Abstract
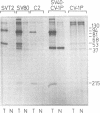
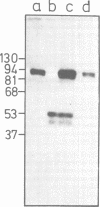
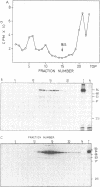
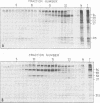
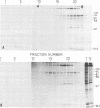
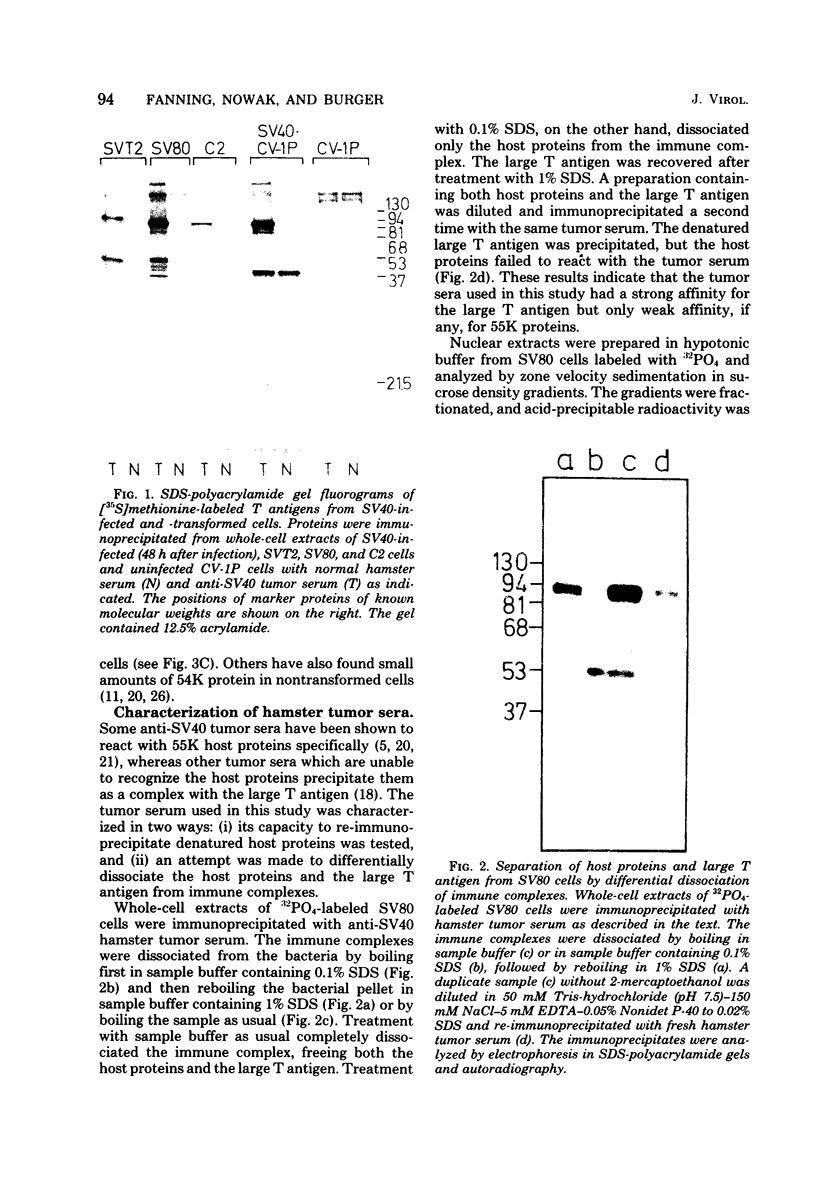
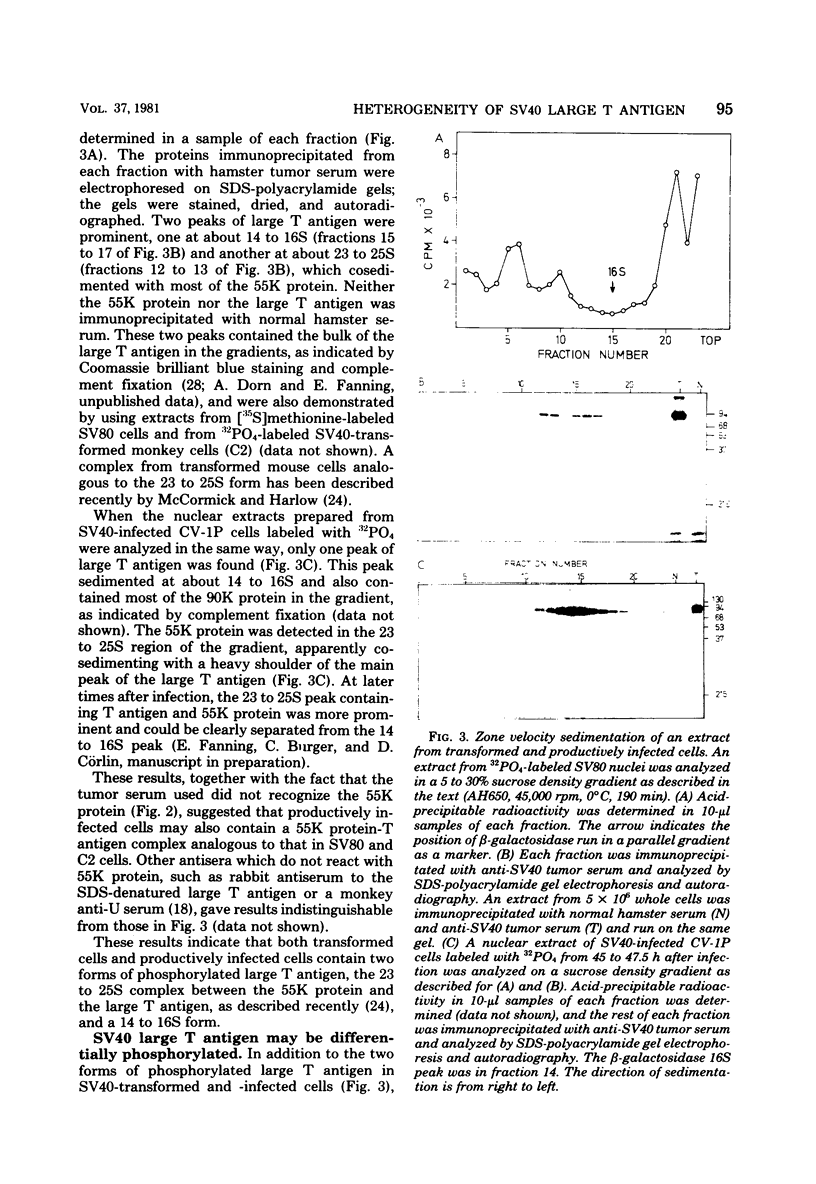
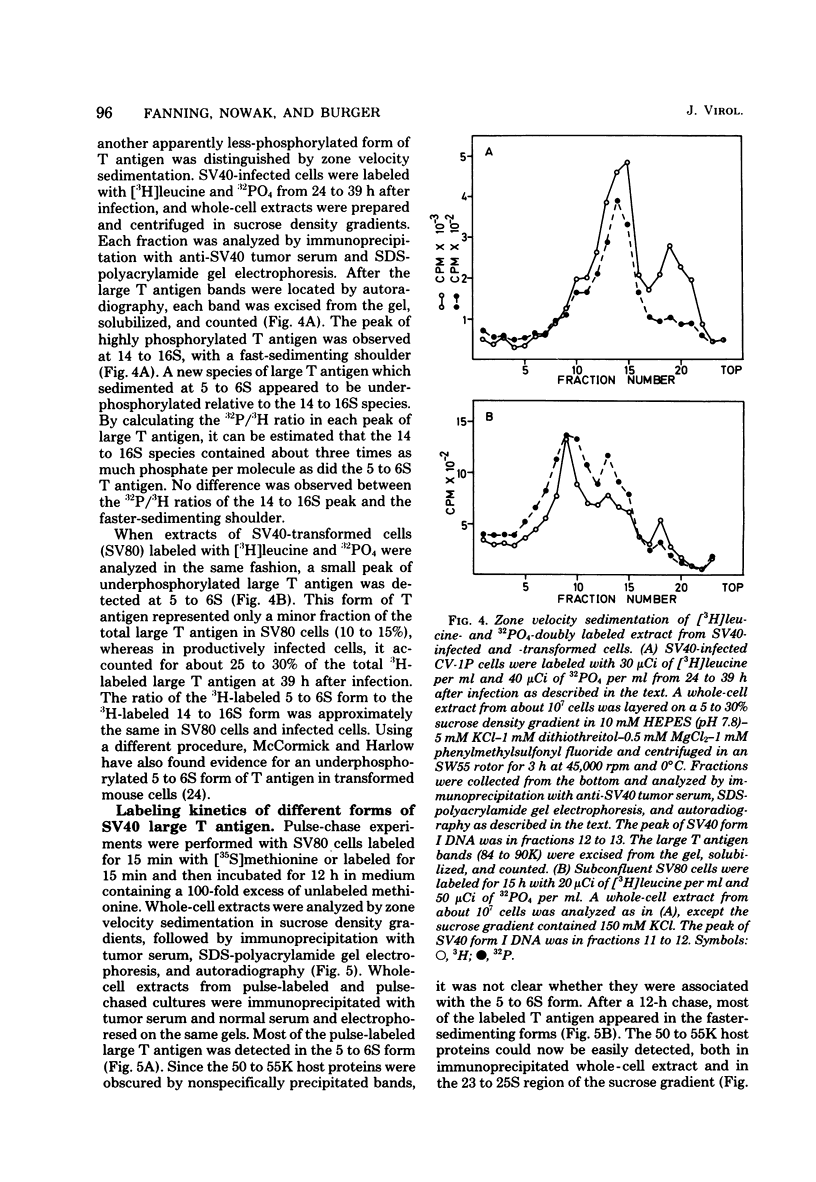
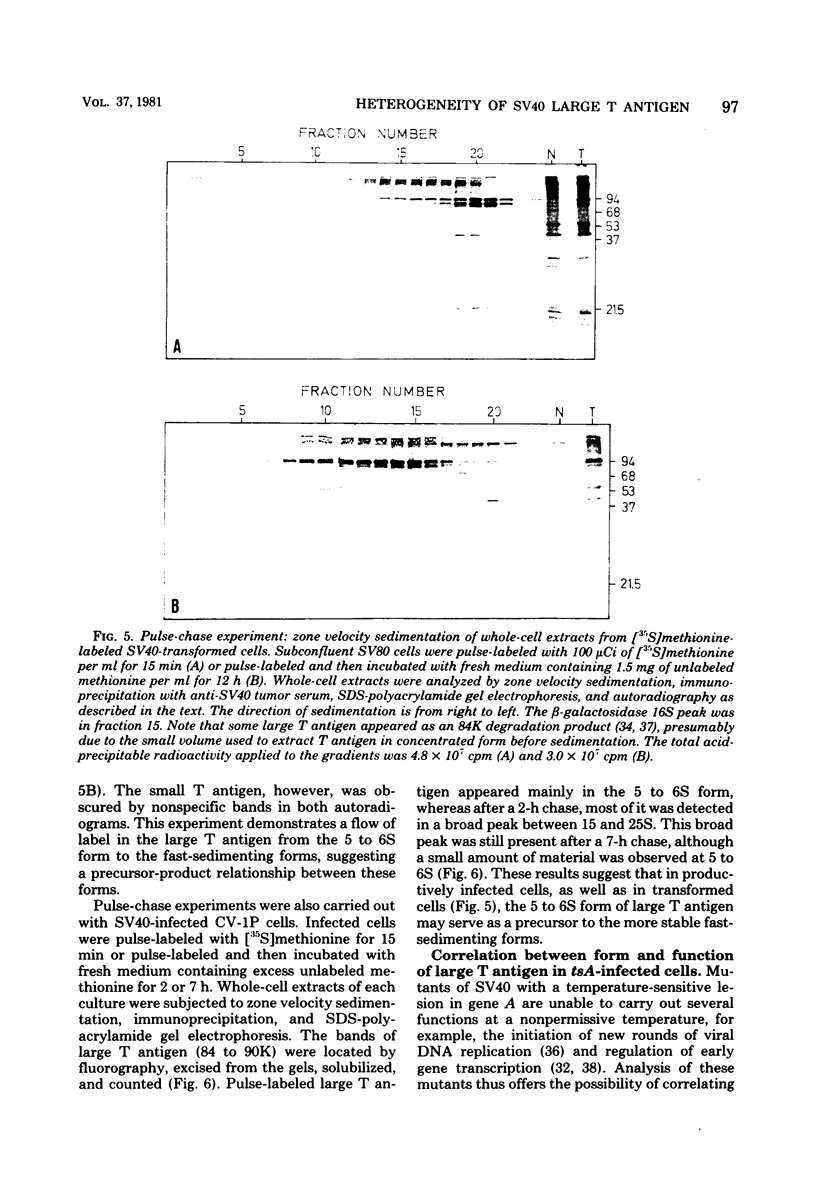
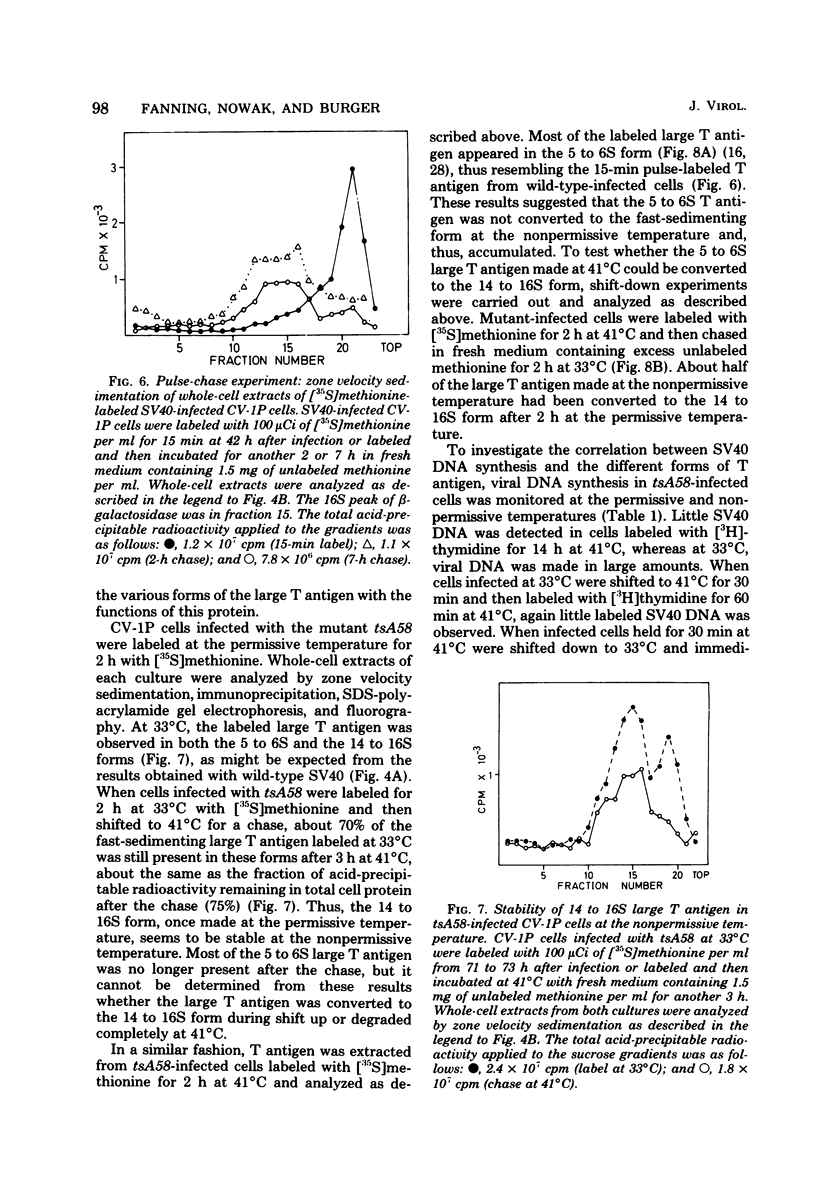
Subclasses of simian virus 40 large T antigen in simian virus 40-transformed and -infected cells separated by zone velocity sedimentation in sucrose density gradients have been characterized. Three forms of large T antigen were distinguished: a 5 to 6S form, a 14 to 16S form, and a 23 to 25S form. These forms appeared to differ biochemically and biologically. Differential labeling experiments suggested that the 5 to 6S form was less highly phosphorylated than the faster-sedimenting forms. The 23 to 25S form which was complexed with one or more host phosphoproteins, as reported recently (D. P. Lane and L. V. Crawford Nature [London] 268:261-263, 1979; F. McCormick and E. Harlow, J. Virol. 34: 213-224, 1980), was prominent in extracts of transformed cells, but was also detected in productively infected cells. Pulse-chase experiments suggested that the 5 to 6S large T antigen is a precursor of the more stable, faster-sedimenting forms of T antigen. Monkey cells infected with a tsA mutant of simian virus 40 at 41 degrees C contained only 5 to 6S large T antigen, implying that this form is not active in the initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication. In pulse-chase, shift-down experiments, DNA replication resumed, and the 5 to 6S large T antigen which had accumulated at 41 degrees C was partially converted at 33 degrees C to a fast-sedimenting form. However, shift-up experiments demonstrated that the fast-sedimenting large T antigen, once formed, remained stable at 41 degrees