Abstract
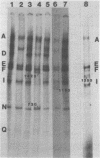
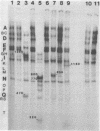
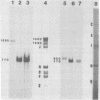
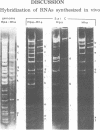
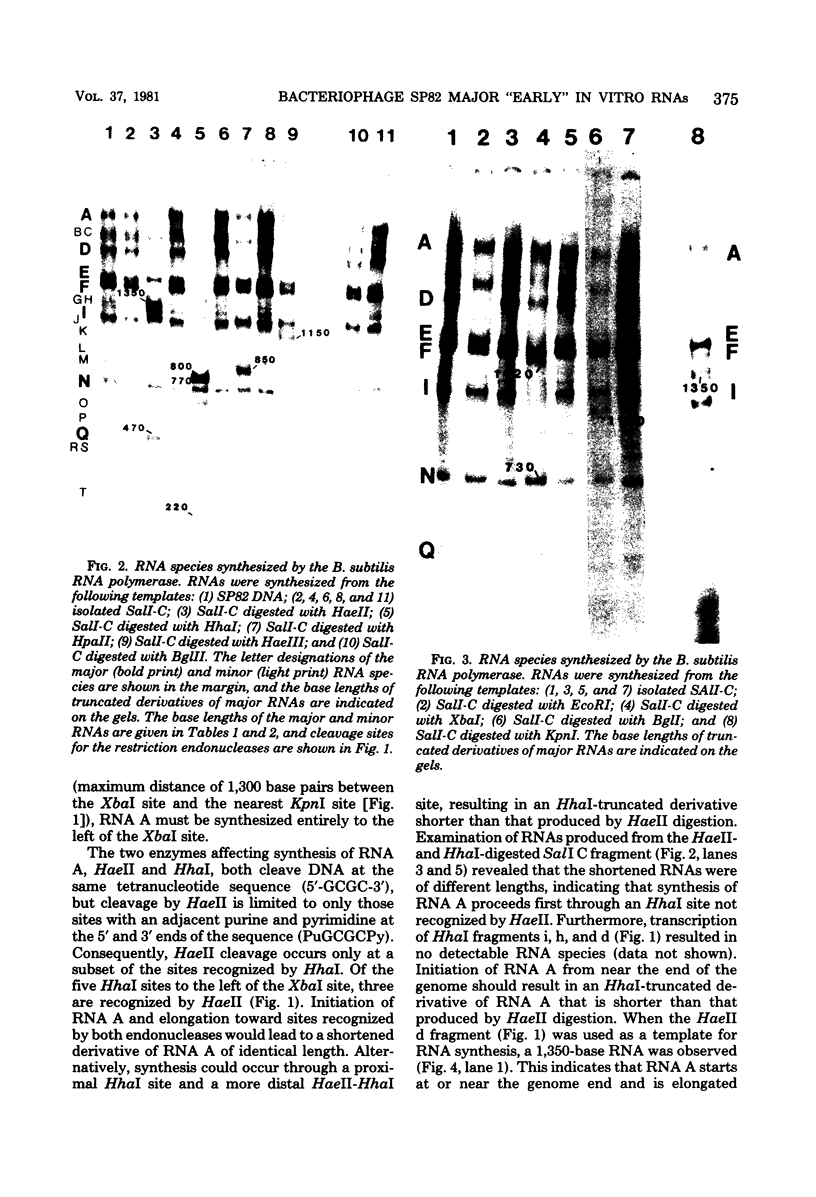
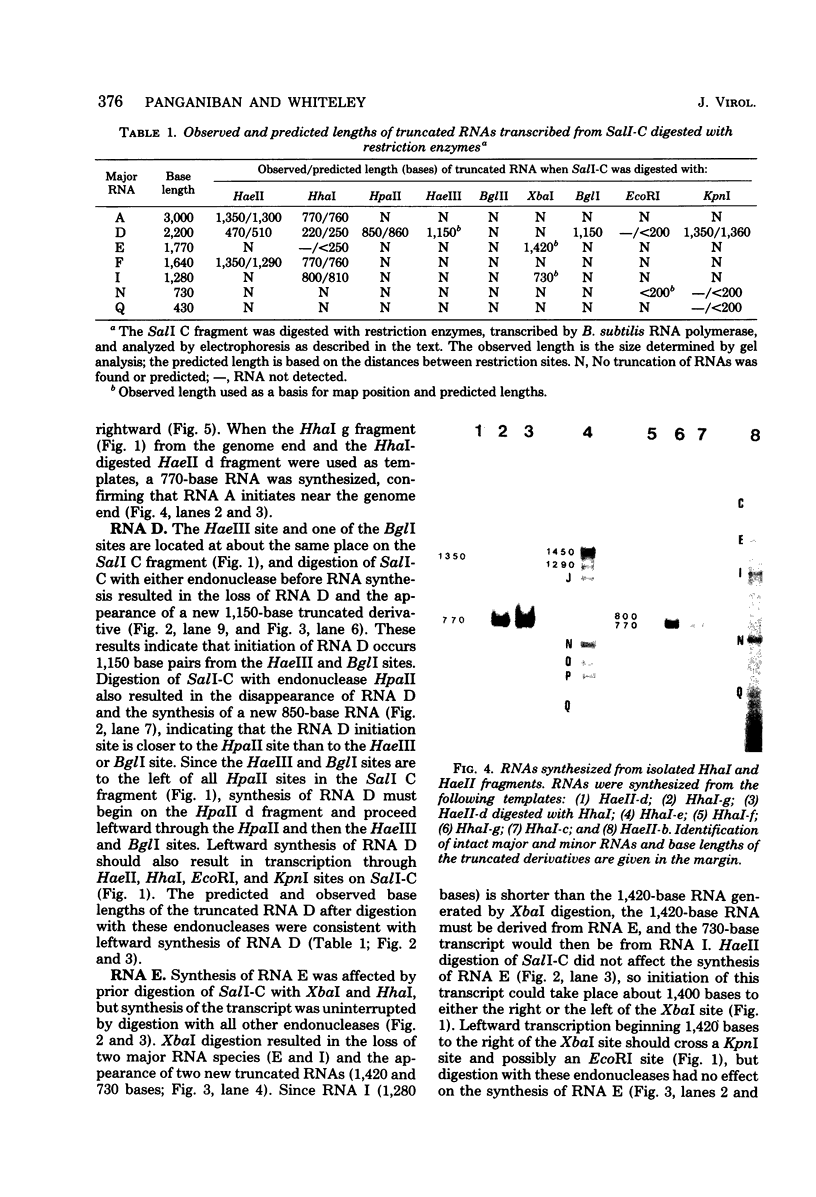
A restriction map was constructed for the 17.5-kilobase SalI C fragment of SP82 DNA. Unfractionated SP82 DNA, the SalI C fragment, and restriction fragments derived from SalI-C were used as templates for in vitro synthesis by the Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase, and the resulting transcripts were analyzed by gel electrophoresis. Comparison of the RNA species obtained from SalI-C with those produced from unfractionated DNA indicated that most of the RNAs and all of the major transcripts originate from the SalI C fragment; this fragment contains one copy of the terminally redundant portion of the genome. Seven major transcripts, a bidirectional terminator site, and 5 of the 13 minor transcripts were located within the 13-kilobase redundant region. The binding of polymerase to fragments of DNA produced by digestion of SalI-C with HpaII and HhaI was used to identify promoter-bearing regions within SalI-C.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamberlin M. J. The selectivity of transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):721–775. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cregg J. M., Stewart C. R. Terminal redundancy of "high frequency of recombination" markers of Bacillus subtilis phage SPO1. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):530–541. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. T7 early RNAs are generated by site-specific cleavages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1559–1563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage L. P., Geiduschek E. P. RNA synthesis during bacteriophage SPO1 development: six classes of SPO1 RNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):279–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage L. P., Geiduschek E. P. RNA synthesis during bacteriphage SPO1 development. II. Some modulations and prerequisites of the transcription program. Virology. 1971 Apr;44(1):200–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegenheimer P., Watson N., Apirion D. Multiple pathways for primary processing of ribosomal RNA in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):3064–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P. J., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Betlach M. C., Covarrubias A. A., Backman K., Russel D. J., Tait R., Boyer H. W. A general method for the purification of restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2373–2380. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiatt W. R., Whiteley H. R. Translation of RNAs synthesized in vivo and in vitro from bacteriophage SP82 DNA. