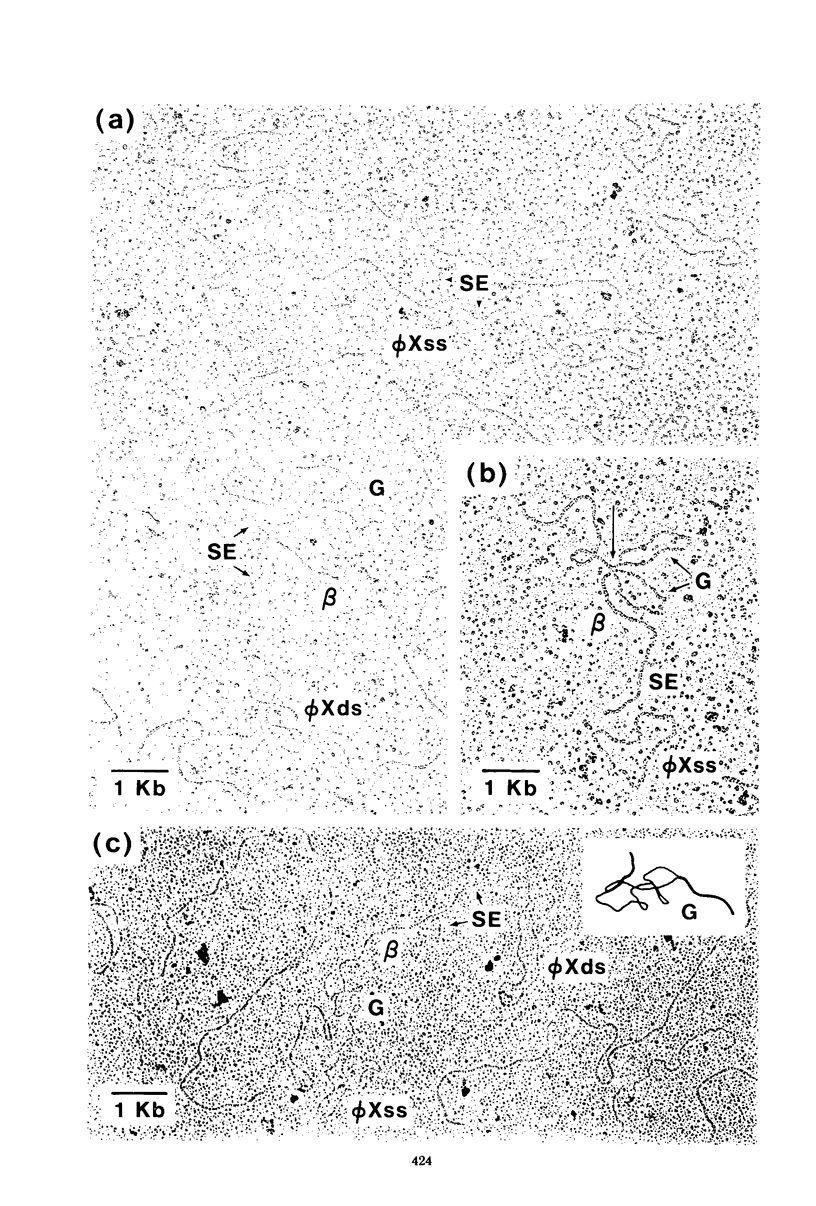
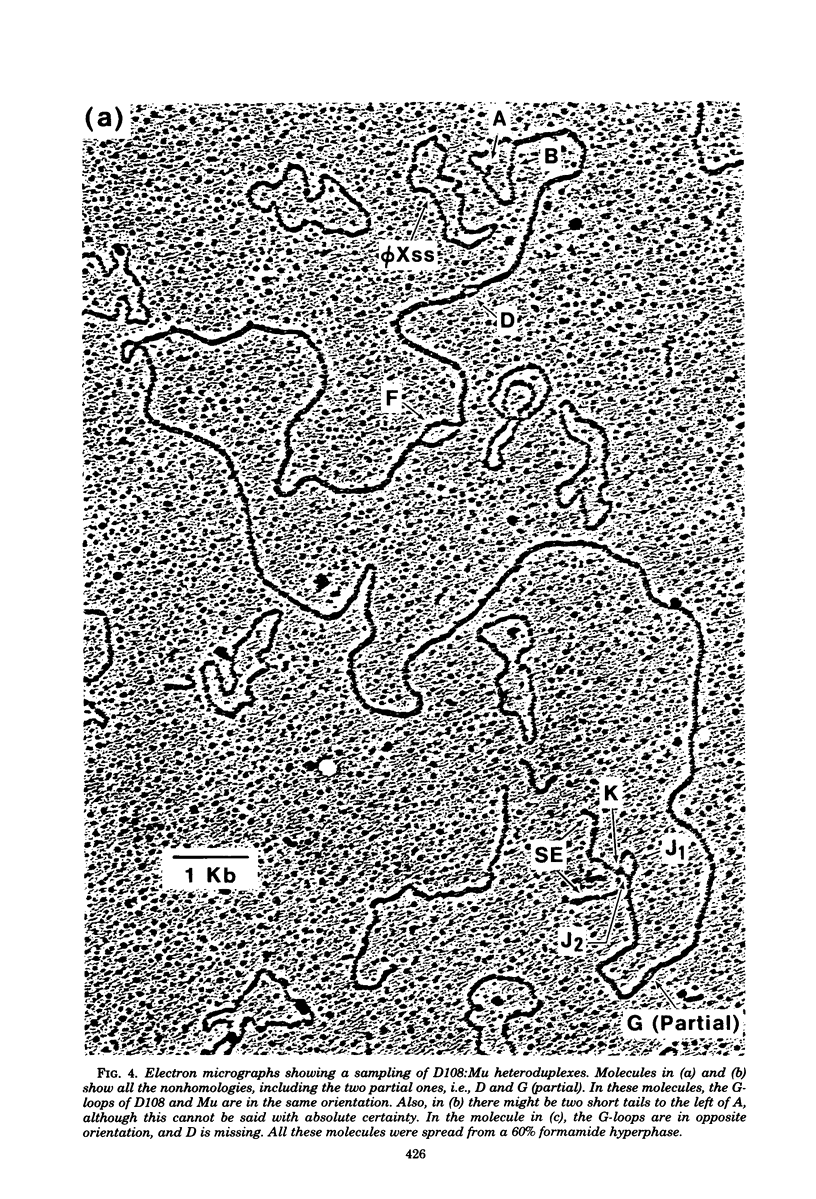
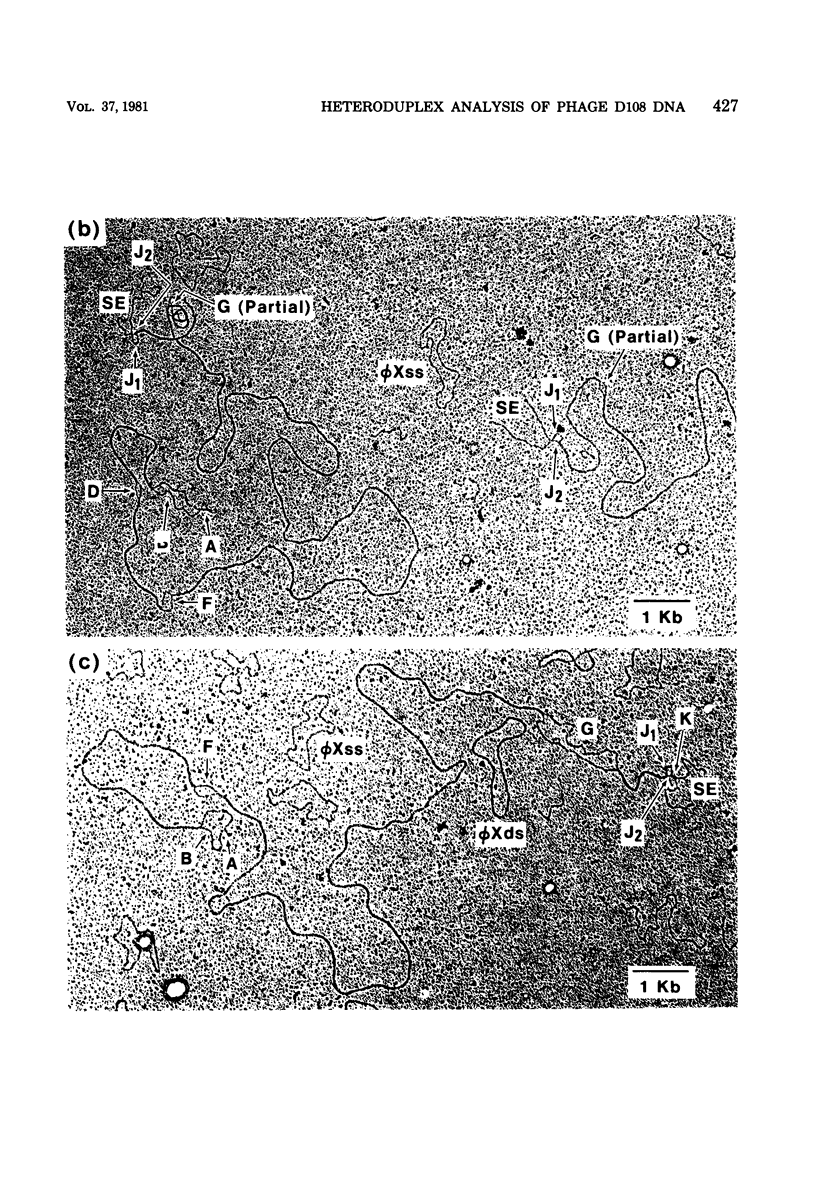
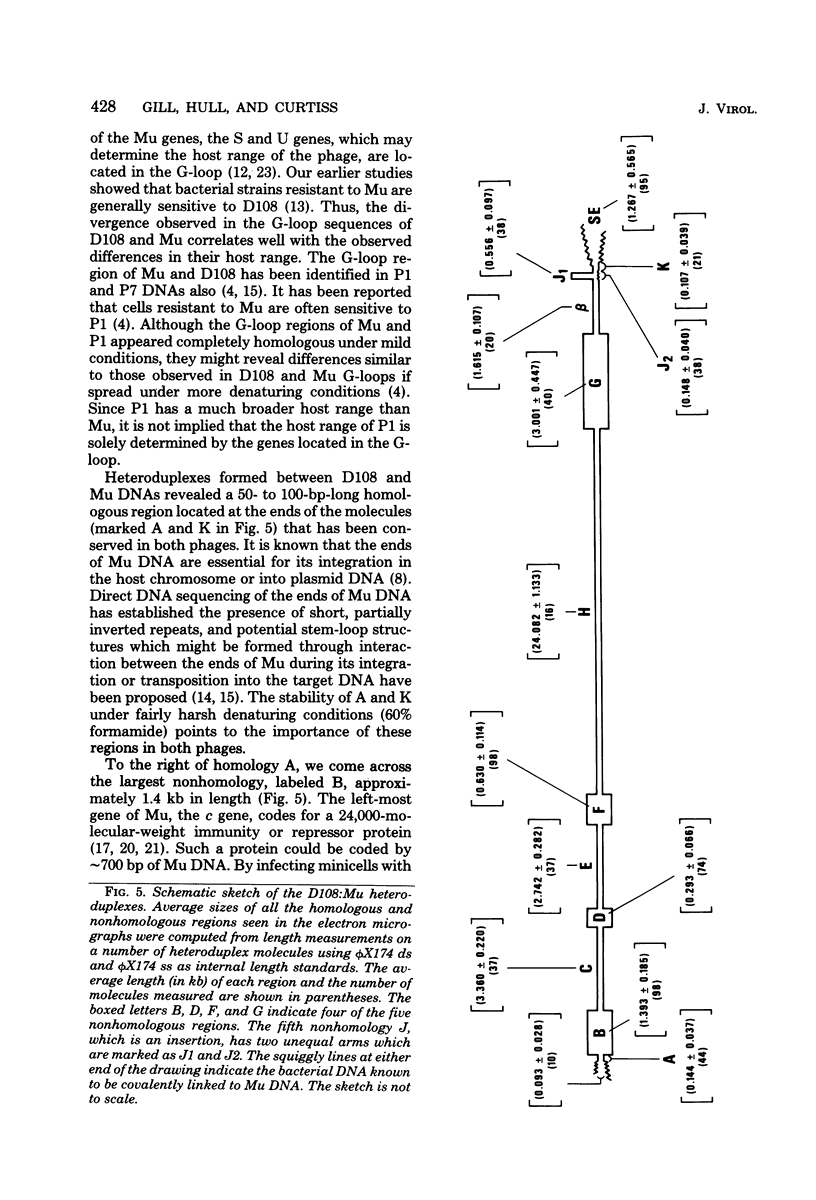
Abstract
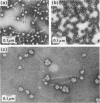
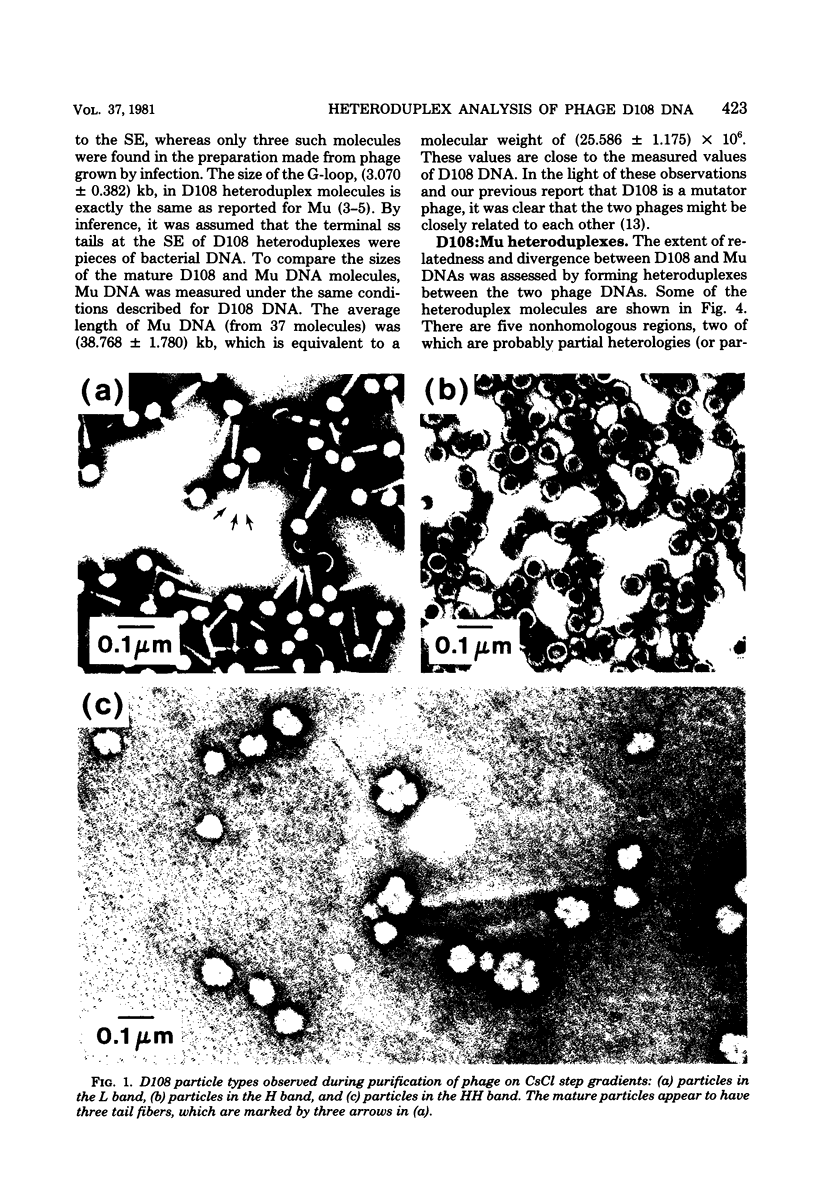
Three types of phage particles were observed on CsCl step gradients when D108 was purified from lysates prepared by induction of a prophage. These particle types were identified to be the mature phage, tailless DNA-filled heads, and a form of nucleoprotein aggregates. The nucleoprotein aggregates banded at a density (rho) of greater than 1.6. DNA molecules isolated from mature phage particles were (38.305 +/- 1.226) kilobases (kb) in length. Denaturation and renaturation of D108 DNA resulted in the formation of linear double-stranded molecules with variable-length single-stranded tails at one end. About 30% of the annealed molecules also carried an internal nonhomology, which was shown to be the region called the G-loop in Mu and P1 DNAs. Following the notation used for different regions of denatured, annealed Mu DNA, we measured the lengths of the equivalent D108 DNA regions to be as alpha-D108 = (32.178 +/- 1.370) kb; G-D108 = (3.07 +/- 0.382) kb; beta-D108 = (2.291 +/- 0.306) kb; SE-D108 = (0.966 +/- 0.433) kb. Formation of D108; Mu heteroduplexes disclosed the presence of five nonhomologies, two of which were partial. One of the partial heterologies was in the G-loop region. The largest nonhomology, (1.393 +/- 0.185) kb in