C, although it was unable to function in initiation. These experiments suggest that different biological functions of large T antigen may be carried out by different subclasses of this protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Development of 3T3-like lines from Balb-c mouse embryo cultures: transformation susceptibility to SV40. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2):141–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK P. H., ROWE W. P. AN ANALYSIS OF SV40-INDUCED TRANSFORMATION OF HAMSTER KIDNEY TISSUE IN VITRO. I. GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:606–613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner I., Kuhn C., Fanning E. Identification and characterization of fast-sedimenting SV40 nucleoprotein complexes. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):54–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Hager L., Dulbecco R. Simian virus 40 T antigen binds to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3754–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Simmons D. T., Martin M. A., Mora P. T. Identification and partial characterization of new antigens from simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.463-471.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo A. B., Jay G., Appella E., Dubois G. C., Law L. W., Old L. J. Detection of a transformation-related antigen in chemically induced sarcomas and other transformed cells of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2420–2424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. A., Khoury G., Martin R. G. Phosphorylation of T-antigen and control T-antigen expression in cells transformed by wild-type and tsA mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):753–762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.753-762.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Baumgartner I. Role of fast-sedimenting SV40 nucleoprotein complexes in virus assembly. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudray P., Rassoulzadegan M., Cuzin F. Expression of simian virus 40 early genes in transformed rat cells is correlated with maintenance of the transformed phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4987–4991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Davison J., Oren M., Winocour E. Properties of permissive monkey cells transformed by UV-irradiated simian virus 40. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):256–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.256-266.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Nathans D. The genome of simian virus 40. Adv Virus Res. 1977;21:85–173. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60762-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Fanning E., Otto B., Knippers R. Maturation of newly replicated chromatin of simian virus 40 and its host cell. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 5;136(4):359–374. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90395-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., May E., Cassingena R., May P. Simian virus 40-transformed cells express new species of proteins precipitable by anti-simian virus 40 tumor serum. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):472–483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.472-483.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino T., Yamaguchi N. Characterization of T antigen in cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1302–1307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1302-1307.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Rowe W. P. Studies on nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. I. A newly characterized simian virus 40 antigen induced by the Ad2+ND 1 virus. J Virol. 1971 Feb;7(2):189–197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.2.189-197.