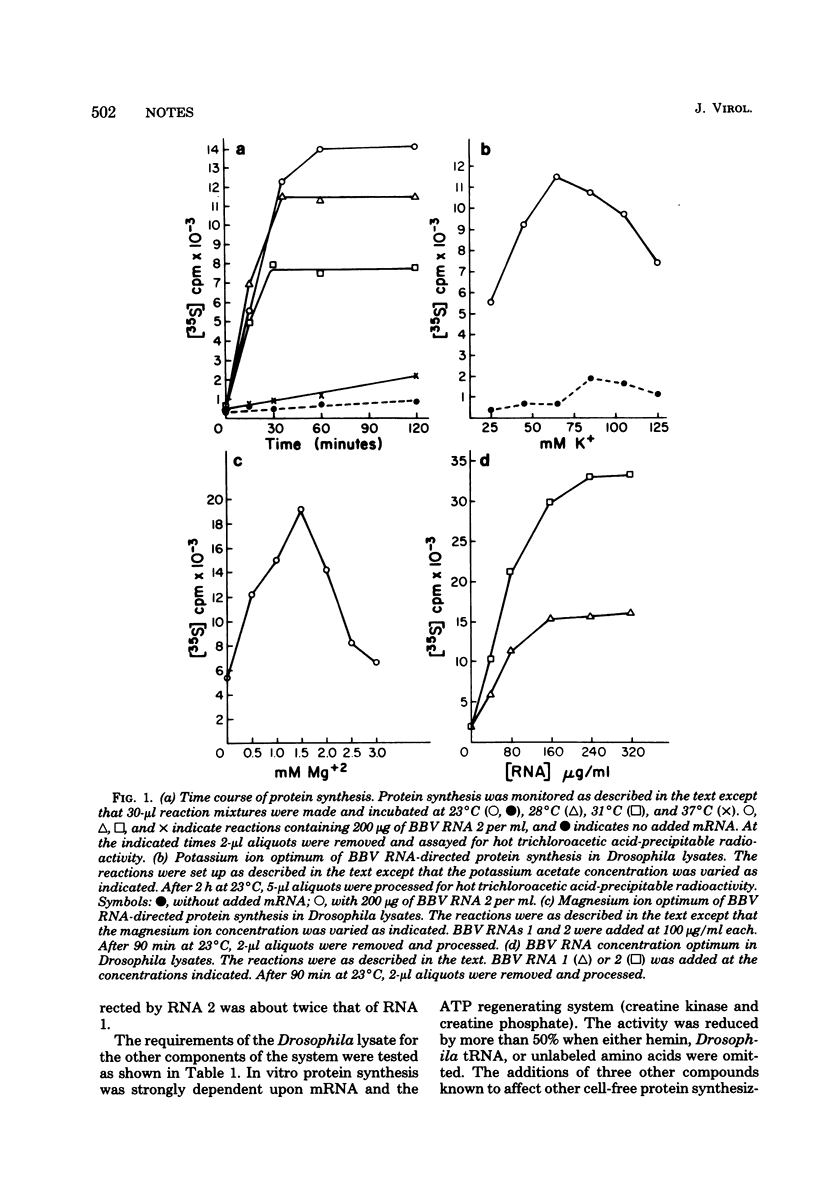
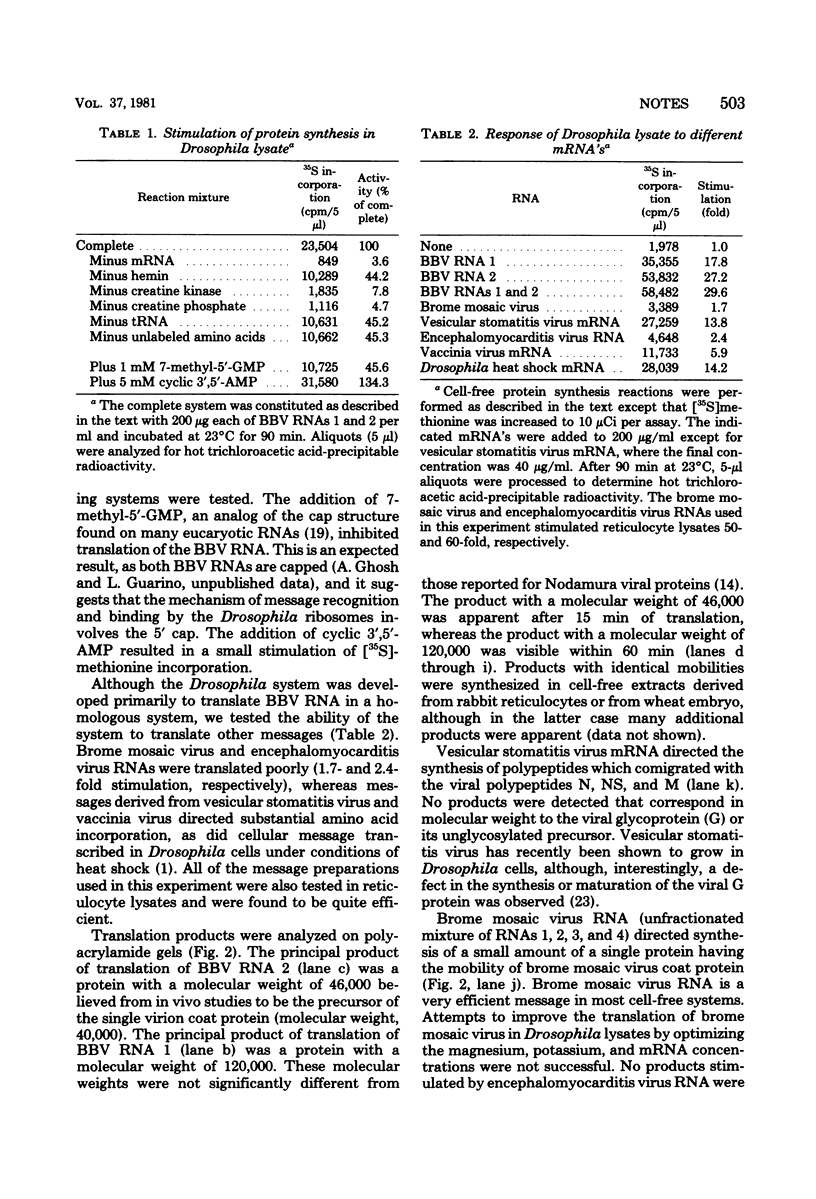
Abstract
A cell-free protein synthesizing system was prepared from cells of Drosophila melanogaster line 1 and made mRNA dependent by treatment with micrococcal nuclease. The system was tested with homologous RNA from black beetle virus propagated in Drosophila cells, with Drosophila heat shock mRNA, and with various heterologous viral mRNA's. Under optimal conditions amino acid incorporation programmed with black beetle virus RNAs was 30-fold higher than endogenous incorporation. RNAs 1 and 2 primarily directed the synthesis of proteins with approximately molecular weights of 120,000 and 46,000, respectively. mRNA's, prepared by transcription from vesicular stomatitis virus or vaccinia virus, were translated efficiently and yielded products that comigrated with authentic viral proteins. Brome mosaic virus RNA and encephalomyocarditis virus RNA were translated poorly. The system retained full activity after freezing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins J. F., Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W., Gesteland R. F. Enhanced differential synthesis of proteins in a mammalian cell-free system by addition of polyamines. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5688–5695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Boime I., Leder P. Protein synthesis directed by encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: properties of a transfer RNA-dependent system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2303–2307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A., White C. N. Coupled transcription and translation in mammalian and avian cell-free systems. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):479–495. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone R. F., Moss B. Sequence complexity and relative abundance of vaccinia virus mRNA's synthesized in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):554–569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.554-569.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX A. S., KAN J., KANG S. H., WALLIS B. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN CELL-FREE PREPARATIONS FROM DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:2059–2065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P., Scotti P., Longworth J., Rueckert R. Black beetle virus: propagation in Drosophila line 1 cells and an infection-resistant subline carrying endogenous black beetle virus-related particles. