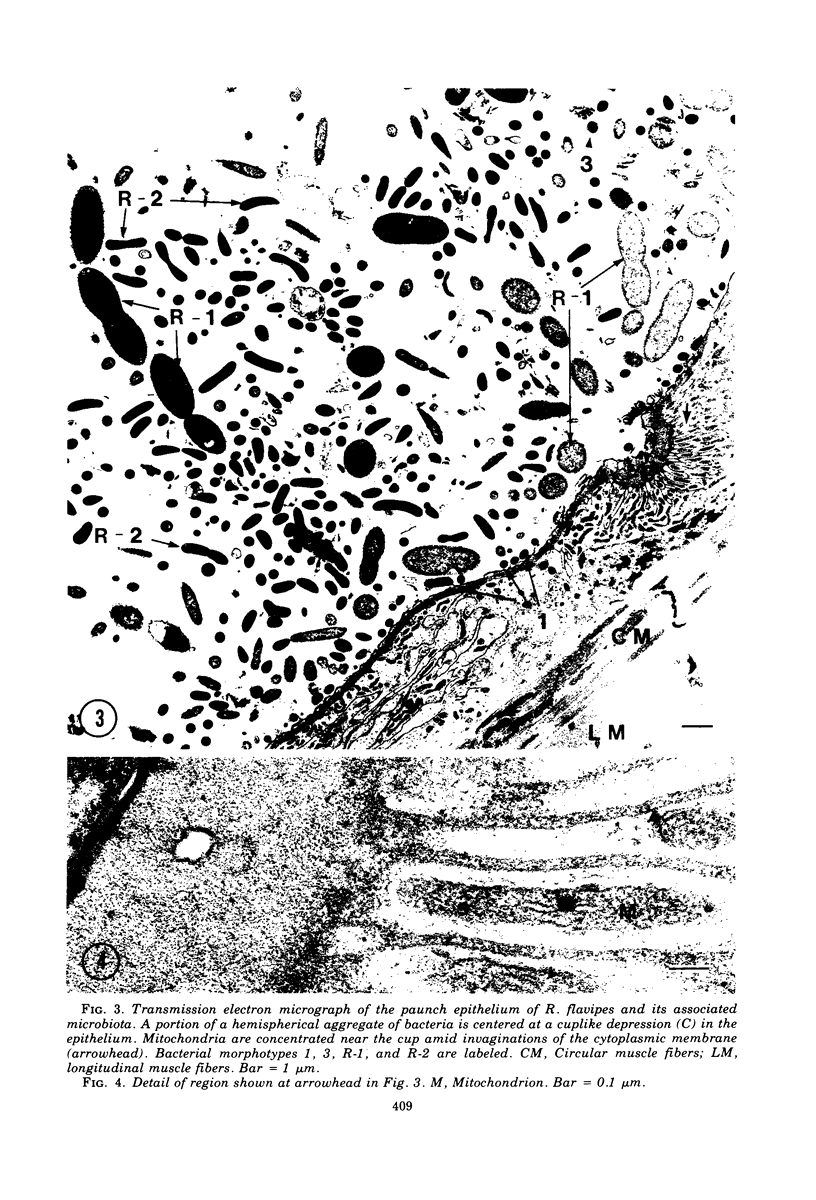
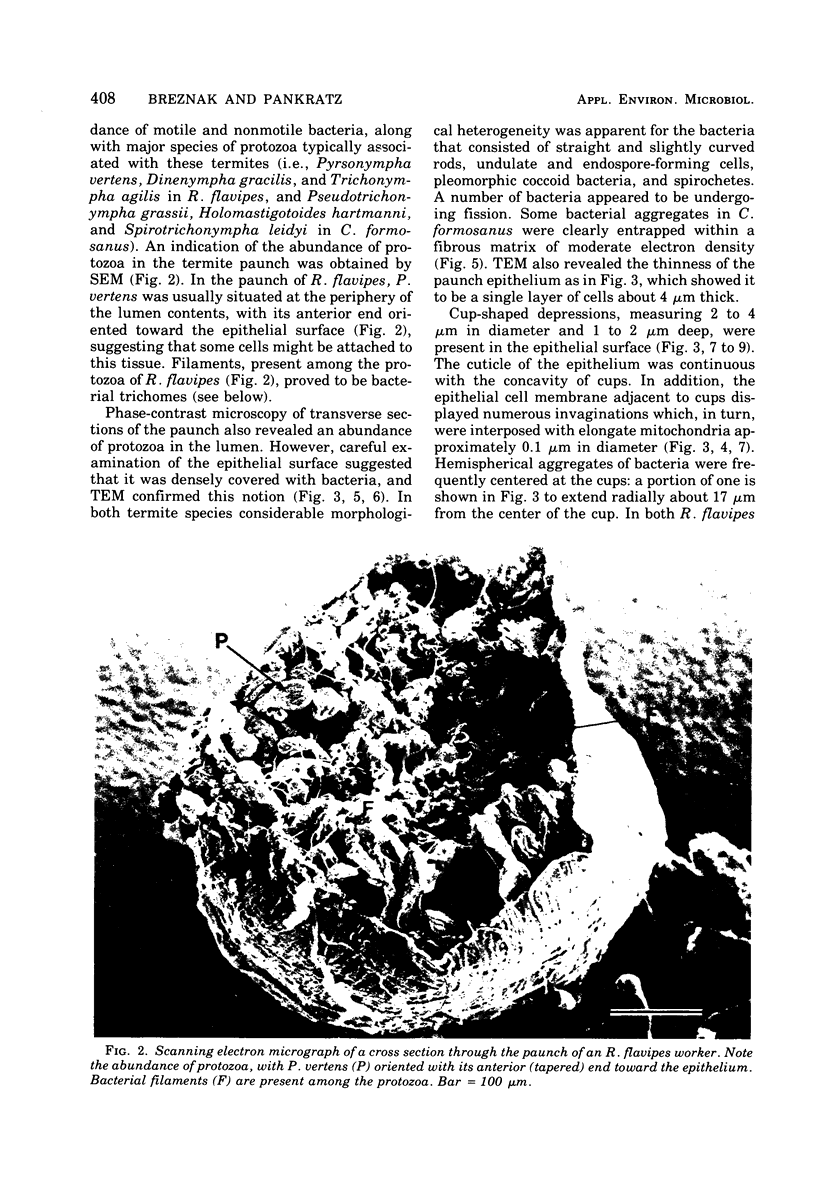
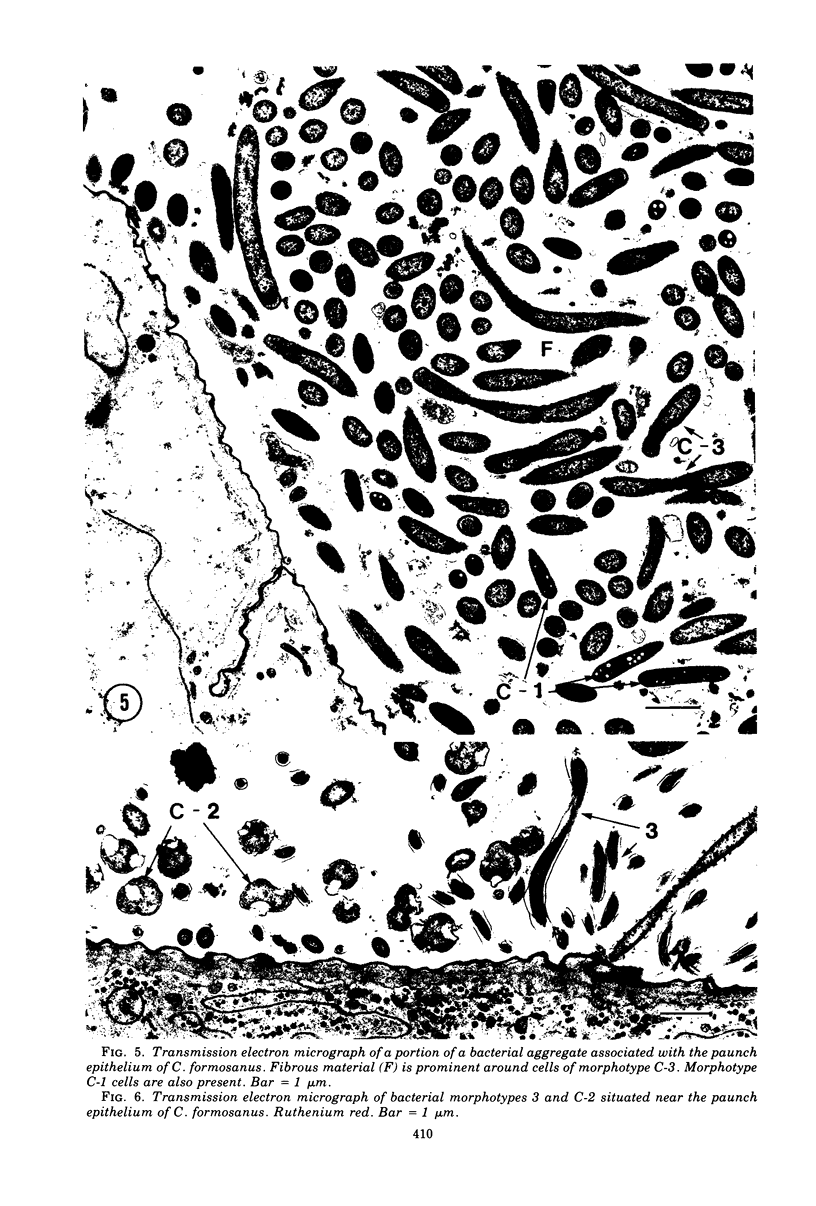
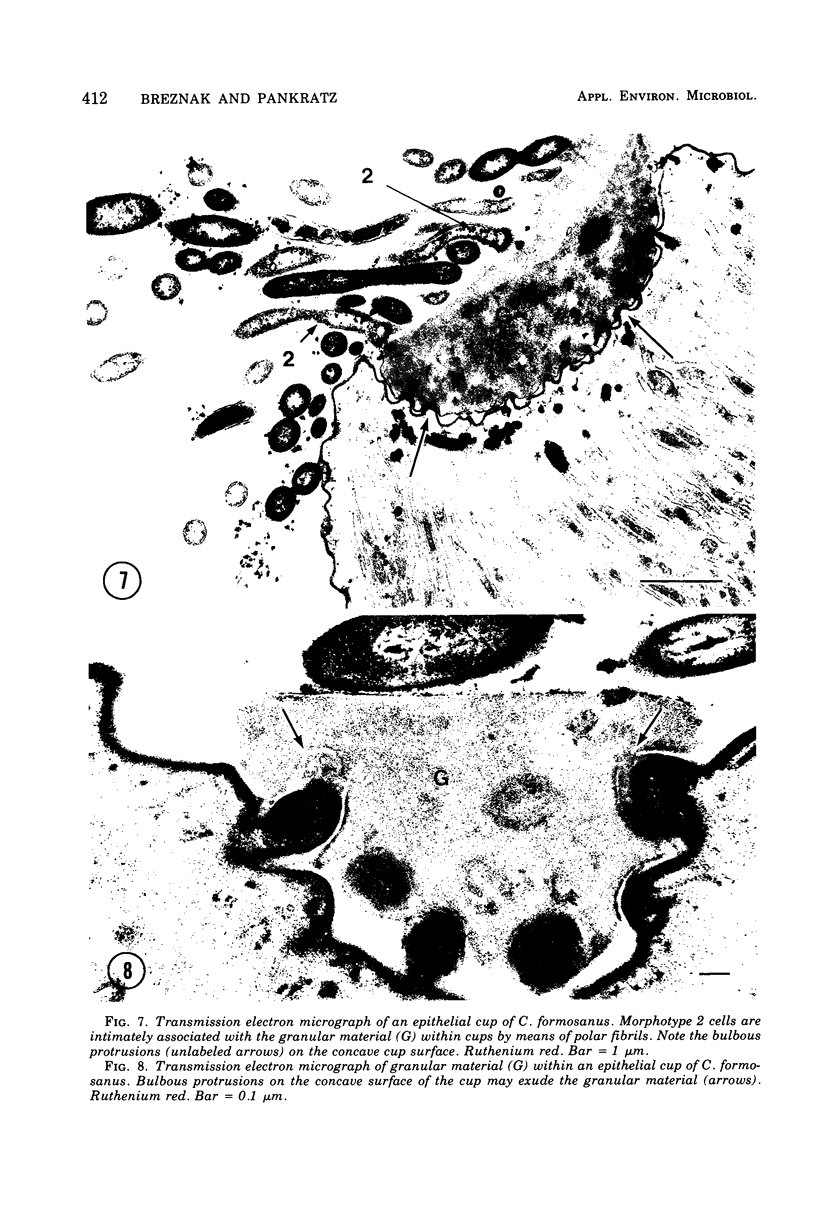
Light microscopy and scanning and transmission electron microscopy were used to examine the in situ morphology of the gut microbiota of Reticulitermes flavipes and Caoptotermes formosanus. Laboratory-maintained termites were used and, for R. flavipes, specimens were also prepared immediately after collection from a natural infestation. The latter endeavor enabled a study of different castes and developmental stages of R. flavipes and revealed differences in the microbiota of field versus laboratory specimens. The termite paunch microbiota consisted of an abundance of morphologically diverse bacteria and protozoa. Thirteen bacterial morphotypes in the paunch were described in detail: seven were observed only in R. flavipes, three were observed only in C. formosanus, and three were common to both termite species. The paunch epithelium was densely colonized by bacteria, many of which possessed holdfast elements that secured them tightly to this tissue and to other bacterial cells. Besides bacteria, the protozoan Pyrsonympha vertens adhered to the paunch epithelium of R. flavipes by means of an attachment organelle. Cuplike indentations were present on the paunch epithelial surface and were sites of bacterial aggregation. Ultrastructural features of cups suggested their involvement in ion absorption. In addition to the paunch, the midgut was also colonized by bacteria that were situated between epithelial microvilli. Results suggest that bacteria are an integral part of the gut ecosystem.