Abstract
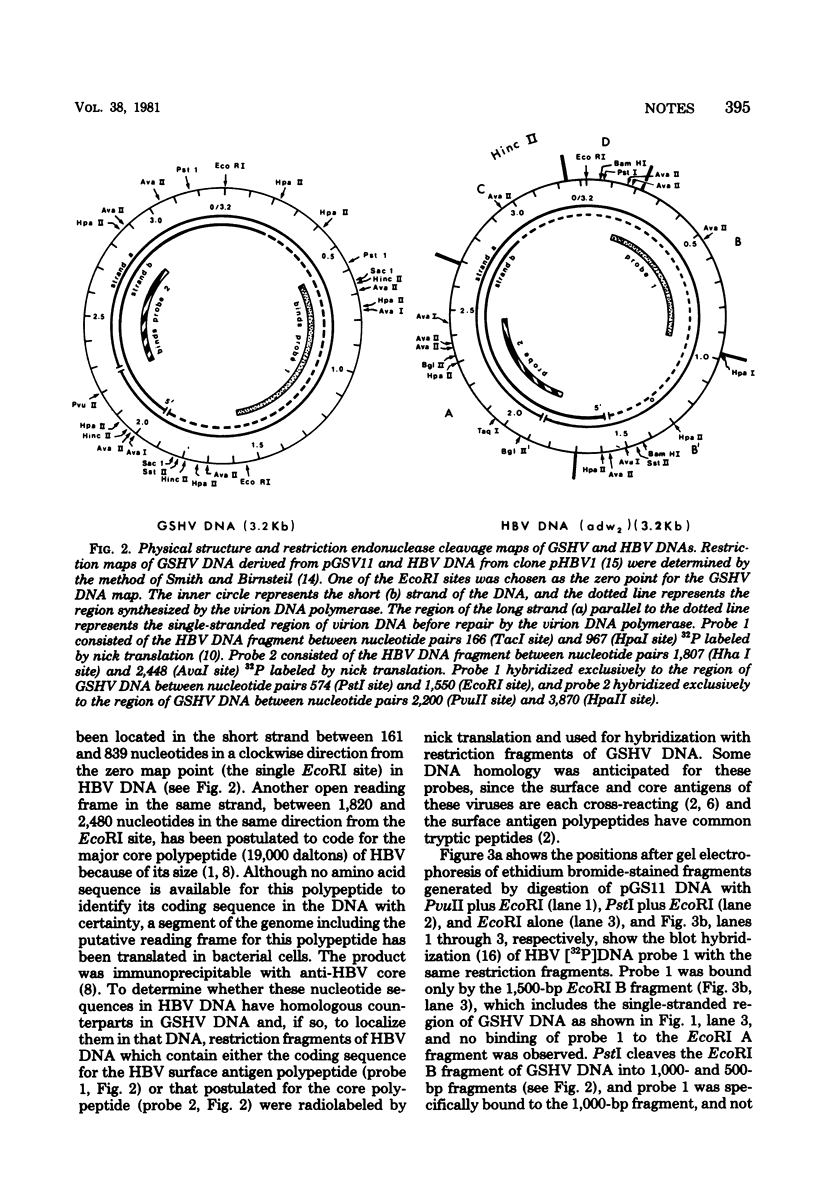
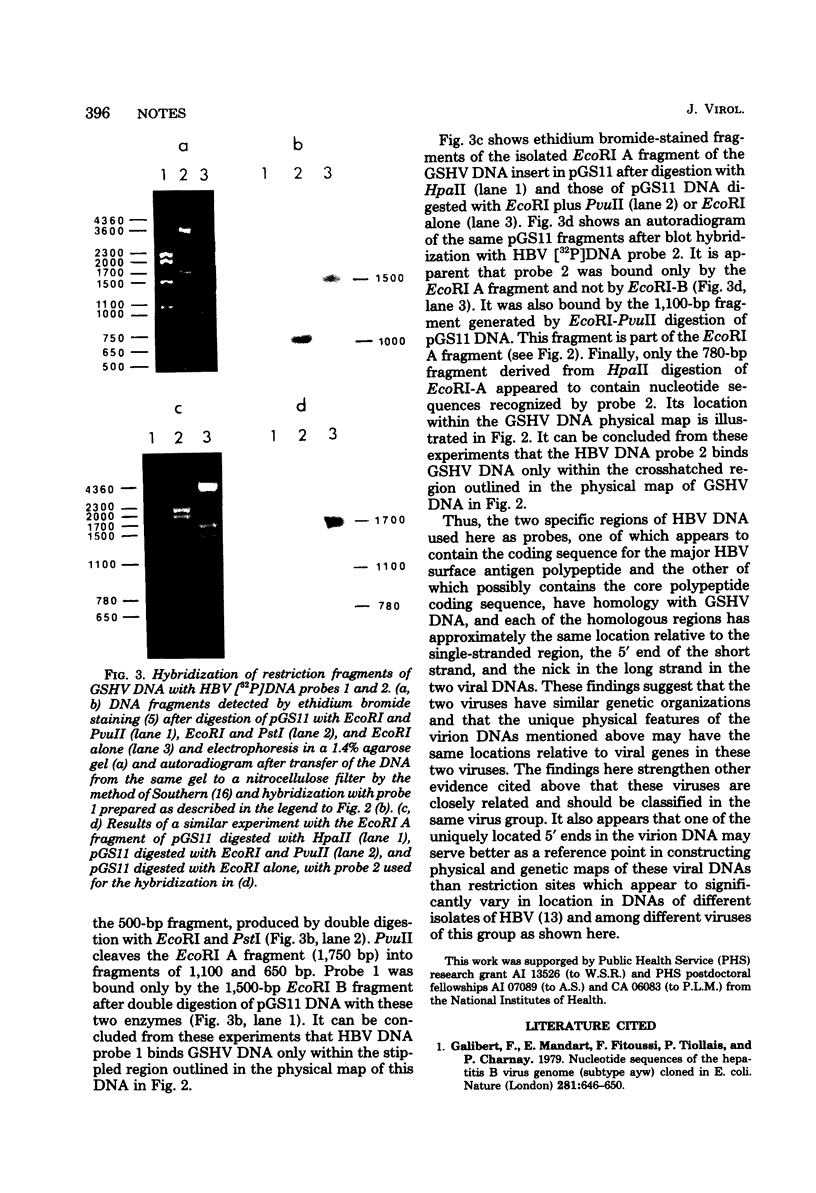
Ground squirrel hepatitis virus (GSHV) shares many ultrastructural antigenic, molecular, and biological features with hepatitis B virus (HBV) of humans, indicating that they are members of the same virus group. Both viruses contain small circular DNA molecules which are partially single stranded. Here, we ligated an endonuclease EcoRI digest of GSHV DNA with EcoRI-cleaved plasmid vector pBR322 and cloned recombinant plasmids in Escherichia coli C600. Two cloned recombinants were characterized. One (pGS2) was found to contain only part of the GSHV genome, and the other (pGS11) was found to contain the entire viral DNA. A restriction endonuclease cleavage map of the GSHV insert in pGS11 and the locations of certain physical features of the virion DNA were determined. The relative positions of the single-stranded region, the unique 5' end of the short DNA strand, and the unique nick in the long DNA strand in GSHV DNA were found to be the same as those previously described for HBV DNA. Hybridization with an HBV [32P]DNA probe containing the apparent coding sequence for the major polypeptide of HBV surface antigen and a probe containing the putative coding sequence for the major polypeptide of the HBV core revealed specific homology with different restriction fragments of GSHV DNA. The two homologous regions had approximately the same locations relative to the single-stranded region, the 5' end of the short strand, and the nick in the long strand in the two viral DNAs. These results suggest that in both viruses the genes for the major HBV surface antigen and core polypeptides have the same locations relative to unique physical features of the viral DNAs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Feitelson M. A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Structural relationships between the surface antigens of ground squirrel hepatitis virus and human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):787–795. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.787-795.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska J. F., Clayton D. A., Rubenstein J. L., Robinson W. S. Structure of hepatitis B Dane particle DNA before and after the Dane particle DNA polymerase reaction. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):666–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.666-672.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers T. A., Greenberg H. B., Robinson W. S. Structure of hepatitis B Dane particle DNA and nature of the endogenous DNA polymerase reaction. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):368–376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.368-376.