Abstract
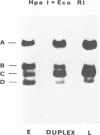
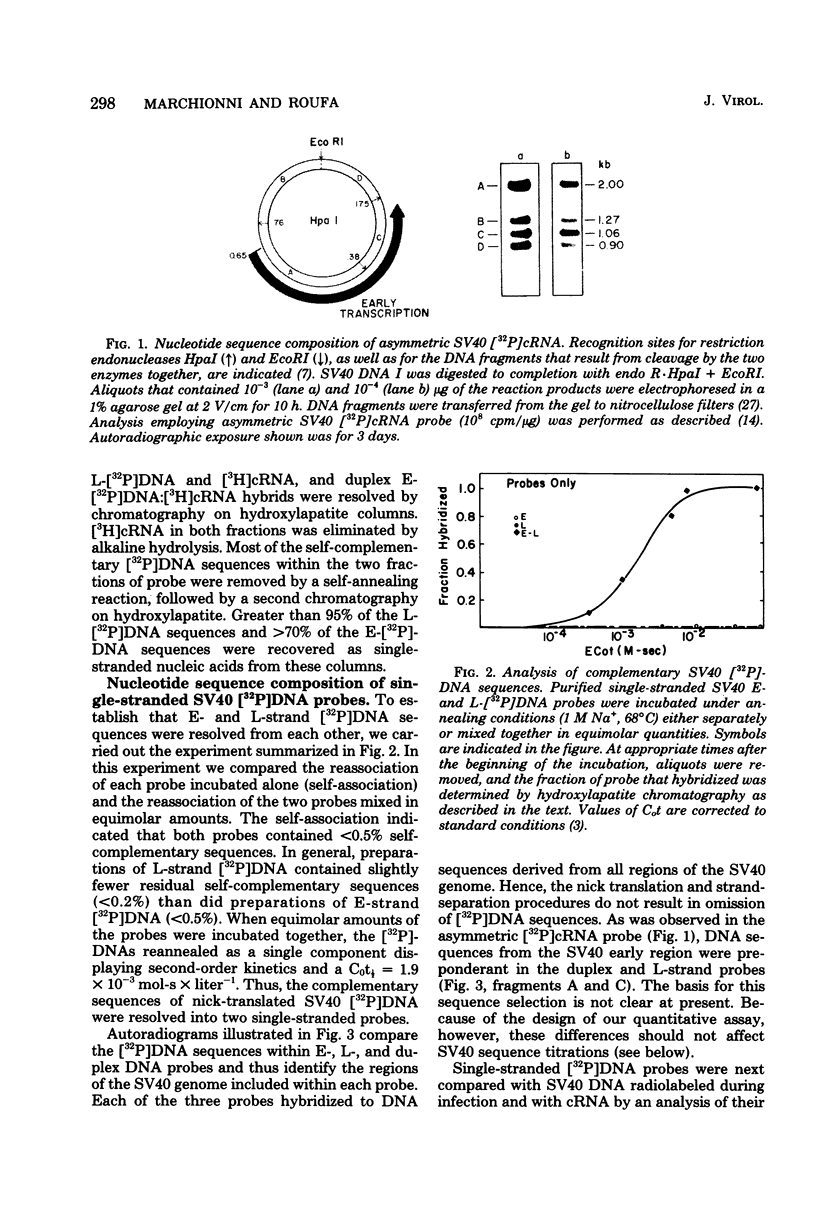
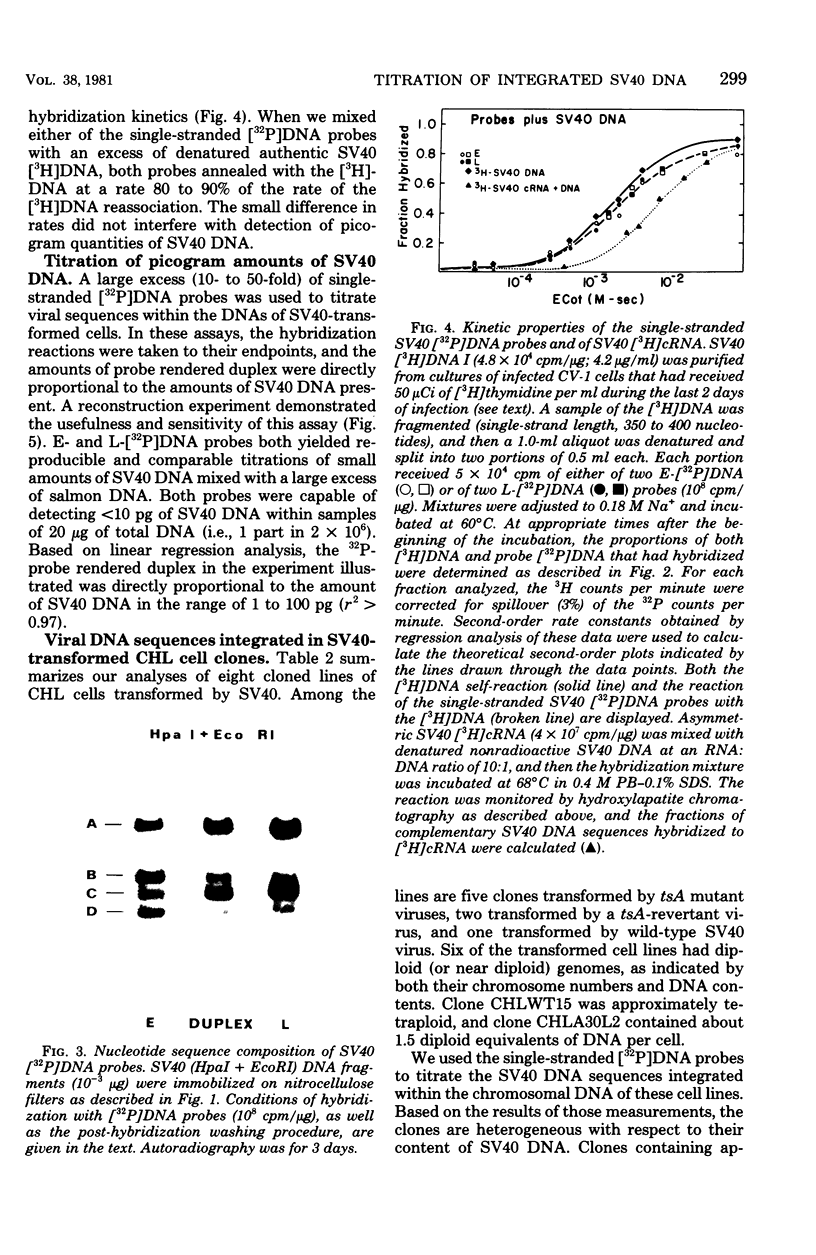
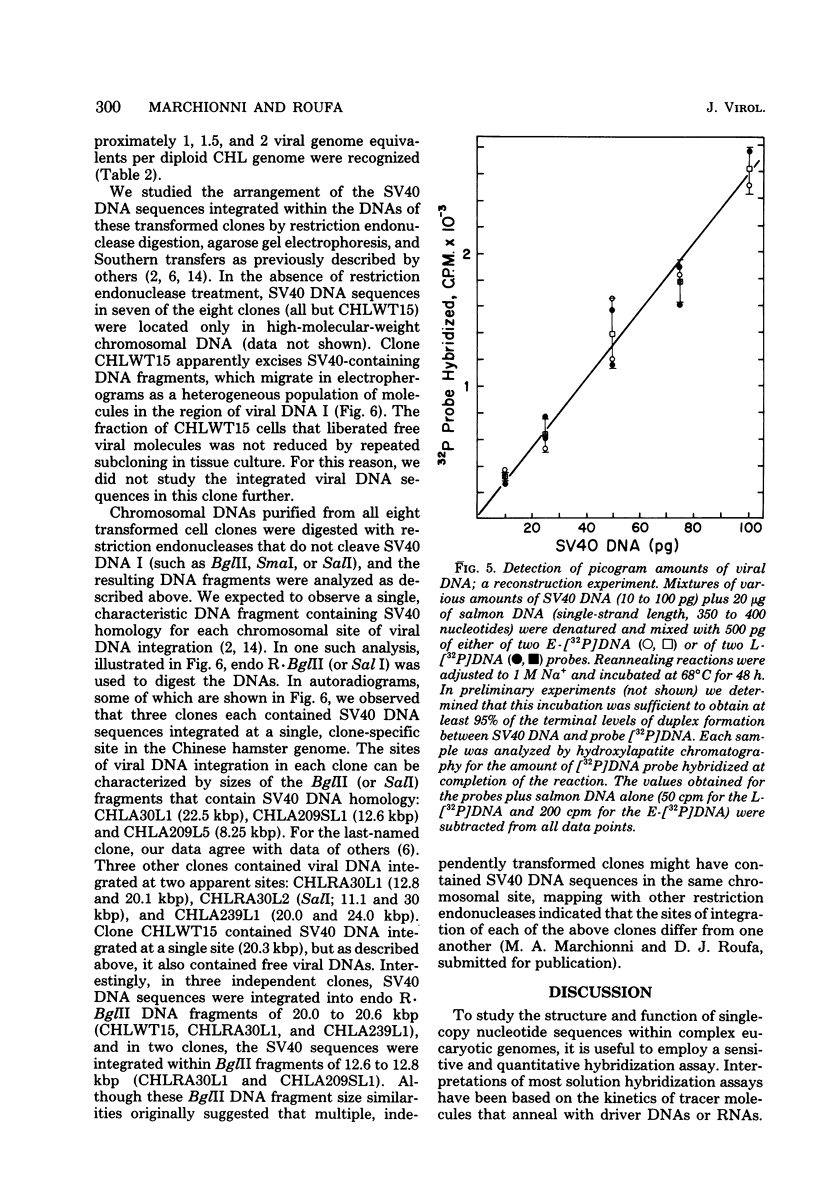
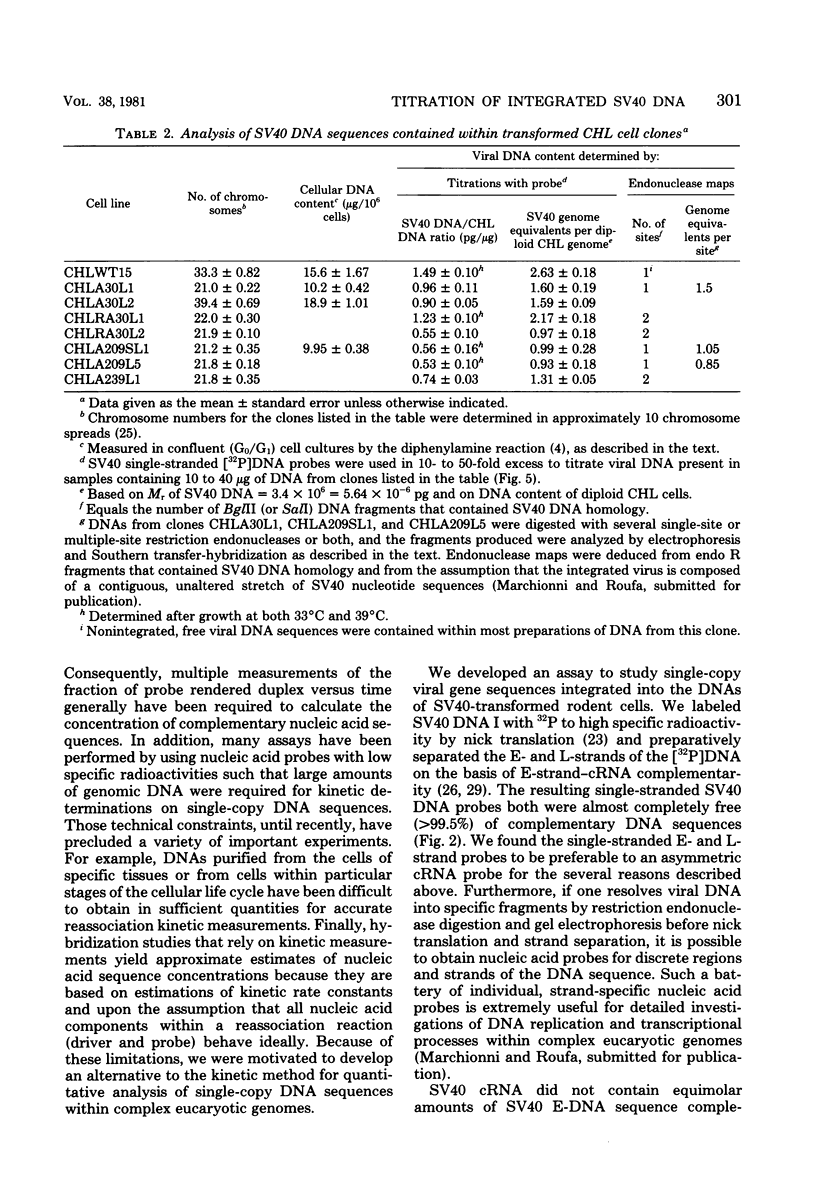
Nick-translated simian virus 40 (SV40) [32P]DNA fragments (greater than 2 X 10(8) cpm/micrograms) were resolved into early- and late-strand nucleic acid sequences by hybridization with asymmetric SV40 complementary RNA. Both single-stranded DNA fractions contained less than 0.5% self-complementary sequences; both included [32P]-DNA sequences that derived from all regions of the SV40 genome. In contrast to asymmetric SV40 complementary RNA, both single-stranded [32P]DNAs annealed to viral [3H]DNA at a rate characteristic of SV40 DNA reassociation. Kinetics of reassociation between the single-stranded [32P]DNAs indicated that the two fractions contain greater than 90% of the total nucleotide sequences comprising the SV40 genome. These preparations were used as hybridization probes to detect small amounts of viral DNA integrated into the chromosomes of Chinese hamster cells transformed by SV40. Under the conditions used for hybridization titrations in solution (i.e., 10- to 50-fold excess of radioactive probe), as little as 1 pg of integrated SV40 DNA sequence was assayed quantitatively. Among the transformed cells analyzed, three clones contained approximately one viral genome equivalent of SV40 DNA per diploid cell DNA complement; three other clones contained between 1.2 and 1.6 viral genome equivalents of SV40 DNA; and one clone contained somewhat more than two viral genome equivalents of SV40 DNA. Preliminary restriction endonuclease maps of the integrated SV40 DNAs indicated that four clones contained viral DNA sequences located at a single, clone-specific chromosomal site. In three clones, the SV40 DNA sequences were located at two distinct chromosomal sites.