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. The SV40 A gene product is required for the production of a 54,000 MW cellular tumor antigen. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):308–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90554-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K., Hunter T., Walter G., Linke H. Evidence for simian virus 40 (SV40) coding of SV40 T-antigen and the SV40-specific proteins in HeLa cells infected with nondefective adenovirus type 2-SV40 hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):151–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.151-169.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Setlow V. P., Edwards C. A., Vembu D. The roles of the simian virus 40 tumor antigens in transformation of Chinese hamster lung cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Harlow E. Association of a murine 53,000-dalton phosphoprotein with simian virus 40 large-T antigen in transformed cells. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):213–224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.213-224.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melero J. A., Stitt D. T., Mangel W. F., Carroll R. B. Identification of new polypeptide species (48-55K) immunoprecipitable by antiserum to purified large T antigen and present in SV40-infected and -transformed cells. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):466–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melero J. A., Tur S., Carroll R. B. Host nuclear proteins expressed in simian virus 40-transformed and -infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):97–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Winocour E., Prives C. Differential affinities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen for DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):220–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. SV40: T antigen, the A function and transformation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):267–276. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. W., McLaughlin B. C., Oxford J. S. Simian virus 40-induced T and tumor antigens. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):574–579. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.574-579.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Gilboa E., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of simian virus 40 early messenger RNA coding for viral T-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):457–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K., Collins J. K., Tegtmeyer P., Ozer H. L., Lai C. J., Nathans D. Identification of simian virus 40 protein A. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):636–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.636-646.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Smith R., Paucha E. Characterization of different tumor antigens present in cells transformed by simian virus 40. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):335–346. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Smith R., Paucha E. Extraction and fingerprint analysis of simian virus 40 large and small T-antigens. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):140–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.140-153.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Rundell K., Collins J. K. Modification of simian virus 40 protein A. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):647–657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.647-657.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Green H., Swift M. R. Susceptibility of human diploid fibroblast strains to transformation by SV40 virus. Science. 1966 Sep 9;153(3741):1252–1254. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3741.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]