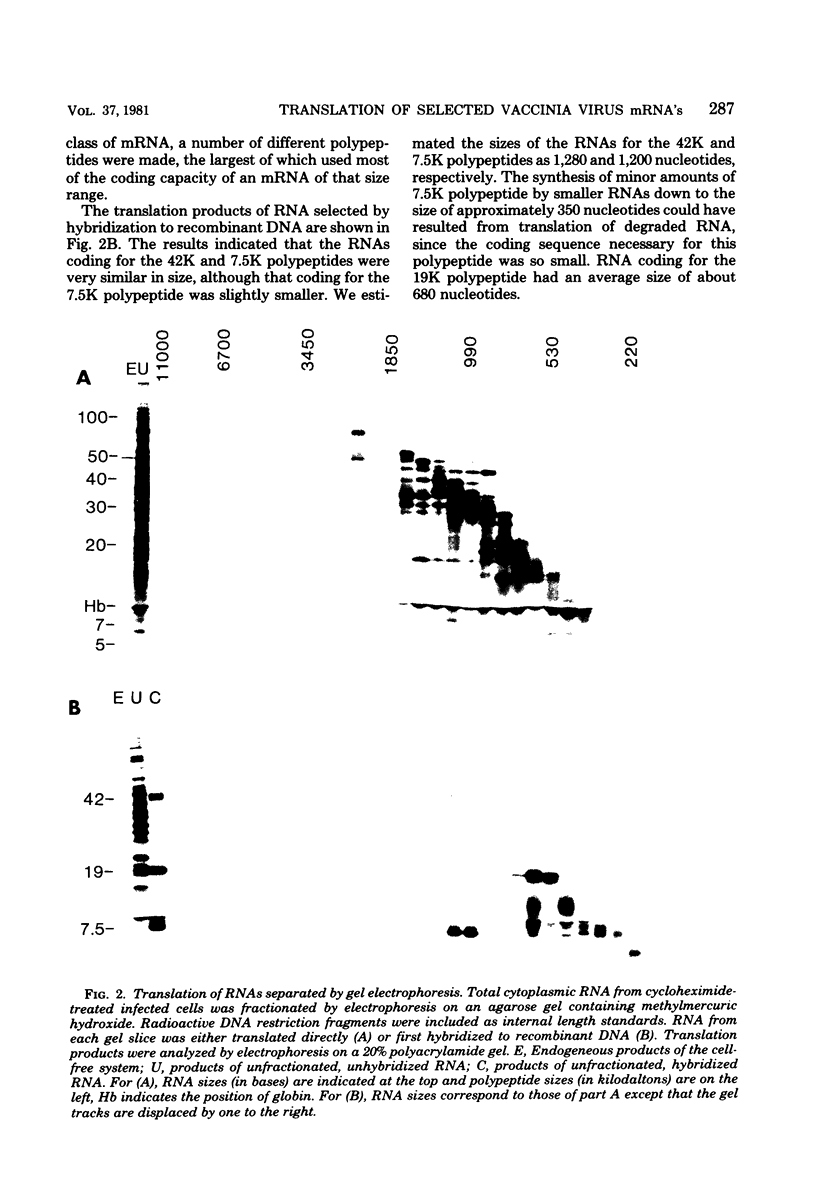
Abstract
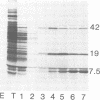
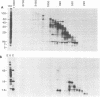
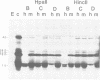
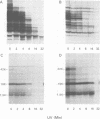
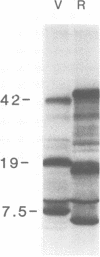
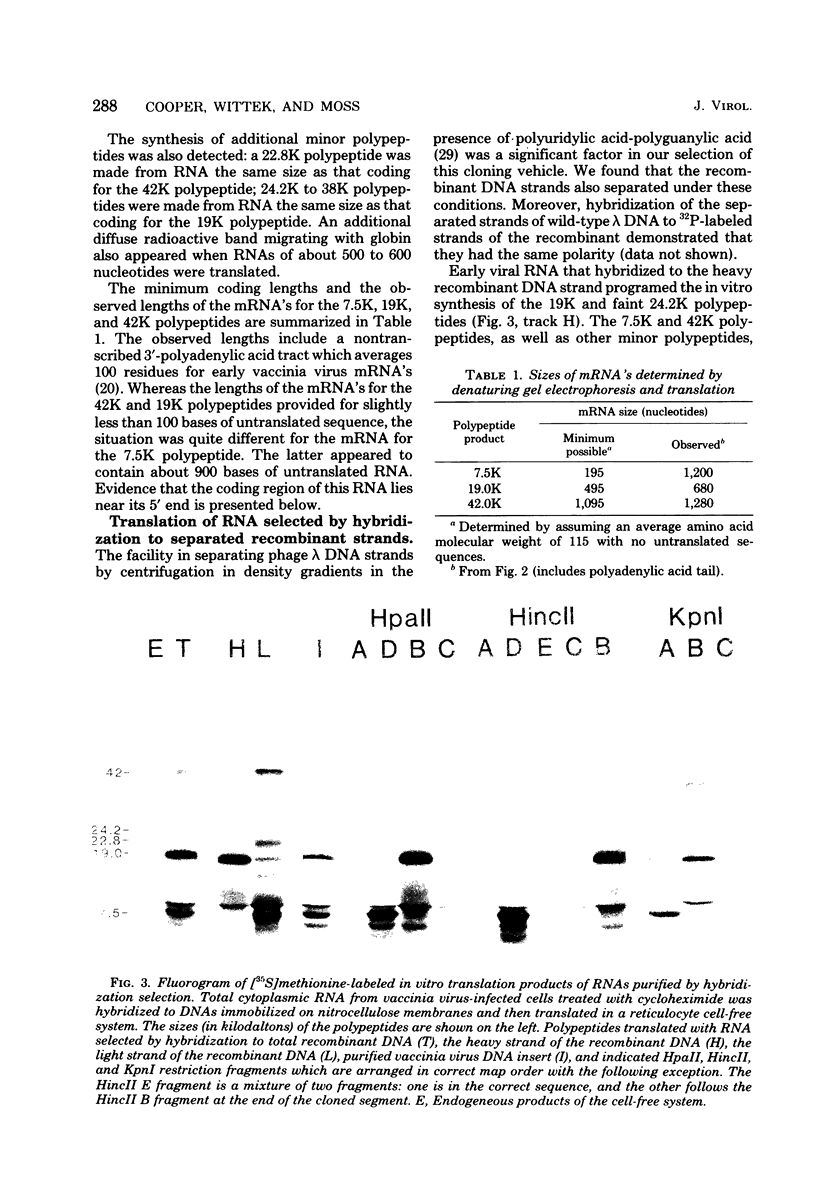
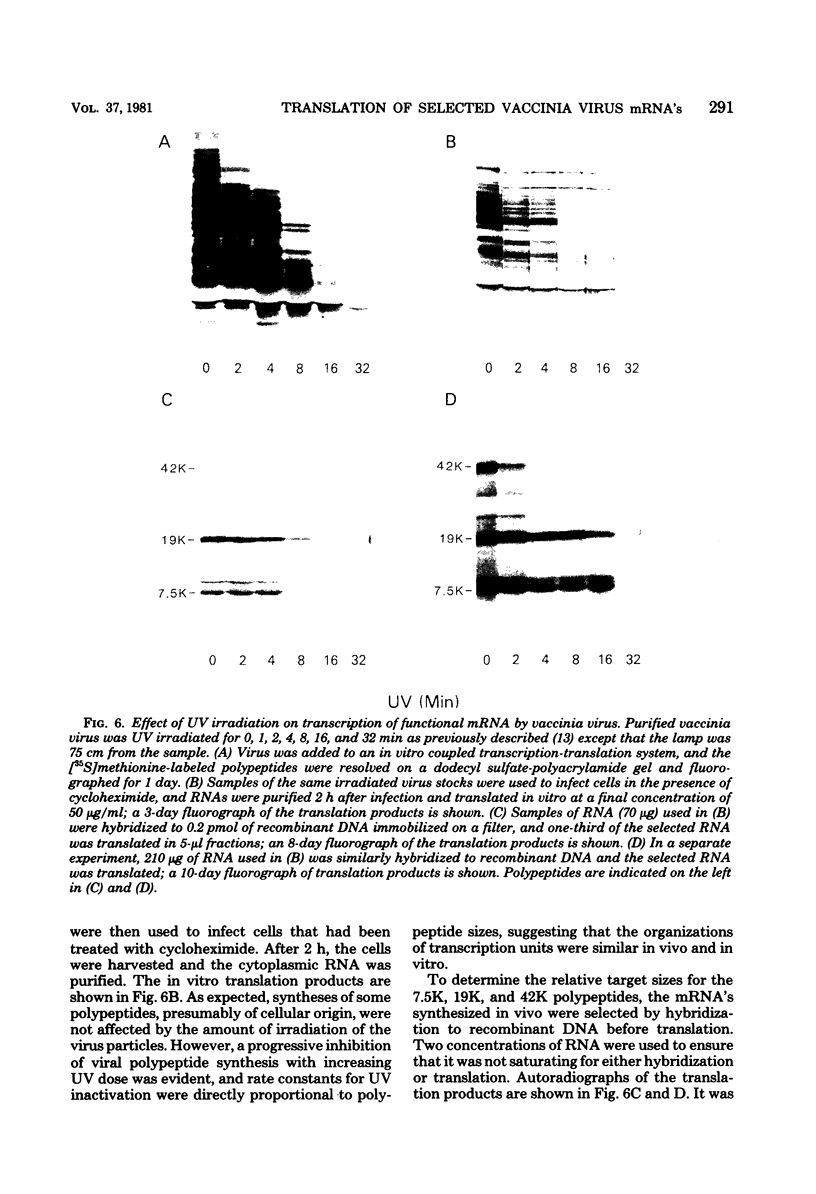
Early polypeptides encoded within the 10,000-base pair terminally repeated region of the vaccinia virus genome were mapped by cell-free translation of mRNA that was selected by hybridization to restriction fragments and to separated strands of a recombinant lambda phage. The results, which were confirmed by hybrid arrest of translation, indicated that polypeptides of 7,500 (7.5K), 19,000 (19K), and 42,000 (42K) daltons mapped at approximately 3.2 to 4.3, 6.5 to 7.2, and 7.2 to 8.3 kilobase pairs from the end of the genome, respectively. mRNA's for the 42K and 7.5K polypeptides were transcribed towards the end of the genome, whereas mRNA for the 19K polypeptide was transcribed in the opposite direction. Including polyadenylic acid tails, the lengths of the mRNA's for the 7.5K, 19K, and 42K polypeptides, determined by gel electrophoresis of denatured RNA, hybridization selection, and cell-free translation, were approximately 1,200, 680, and 1,280 nucleotides, respectively. mRNA's for the 42K and 19K polypeptides were only about 100 nucleotides longer than the minimums required to code for their respective polypeptides, whereas mRNA for the 7.5K polypeptide contained 900 nucleotides of untranslated sequence. This long untranslated portion of the latter mRNA was probably located near the 3' end, because this gene was only inactivated by high doses of UV irradiation. This small target size also excluded certain models for RNA processing involving formation of the mRNA's for the 42K and 7.5K polypeptides from a common promoter. Rabbitpox virus, which has an inverted terminal repetition approximately half that of vaccinia virus, was also shown to encode mRNA's that hybridized to the cloned terminal segment of vaccinia virus DNA.