Abstract
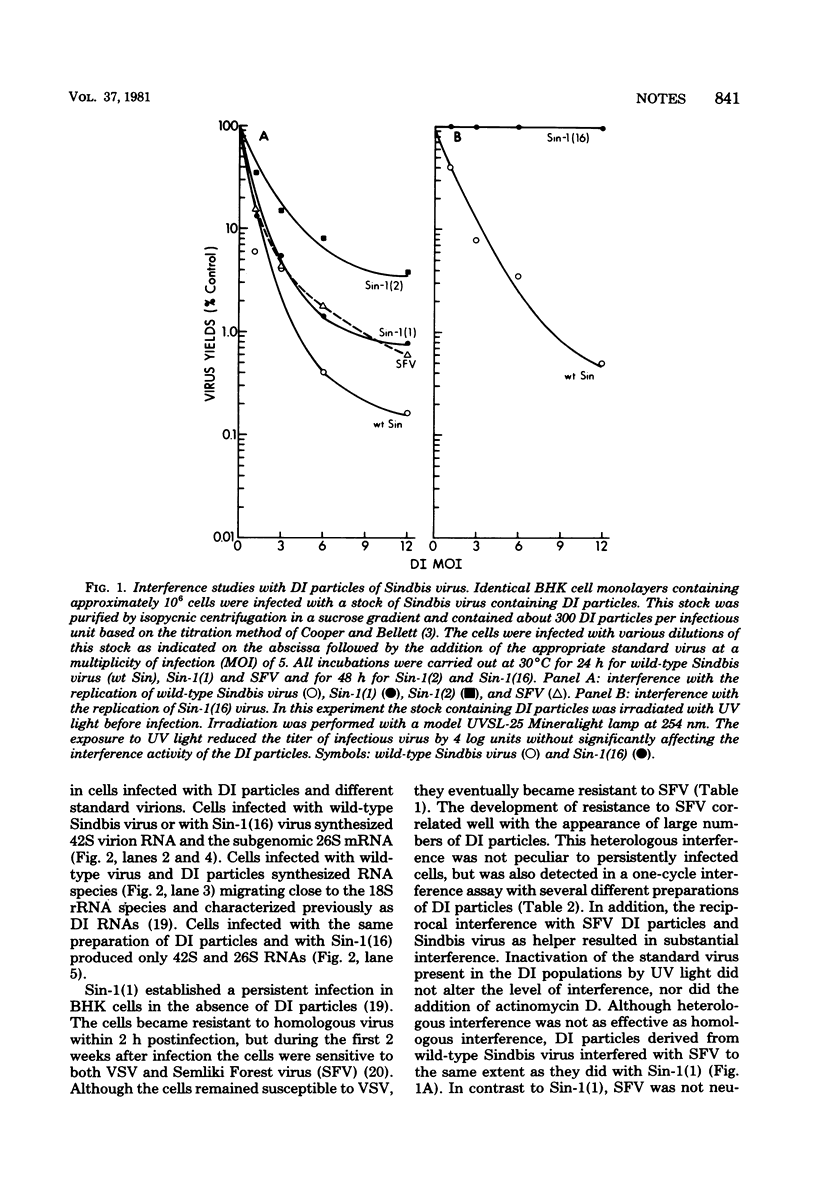
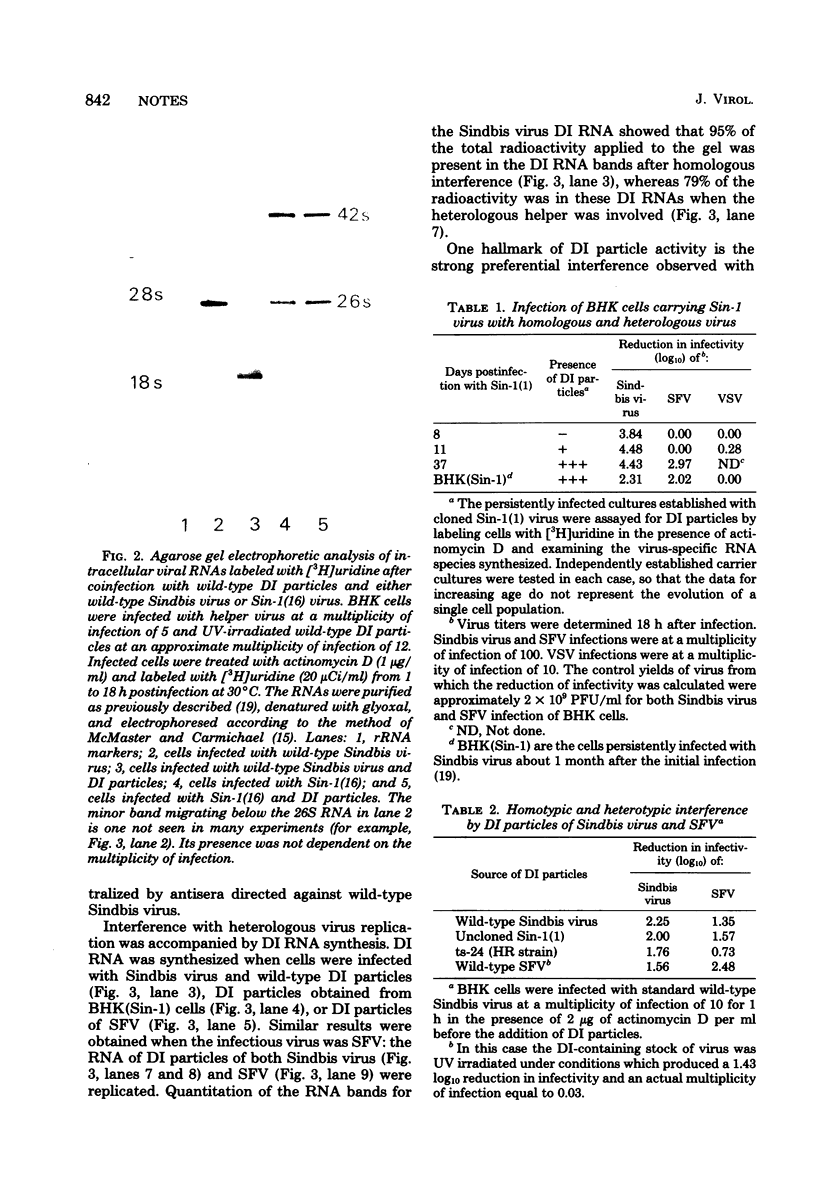
Defective interfering particles derived from wild-type Sindbis virus no longer interfere with the infectious virus cloned from BHK cells persistently infected with Sindbis virus for 16 months. These particles do interfere with the replication of Semliki Forest virus.
Full text
PDF
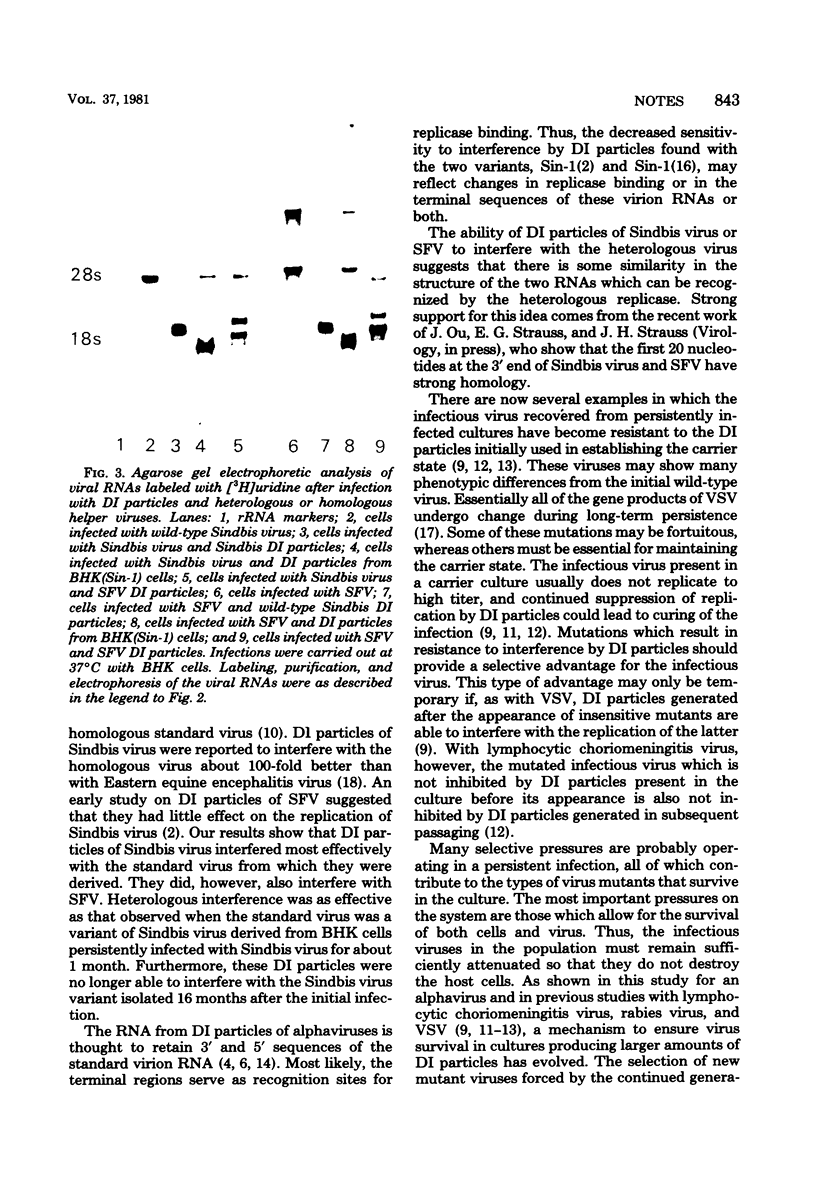

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi T., Lazzarini R. A. Elementary aspects of autointerference and the replication of defective interfering virus particles. Virology. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):152–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruton C. J., Kennedy S. I. Defective-interfering particles of Semliki Forest Virus: structural differences between standard virus and defective-interfering particles. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):383–395. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D., BELLETT A. J. A transmissible interfering component of vesicular stomatitis virus preparations. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Dec;21:485–497. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-3-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohner D., Monroe S., Weiss B., Schlesinger S. Oligonucleotide mapping studies of standard and defective Sindbis virus RNA. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):794–798. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.794-798.