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):741–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.741-747.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E. S., Snyder L. A. A cell-free system for protein synthesis from newly fertilized eggs of Drosophila melanogaster. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 29;281(1):130–139. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Roberts W. K. Encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: variations in polyadenylic acid content and biological activity. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.325-330.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilan J., Lipmann F. A cell-free protein synthesis system from pupae of Tenebrio molitor. Acta Biochim Pol. 1966;13(4):353–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane L. C., Kaesberg P. Multiple genetic components in bromegrass mosaic virus. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 14;232(28):40–43. doi: 10.1038/newbio232040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longworth J. F., Carey G. P. A small RNA virus with a divided genome from Heteronychus arator (F.) [Coleoperai Scarabaeidae]. J Gen Virol. 1976 Oct;33(1):31–40. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER I. DIFFERENTIATION OF LARVAL DROSOPHILA EYE-ANTENNAL DISCS IN VITRO. J Exp Zool. 1964 Jun;156:91–103. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401560107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider I. Cell lines derived from late embryonic stages of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1972 Apr;27(2):353–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Storti R. V., Pardue M. L., Rich A. Cell-free protein synthesis in lysates of Drosophila melanogaster cells. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1588–1594. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Zimmern D., Rueckert R. R., Kaesberg P. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in reticulocyte lysates: kinetic analysis of the formation of virion proteins and a protein required for processing. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):472–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.472-480.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyers F., Richard-Molard C., Blondel D., Dezelee S. Vesicular stomatitis virus growth in Drosophila melanogaster cells: G protein deficiency. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):411–422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.411-422.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]