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone R. F., Moss B. Sequence complexity and relative abundance of vaccinia virus mRNA's synthesized in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):554–569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.554-569.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossart W., Paoletti E., Nuss D. L. Cell-free translation of purified virion-associated high-molecular-weight RNA synthesized in vitro by vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):905–916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.905-916.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Polarity in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B. In vitro translation of immediate early, early, and late classes of RNA from vaccinia virus-infected cells. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):368–380. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B. Transcription of vaccinia virus mRNA coupled to translation in vitro. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):149–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B. Translation of specific vaccinia virus RNAs purified as RNA-DNA hybrids on potassium iodide gradients. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3599–3612. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Multiple keratins of cultured human epidermal cells are translated from different mRNA molecules. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garon C. F., Barbosa E., Moss B. Visualization of an inverted terminal repetition in vaccinia virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4863–4867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershowitz A., Boone R. F., Moss B. Multiple roles for ATP in the synthesis and processing of mRNA by vaccinia virus: specific inhibitory effects of adenosine (beta,gamma-imido) triphosphate. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):399–408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.399-408.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershowitz A., Moss B. Abortive transcription products of vaccinia virus are guanylylated, methylated, and polyadenylylated. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):849–853. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.849-853.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter A. R., Farrell P. J., Jackson R. J., Hunt T. The role of polyamines in cell-free protein synthesis in the wheat-germ system. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):149–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Garrels J. I. Characterization of the mRNAs for alpha-, beta- and gamma-actin. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):767–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90276-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. THE INTRACELLULAR UNCOATING OF POXVIRUS DNA. I. THE FATE OF RADIOACTIVELY-LABELED RABBITPOX VIRUS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Feb;8:263–276. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan M., Spector D. J., Goldenberg C. J., Halbert D., Raskas H. J. Purification of specific adenovirus 2 RNAs by preparative hybridization and selective thermal elution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):593–607. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis by the vaccinia virion. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1028–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1028-1037.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Joklik W. K. Poly (A) sequences of vaccinia virus messenger RNA: nature, mode of addition and function during translation in vitra and in vivo. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90365-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Grady L. J. Transcriptional complexity of vaccinia virus in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):608–615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.608-615.