size, was near the c end (immunity region) and probably spans the c and the ner genes of Mu. beta-D108 was shown to carry a (0.556 +/- 0.097)-kb insertion close to its right end. A short 100-base-pair region appeared to have been conserved at the ends of D108 and Mu. Occasionally, a 50-to 100-base-pair-long unpaired region was also observed at the left end of D108: Mu heteroduplexes. These sequences were presumably of bacterial DNA. Taken together, our results complement and extend our earlier genetic studies which established that D108 was a mutator phage heteroimmune to Mu with a host range different from Mu's.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allet B., Bukhari A. I. Analysis of bacteriophage mu and lambda-mu hybrid DNAs by specific endonucleases. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 15;92(4):529–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I., Froshauer S., Botchan M. Ends of bacteriophage mu DNA. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):580–583. doi: 10.1038/264580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I., Taylor A. L. Influence of insertions on packaging of host sequences covalently linked to bacteriophage Mu DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4399–4403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Bukhari A. I. The invertible DNA segments of coliphages Mu and P1 are identical. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell E., Abelson J., Kim J. S., Davidson N. Heteroduplex structures of bacteriophage Mu DNA. Virology. 1973 Jan;51(1):237–239. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90385-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell E., Kohne D. E., Abelson J. Characterization of the inhomogeneous DNA in virions of bacteriophage Mu by DNA reannealing kinetics. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):739–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.739-743.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faelen M., Resibois A., Toussaint A. Mini-mu: an insertion element derived from temperate phage mu-1. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1169–1177. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. S., MacHattie L. A. Limited permutations of the nucleotide sequence in bacteriophage T1 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):505–515. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giphart-Gassler M., Goosen T., van Meeteren A., Wijffelman C., van de Putte P. Properties of the recombinant plasmid pGP1 containing part of the early region of bacteriophage mu. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1179–1185. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. DNA structure: evidence from electron microscopy. Science. 1978 Aug 11;201(4355):525–527. doi: 10.1126/science.663672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M. M., Schumm J. W., Taylor A. L. The S and U genes of bacteriophage mu are located in the invertible G segment of mu DNA. