Abstract
Asparaginase was found in the soluble fraction of cells of Azotobacter vinelandii, and its activity remained the same during growth of the organism in a nitrogen-free medium. The specific activity and the yield of A. vinelandii increased twofold in the presence of ammonium sulfate. Within limits, the temperature (30 to 37°C) and pH (6.5 to 8.0) of the medium showed little effect on the levels of enzyme activity. The enzyme was purified to near homogeneity by standard methods of enzyme purification, including affinity chromatography, and had optimum activity at pH 8.6 and 48°C. The approximate molecular weight was 84,000. The apparent Km value for the substrate was 1.1 × 10-4 M. Metal ions or sulfhydryl reagents were not required for enzyme activity. Cu2+, Zn2+, and Hg2+ showed concentration-dependent inhibition, whereas amino and keto acids had no effect on the enzyme activity. Asparaginase was stable when incubated with rat serum and ascites fluid. The enzyme had no effect on the membrane of sheep erythrocytes and did not inhibit the incorporation of radioactive precursors into deoxyribonucleic acid, ribonucleic acid, and protein in Yoshida ascites sarcoma cells. Asparaginase activity was not detected in the tumor cells.
Full text
PDF

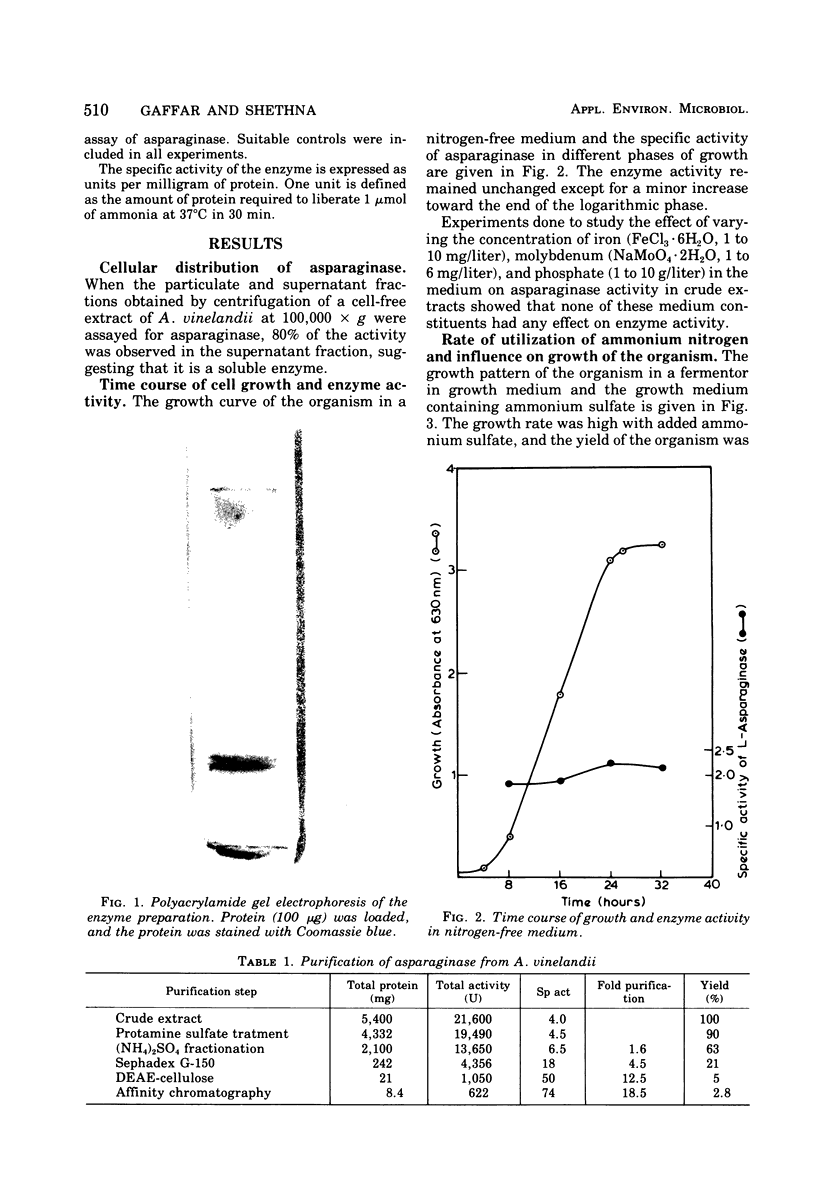
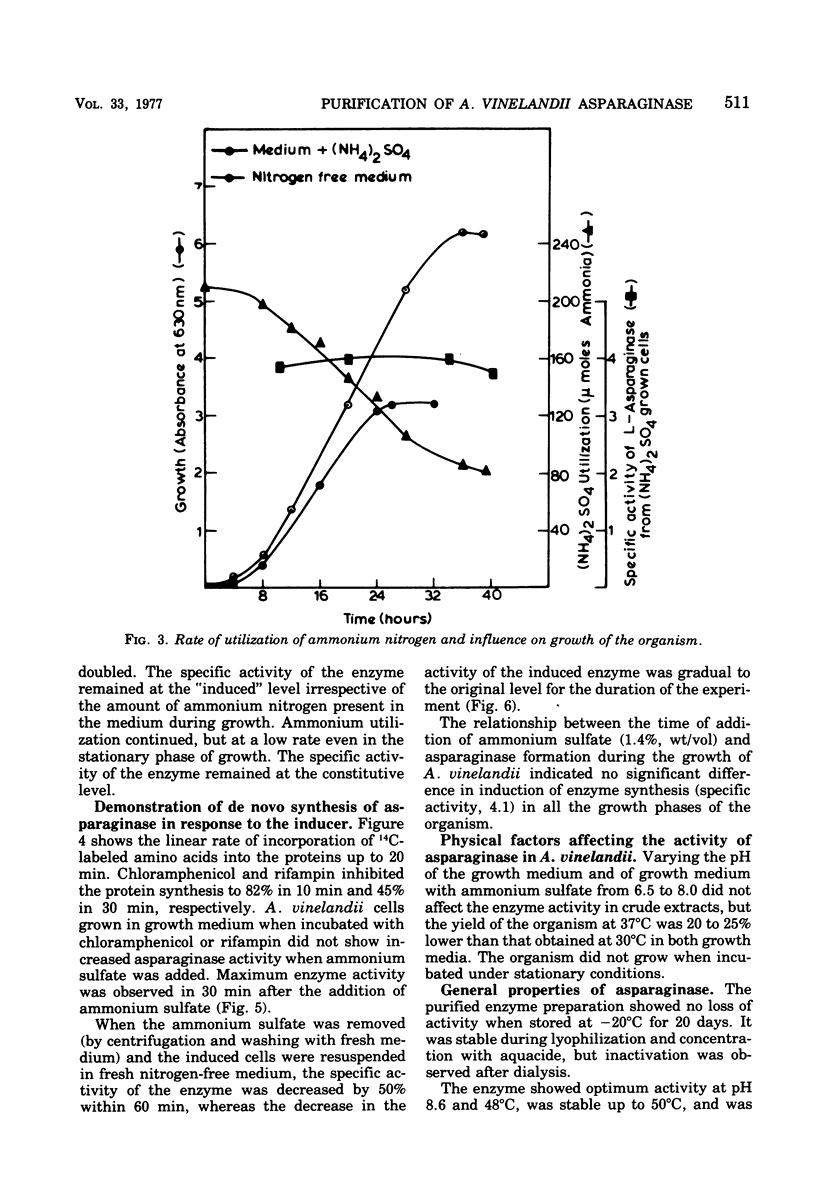
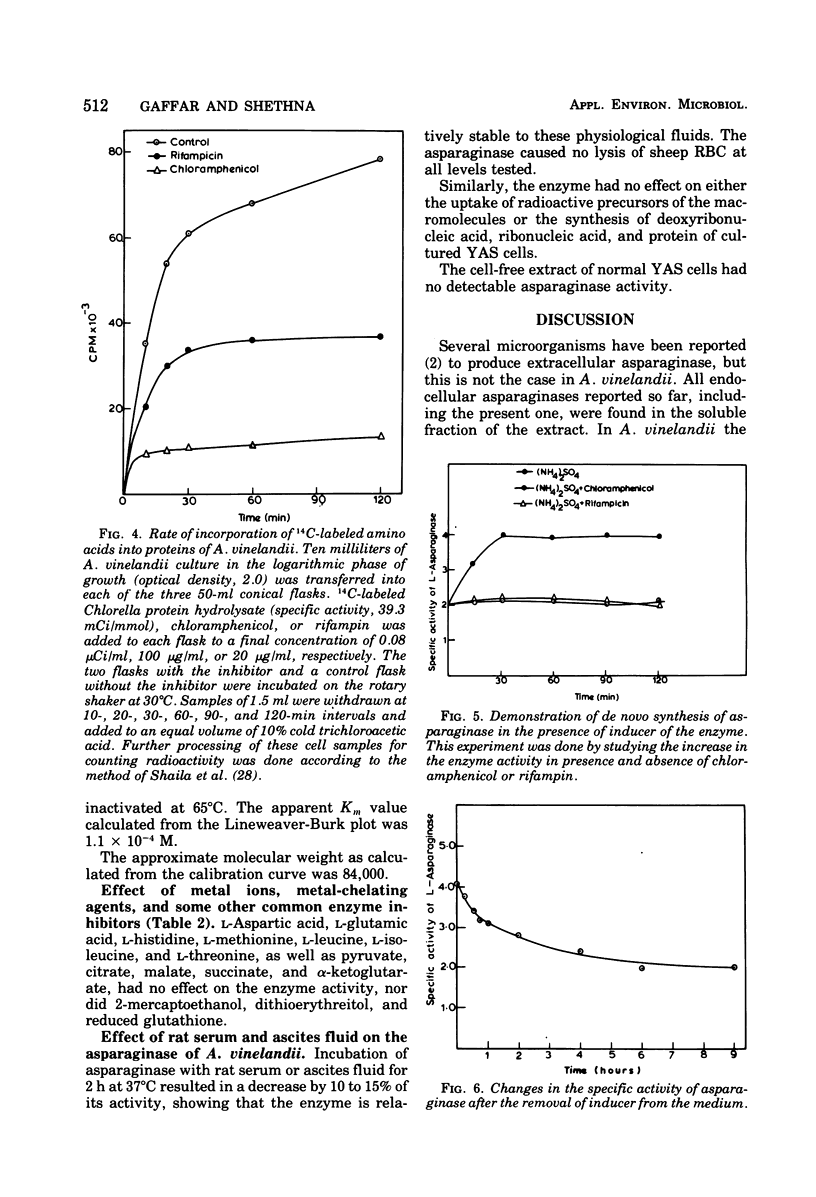


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULEN W. A., LECOMTE J. R. Isolation and properties of a yellow-green fluorescent peptide from azotobacter medium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Dec 19;9:523–528. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezov T. T., Hisamov G. Z., Zanin V. A. On the regulation of asparaginase synthesis in Pseudomonas Boreopolis 526. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):10–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney D. A., Handschumacher R. E. L-asparaginase and L-asparagine metabolism. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1970;10:421–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.10.040170.