Abstract
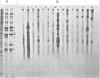
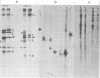
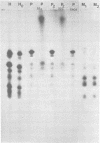
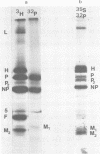
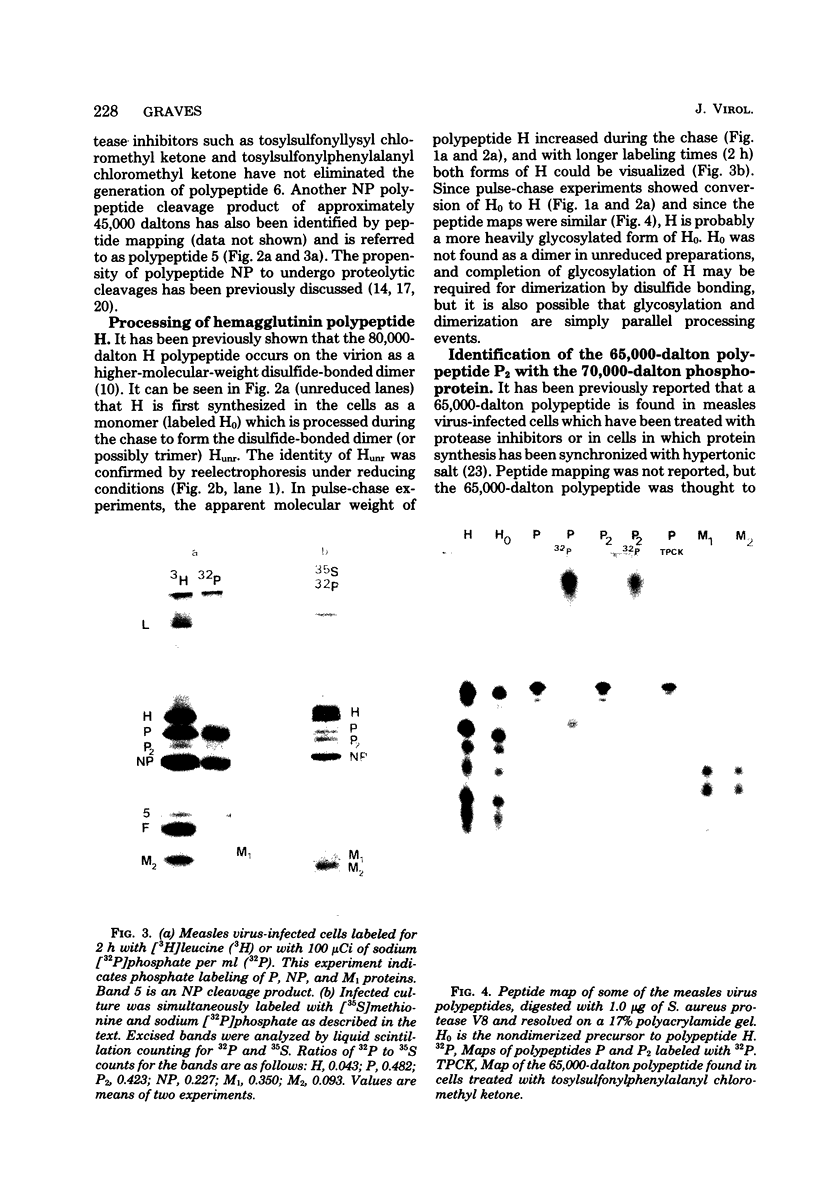
Measles virus does not turn off host cell polypeptide synthesis, making it difficult to precisely identify the polypeptides specified by the virus during the infectious cycle. By using the technique of immune precipitation with measles-specific antisera, the host cell background has been eliminated, and new observations have been made concerning measles virus polypeptides H, P, NP, F, and M. The H polypeptide is first synthesized as a monomer which is processed by further glycosylation and by the formation of disulfide-bonded dimers. Polypeptide P (70,000 daltons) has been found to occur also as a 65,000-dalton molecule, P2, and both forms of the molecule are equally phosphorylated. Polypeptide NP is processed from a cleavage-sensitive form (which undergoes cleavage during the process of isolation to form polypeptide 6 [41,000 daltons]) to a form which is resistant to this cleavage. The fusion and hemolysin polypeptide is first found in the cells as a 55,000-dalton precursor, F0, which is clearly resolved from the NP polypeptide on gel electrophoresis. The measles virus F0 protein identified in previous reports had not been resolved from the 60,000-dalton NP polypeptide. The M protein occurs in the infected cells as two distinct bands, and, as in the case of Sendai virus, one of these two M protein bands represents a phosphorylated form of the other.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D., Pringle C. R., Szilágyi J. F. Temperature-sensitive mutants of complementation group E of vesicular stomatitis virus New Jersey serotype possess altered NS polypeptides. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):325–333. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.325-333.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Alterations in expression of measles virus polypeptides by antibody: molecular events in antibody-induced antigenic modulation. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):78–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Choppin P. W. Evidence for lack of synthesis of the M polypeptide of measles virus in brain cells in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):443–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Measles and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus proteins: lack of antibodies to the M protein in patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2047–2051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The polypeptides of canine distemper virus: synthesis in infected cells and relatedness to the polypeptides of other morbilliviruses. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Bussell R. H. Glycoproteins of measles virus under reducing and nonreducing conditions. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):687–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.687-692.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsford L., Emerson S. U. Transcriptional activities of different phosphorylated species of NS protein purified from vesicular stomatitis virions and cytoplasm of infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1097–1105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1097-1105.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Determination by peptide mapping of the unique polypeptides in Sendai virions and infected cells. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The synthesis of Sendai virus polypeptides in infected cells. III. Phosphorylation of polypeptides. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):382–397. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesnaw J. A., Dickson L. R., Curry R. H. Proposed replicative role of the NS polypeptide of vesicular stomatitis virus: structural analysis of an electrophoretic variant. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.8-15.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle W. E., Choppin P. W. A comparison of the polypeptides of four measles virus strains. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle W. E., Compans R. W., Lackland H., Choppin P. W. Proteolytic cleavage of subunits of the nucleocapsid of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1253–1261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1253-1261.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Krag S. S., Liu T. Effects of UDP-glucose addition on the synthesis of mannosyl lipid-linked oligosaccharides by cell-free fibroblast preparations. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1780–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins S. J., Bussell R. H. Structural phosphoproteins associated with purified measles virions and cytoplasmic nucleocapsids. Intervirology. 1979;12(2):96–102. doi: 10.1159/000149074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague J., Eron L. J., Seifried A. S., Milstien J. B. Cell-free synthesis of measles virus proteins. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):688–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.688-691.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa D., Chanda P. K., Banerjee A. K. In vitro synthesis of the full-length complement of the negative-strand genome RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):294–298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. L., Norrby E. Structural polypeptides of measles virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 May;39(2):219–229. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-2-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainionpä R. Measles virus-specified polypeptides in infected cells. Arch Virol. 1979;60(3-4):239–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01317495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Fields B. N. Intracellular synthesis of measles virus-specified polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):285–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.285-297.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]