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):616–629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.616-629.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. B., Chan H., Rothstein S., Wells R. D., Reznikoff W. S. RNA polymerase binding sites in lambdaplac5 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4914–4918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrie J. M. DNA strand specificity of transcripts produced in vivo and in vitro by RNA polymerase from SP82-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1286–1288. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1286-1288.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrie J. M., Spiegelman G. B., Whiteley H. R. DNA strand specificity of temporal RNA classes produced during infection of Bacillus subtilis by SP82. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):359–373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.359-373.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pero J., Hannett N. M., Talkington C. Restriction cleavage map of SP01 DNA: general location of early, middle, and late genes. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):156–171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.156-171.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. A., Thomas C. A., Jr, MacHattie L. A., Wensink P. C. Terminal repetition in non-permuted T3 and T7 bacteriophage DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1967 Feb 14;23(3):365–376. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman G. B., Hiatt W. R., Whiteley H. R. Role of the 21,000 molecular weight polypeptide of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase in RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1756–1765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman G. B., Whiteley H. R. Bacteriophage SP82 induced modifications of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase result in the recognition of additional RNA synthesis initiation sites on phage DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):1058–1065. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91458-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman G. B., Whiteley H. R. In vivo and in vitro transcription by ribonucleic acid polymerase from SP82-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1483–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford D. W., Bieber D. Concentration of DNA solutions by extraction with 2-butanol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 6;378(1):18–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. D. Origin of concatemeric T7 DNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 18;239(94):197–201. doi: 10.1038/newbio239197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]