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akin D. E. Ultrastructure of rumen bacterial attachment to forage cell walls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):562–568. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.562-568.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauchop T., Clarke R. T., Newhook J. C. Scanning electron microscope study of bacteria associated with the rumen epithelium of sheep. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):668–675. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.668-675.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith T. D., Light S. F. THE SPIRALS WITHIN THE TERMITE GUT FOR CLASS USE. Science. 1927 Dec 30;66(1722):656–657. doi: 10.1126/science.66.1722.656-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznak J. A., Brill W. J., Mertins J. W., Coppel H. C. Nitrogen fixation in termites. Nature. 1973 Aug 31;244(5418):577–580. doi: 10.1038/244577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznak J. A. Symbiotic relationships between termites and their intestinal microbiota. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1975;(29):559–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker B. E., Fuller R. Adhesion of Lactobacilli to the chicken crop epithelium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jul;52(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foglesong M. A., Walker D. H., Jr, Puffer J. S., Markovetz A. J. Ultrastructal morphology of some prokaryotic microorganisms associated with the hindgut of cockroaches. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):336–345. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.336-345.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbandian J., Freedman M. L., Tanzer J. M., Lovelace S. M. Ultrastructure of Mutants of Streptococcus mutans with Reference to Agglutination, Adhesion, and Extracellular Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1170–1179. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1170-1179.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. P., Mata L. J. Bacterial flora associated with the human gastrointestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jan;58(1):56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Ordal E. J. The fine structure of Chondrococcus columnaris. 3. The surface layers of Chondrococcus columnaris. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):37–51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Associations and physiological interactions of indigenous microorganisms and gastrointestinal epithelia. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1372–1379. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Associations of indigenous microorganisms with gastrointestinal mucosal epithelia. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Nov;23(11):1495–1501. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.11.1495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Blumershine R. V. Surface-surface associations in microbial communities populating epithelial habitats in the murine gastrointestinal ecosystem: scanning electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):240–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.240-250.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea S. M. Lanthanum staining of the surface coat of cells. Its enhancement by the use of fixatives containing Alcian blue or cetylpyridinium chloride. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):611–620. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. E., Arnott H. J. EPI- and endobiotic bacteria associated with Pyrsonympha vertens, a symbiotic protozoon of the termite Reticulitermes flavipes. Trans Am Microsc Soc. 1974 Apr;93(2):180–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. E., Buhse H. E., Jr, Stamler S. J. Possible formation and development of spirochaete attachment sites found on the surface of symbiotic polymastigote flagellates of the termite Reticulitermes flavipes. Biosystems. 1975 Nov;7(3-4):374–379. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(75)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Zeller J. A. Ultrastructural identification of spirochetes and flagellated microbes at the brush border of the large intestinal epithelium of the rhesus monkey. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):1008–1018. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.1008-1018.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Savage D. C. Association of microorganisms with the epithelium in the alimentary tract of Aspicularis tetraptera. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):475–476. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.475-476.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Smith J. M. The microflora of the pig stomach and its possible relationship to ulceration of the pars oesophagea. J Comp Pathol. 1970 Jul;80(3):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(70)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. S., Lundgren D. G. Poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate in the chemolithotrophic bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):947–950. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.947-950.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]