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E. High molecular weight virion-associated RNA of vaccinia. A possible precursor to 8 to 12 S mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):872–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Kuff E. L. Structural gene identification and mapping by DNA-mRNA hybrid-arrested cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4370–4374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Leaky UAG termination codon in tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):469–471. doi: 10.1038/272469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Use of coupled transcription and translation to study mRNA production by vaccinia cores. Nature. 1977 Oct 6;269(5628):532–534. doi: 10.1038/269532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümperli D., Menna A., Schwendimann F., Wittek R., Wyler R. Symmetrical arrangement of the heterologous regions of rabbit poxvirus and vaccinia virus DNA. J Gen Virol. 1980 Apr;47(2):385–398. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-2-385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittek R., Barbosa E., Cooper J. A., Garon C. F., Chan H., Moss B. Inverted terminal repetition in vaccinia virus DNA encodes early mRNAs. Nature. 1980 May 1;285(5759):21–25. doi: 10.1038/285021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittek R., Cooper J. A., Barbosa E., Moss B. Expression of the vaccinia virus genome: analysis and mapping of mRNAs encoded within the inverted terminal repetition. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90485-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittek R., Menna A., Müller H. K., Schümperli D., Boseley P. G., Wyler R. Inverted terminal repeats in rabbit poxvirus and vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):171–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.171-181.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittek R., Menna A., Schümperli D., Stoffel S., Müller H. K., Wyler R. HindIII and Sst I restriction sites mapped on rabbit poxvirus and vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):669–678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.669-678.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittek R., Moss B. Tandem repeats within the inverted terminal repetition of vaccinia virus DNA. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]