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eremenko V. V., Evseev L. P., Nikolaev A. Ia. Asparaginaza Bacterium cadaveris. Mikrobiologiia. 1968 Mar-Apr;37(2):207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evseev L. P., Nikolaev A. Ia, Eremenko V. V., Mardashev S. R. Indutsirovannyi sintez asparaginazy i gliutaminazy u Pseudomonas sp. Biokhimiia. 1967 Jul-Aug;32(4):873–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaram H. N., Ramakrishnan R., Vaidyanathan C. S. L-asparaginases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains H37Rv and H37Ra. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90570-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansen T., Einarsson M., Sundberg L., Porath J. Purification of L-asparaginase from E. coli by specific adsorption and desorption. FEBS Lett. 1970 Apr 16;7(3):294–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80186-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law A. S., Wriston J. C., Jr Purification and properties of Bacillus coagulans L-asparaginase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Dec;147(2):744–752. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90434-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. S., Zajic J. E. L-Asparaginase synthesis by Erwinia aroideae. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):667–668. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.667-668.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTENSON L. E. A simple method for measuring nitrogen fixation by cell-free enzyme preparations of Clostridium pasteurianum. Anal Biochem. 1961 Jun;2:216–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(61)80003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Netrval J. Effect of organic and amino acids on L-asparaginase production by Escherichia coli. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;92(4):345–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00409287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North A. C., Wade H. E., Cammack K. A. Physicochemical studies of L-asparaginase from Erwinia carotovora. Nature. 