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):108–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A., Gill G. S., Curtiss R., 3rd Genetic characterization of Mu-like bacteriophage D108. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):513–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.513-518.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R., Kamp D. Nucleotide sequences of the attachment sites of bacteriophage Mu DNA. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):247–250. doi: 10.1038/280247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Kwoh D., Zipser D., Kahmann R. Site-specific recombination in phage mu. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1159–1167. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. S., Davidson N. Electron microscope heteroduplex study of sequence relations of T2, T4, and T6 bacteriophage DNAs. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):93–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwoh D., Zipser D. Specific binding of mu repressor to DNA. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):489–491. doi: 10.1038/277489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungquist E., Khatoon H., DuBow M., Ambrosio L., De Bruijn F., Bukhari A. I. Integration of bacteriophage mu DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1151–1158. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacHattie L. A., Gill G. S. DNA maturation by the "headful" mode in bacteriophage T1. J Mol Biol. 1977 Mar 5;110(3):441–465. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazin M., Allet B. Synthesis of bacteriophage Mu proteins in vitro. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):84–97. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90413-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mise K. Isolation and characterization of a new generalized transducing bacteriophage different from P1 in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):168–175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.168-175.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades M., MacHattie L. A., Thomas C. A., Jr The P22 bacteriophage DNA molecule. I. The mature form. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):21–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streisinger G., Emrich J., Stahl M. M. Chromosome structure in phage t4, iii. Terminal redundancy and length determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):292–295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye B. K., Huberman J. A., Botstein D. Non-random circular permutation of phage P22 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):501–528. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner B. T., Pato M. L. Early events in the replication of Mu prophage DNA. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):587–594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.587-594.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]