Abstract
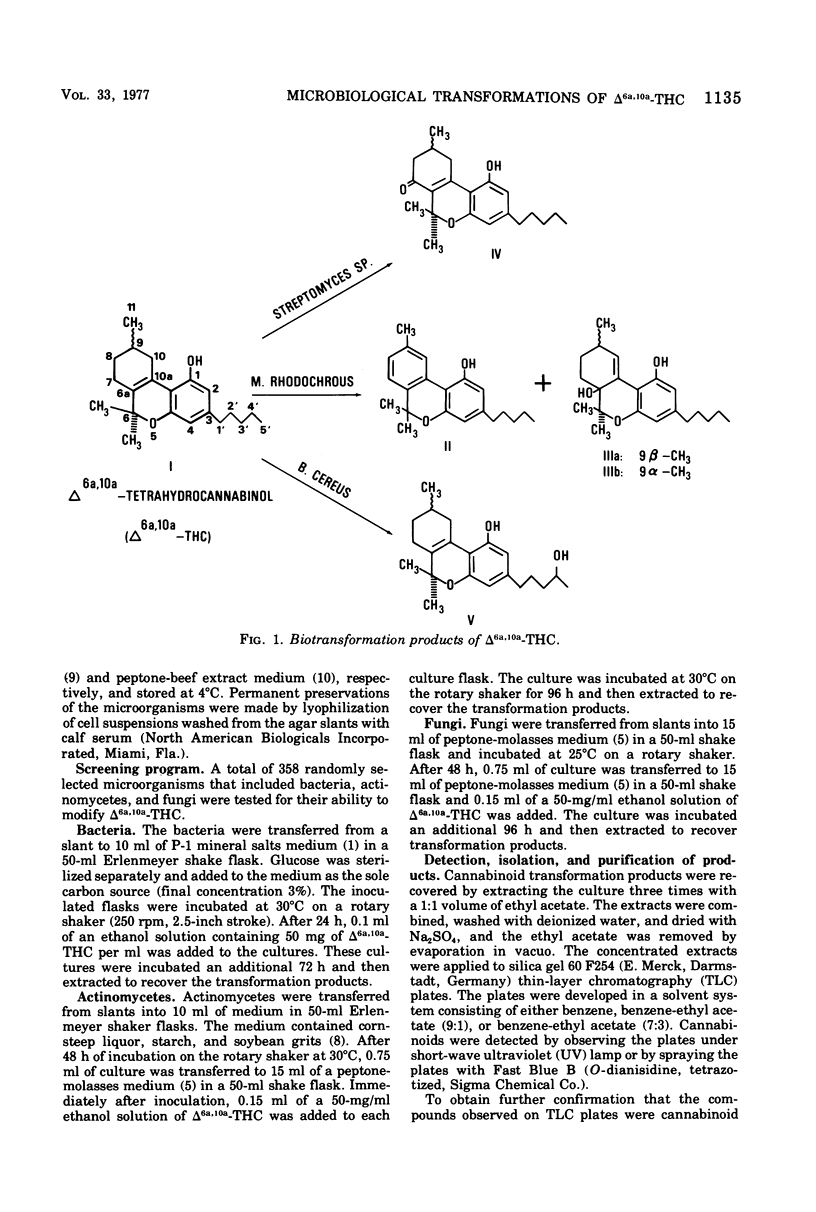
A screening program was conducted to find microorganisms that catalyze transformation reactions with cannabinoids. Three hundred fifty-eight cultures, consisting of 97 bacteria, 175 actinomycetes, and 86 molds, were incubated in media containing 0.5 mg of Δ6a,10a-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ6a,10a-THC) per ml. After 120 h of cultivation, ethyl acetate extracts of the cultures were examined by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) for transformation products. About 18% of the cultures modified Δ6a,10a-THC. The ability to modify the substrate did not predominate among any particular group of microorganisms. After purification, the products from three cultures were analyzed by high-resolution mass spectrometry, 100-mHz proton magnetic resonance spectrometry, ultraviolet spectrometry, and infrared spectrometry. These spectral data indicated that a Mycobacterium sp. oxidized Δ6a,10a-THC to cannabinol and a diastereomeric pair of 6a-hydroxy-Δ10,10a-THC isomers; a Streptomyces sp. and a Bacillus sp. oxidized Δ6a,10a-THC to 7-keto-Δ6a,10a-THC and 4′-hydroxy-Δ6a,10a-THC, respectively. The occurrence of these products and the presence of others that have not yet been isolated or identified indicate that microbial transformation may be a useful tool for the preparation of new cannabinoids that have desirable pharmacological properties.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott B. J., Laskin A. I., McCoy C. J. Growth of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus on ethanol. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):787–792. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.787-792.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer R. A., Boyd D. B., Demarco P. V., Tyminski I. J., Allinger N. L. Structural studies of cannabinoids. A theoretical and proton magnetic resonance analysis. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Aug 26;92(17):5200–5206. doi: 10.1021/ja00720a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeck L. D., Hoehn M. M., Westhead J. E., Wolter R. K., Thomas D. N. New azasteroidal antifungal antibotics from Geotrichum flavo-brunneum. I. Discovery and fermentation studies. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975 Feb;28(2):95–101. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKEY R. J., TRESNER H. D. A cobalt-containing medium for sporulation of Streptomyces species. J Bacteriol. 1952 Dec;64(6):891–892. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.6.891-892.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamil R. L., Hoehn M. M. A9145, a new adenine-containing antifungal antibiotic. I. Discovery and isolation. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1973 Aug;26(8):463–465. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.26.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn M. M., Murphy H. W., Pugh C. T., Davis N. E. Paper chromatographic techniques for the determination of cephalothin and desacetylcephalothin in body fluids. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Nov;20(5):734–736. doi: 10.1128/am.20.5.734-736.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechoulam R., Gaoni Y. The absolute configuration of delta-1-tetrahydrocannabinol, the major active constituent of hashish. Tetrahedron Lett. 1967 Mar;12:1109–1111. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)90646-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