1969 Nov 8;224(5219):594–595. doi: 10.1038/224594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. F., Tallal L., Tan C. C., Murphy M. L., Clarkson B. D., Golbey R. D., Krakoff I. H., Karnofsky D. A., Burchenal H. J. Clinical experience with L-asparaginase. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1970;33:219–235. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-99984-0_27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison R. S., Berk B. L-asparaginase synthesis by Escherichia coli B. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1969 Nov;11(6):1211–1225. doi: 10.1002/bit.260110615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley B., Wriston J. C., Jr Partial purification and antilymphoma activity of Serratia marcescens L-asparaginase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jul 21;28(2):160–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaila M. S., Gopinathan K. P., Ramakrishnan T. Protein synthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and the effect of streptomycin in streptomycin-susceptible and -resistant strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):205–213. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shethna Y. I., Wilson P. W., Beinert H. Purification of a non-heme iron protein and other electron transport components from Azotobacter extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 14;113(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOWER D. B., PETERS E. L., CURTIS W. C. Guinea pig serum L-asparaginase. Properties, purification, and application to determination of asparagine in biological samples. J Biol Chem. 1963 Mar;238:983–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellin T. O., Wriston J. C., Jr Purification and properties of guinea pig serum asparaginase. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1605–1612. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]