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G. Chromatography of nucleic acids on hydroxyapatite. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):779–783. doi: 10.1038/206779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. The arrangement of simian virus 40 sequences in the DNA of transformed cells. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):269–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Graham D. E., Neufeld B. R. Analysis of repeating DNA sequences by reassociation. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:363–418. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. E., Galau G. A., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Studies on nucleic acid reassociation kinetics: V. Effects of disparity in tracer and driver fragment lengths. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):2073–2094. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.2073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chepelinsky A. B., Seif R., Martin R. G. Integration of the simian virus 40 genome into cellular DNA in temperature-sensitive (N) and temperature-insensitive (A) transformants of 3T3 rat and Chinese hamster lung cells. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):184–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.184-193.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K. J., Sack G. H., Jr, Nathans D. Studies of simian virus 40 DNA. VII. A cleavage map of the SV40 genome. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 5;78(2):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Smith M. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Studies on nucleic acid reassociation kinetics: retarded rate of hybridization of RNA with excess DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2306–2310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb L. D., Kohne D. E., Martin M. A. Quantitation of Simian virus 40 sequences in African green monkey, mouse and virus-transformed cell genomes. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 14;57(1):129–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Vogt M., Dulbecco R. Loss of simian virus 40 DNA-RNA hybrids from nitrocellulose membranes; implications for the study of virus--host DNA interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Defendi V. Factors affecting the process and extent of integration of the viral genome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):325–333. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketner G., Kelly T. J., Jr Integrated simian virus 40 sequences in transformed cell DNA: analysis using restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1102–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Howley P., Brown M., Martin M. The detection and quantitation of SV40 nucleic acid sequences using single-stranded SV40 DNA probes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):147–152. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchionni M. A., Roufa R. J. Digestion of 5-bromodeoxyuridine-substituted lambda-DNA by restriction endonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9075–9081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y. Simian virus 40 functions required for the establishment and maintenance of malignant transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):599–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.599-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Setlow V. P., Edwards C. A. Roles of the simian virus 40 tumor antigens in transformation of Chinese hamster lung cells: studies with simian virus 40 double mutants. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):596–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.596-607.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patch C. T., Hauser J., Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S. Method for determining the extent and copy number of overlapping and nonoverlapping segments of integrated viral genomes. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):575–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.575-578.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roufa D. J. 5-bromodeoxyuridine-DNA strand symmetry and the repair of photolytic breaks in Chinese hamster cell chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3905–3909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roufa D. J., Sadow B. N., Caskey C. T. Derivation of TK- clones from revertant TK+ mammalian cells. Genetics. 1973 Nov;75(3):515–530. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Sharp P. A., Keller W. Transcription of Simian virus 40. I. Separation of the strands of SV40 DNA and hybridization of the separated strands to RNA extracted from lytically infected and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 14;70(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Martin R. G., Anderson J., Livingston D. M. Biological and biochemical studies of cells transformed by simian virus 40 temperature-sensitive gene A mutants and A mutant revertants. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):210–218. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.210-218.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal H., Dulbecco R. Viral DNA in polyoma- and SV40-transformed cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1158–1165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal H. SV40 DNA strand selection by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):407–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90201-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]