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Oshiro L. S., Regnery D. C., Scullard G. H., Robinson W. S. A virus in Beechey ground squirrels that is related to hepatitis B virus of humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Seal G., Summers J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.829-836.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L., Roberts I. M., Vyas G. N. Partial amino acid sequence of two major component polypeptides of hepatitis B surface antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1530–1534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Clayton D. A., Greenman R. L. DNA of a human hepatitis B virus candidate. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):384–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.384-391.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler F., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B viral DNA molecules have cohesive ends. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):226–233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.226-233.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Sattler F., Robinson W. S. Restriction endonuclease cleavage map and location of unique features of the DNA of hepatitis B virus, subtype adw2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4664–4668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sninsky J. J., Siddiqui A., Robinson W. S., Cohen S. N. Cloning and endonuclease mapping of the hepatitis B viral genome. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):346–348. doi: 10.1038/279346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., O'Connell A., Millman I. Genome of hepatitis B virus: restriction enzyme cleavage and structure of DNA extracted from Dane particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4597–4601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smolec J. M., Snyder R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W. Hepatocellular carcinoma and the hepatitis B virus: evidence for a causal association. Prog Med Virol. 1978;24:40–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Gray P., Quiroga M., Zaldivar J., Goodman H. M., Rutter W. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the major protein of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nature. 1979 Aug 30;280(5725):815–819. doi: 10.1038/280815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner B. G., Smolec J. M., Snyder R., Summers J. Serological relationship of woodchuck hepatitis virus to human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):314–322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.314-322.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]