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Ramseur J. M. Mechanisms of persistent infections by cytopathic viruses in tissue culture. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1979;60(2):83–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01348025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild G. M., Stollar V. Defective interfering particles of Sindbis virus. V. Sequence relationships between SVSTD 42 S RNA and intracellular defective viral RNAs. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):175–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Grabau E. A., Jones C. L., Semler B. L. Evolution of multiple genome mutations during long-term persistent infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P., Welsh R. M., Oldstone M. B., Kohne D., Lazzarini R., Scolnick E. Long-term persistent vesicular stomatitis virus and rabies virus infection of cells in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1976 Nov;33(2):193–211. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-2-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodyski F. M., Holland J. J. Viruses isolated from cells persistently infected with vesicular stomatitis virus show altered interactions with defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):627–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.627-631.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Dutko F. J., Pfau C. J. Determinants of spontaneous recovery and persistance in MDCK cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):113–122. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Pfau C. J. Viral pathogenesis and resistance to defective interfering particles. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):311–313. doi: 10.1038/283311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai A., Matsumoto S. Interfering and noninterfering defective particles generated by a rabies small plaque variant virus. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):60–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I. Sequence relationships between the genome and the intracellular RNA species of standard and defective-interfering Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):491–511. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preble O. T., Youngner J. S. Temperature-sensitive viruses and the etiology of chronic and inapparent infections. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):467–473. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands K., Grabau E., Spindler K., Jones C., Semler B., Holland J. Virus protein changes and RNA termini alterations evolving during persistent infection. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Stollar V. Defective-interfering particles of Sindbis virus. II. Homologous interference. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):530–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Rosenthal R., Schlesinger S. Establishment and maintenance of persistent infection by Sindbis virus in BHK cells. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):463–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.463-474.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]