Abstract
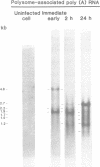
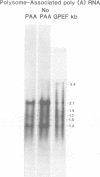
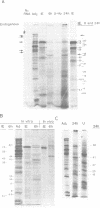
The immediate early transcripts of human cytomegalovirus originated from restricted regions of the viral genome. In contrast, transcription at early times was complementary to all regions of the viral genome that were fractionated by restriction endonuclease treatment followed by agarose gel electrophoresis. The viral genome was also extensively transcribed when 2 h of protein synthesis or longer was permitted after infection in permissive cells treated with an inhibitor of viral DNA replication or in nonpermissive cells of animal origin that permit little or no viral DNA replication. The size and in vitro translation products of the cytomegalovirus-specified mRNA's at immediate early and early times after infection were determined. Discrete size classes of virus-specified polyadenylated RNA accumulated on the polyribosomes of cells infected in the presence of an inhibitor of protein synthesis. When 2 or 24 h of protein synthesis occurred after infection, there were changes in the relative abundance of the virus-specified RNAs that accumulated on polyribosomes. Treatment of nonpermissive cells had little effect on the size classes of viral RNA found associated with the polyribosomes at early times after infection. These viral mRNA's were assumed to represent early viral gene expression. In vitro translation of the viral mRNA isolated from polyribosomes at immediate early and early times after infection identified many of the virus-specified gene products and demonstrated (i) a switch from immediate early to early viral gene expression and (ii) a prolonged phase of early viral gene expression. The data also indicated that the initiation of viral RNA synthesis does not depend on the formation of viral protein, but that de novo viral protein synthesis may influence the extent of transcription of the viral genome.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Steinhart W. L., Hill C. W. Transcription of herpes simplex type 1 DNA in nuclei isolated from infected HEp-2 and KB cells. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):302–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90390-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Costa R. H., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA present in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):9–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.9-27.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Spiegelman S. Electrophoretic separation of viral nucleic acids on polyacrylamide gels. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):373–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi B., Arber W. Physical mapping of BglII, BamHI, EcoRI, HindIII and PstI restriction fragments of bacteriophage P1 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 24;153(3):311–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00431596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., McGrath J., Waskell L. New RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T7. Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):227–231. doi: 10.1038/228227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., McLauchlan J., McGeoch D. J. Orientation of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNA's. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):77–91. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M., Blankenship M. L., Brown G. D., Kaplan A. S. Size and complexity of human cytomegalovirus DNA. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M., Schmidt C. A., Kaplan A. S. Patterns of transcription of human cytomegalovirus in permissively infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):277–286. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.277-286.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton A. J., Clements J. B. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 2 transcription and characterization of virus immediate early mRNA's. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2627–2645. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L., Rixon F. J., Jean J. H., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Transcription of the genome of pseudorabies virus (A herpesvirus) is strictly controlled. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):316–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Fioretti A., Plotkin S. Growth characteristics of cytomegalovirus in human fibroblasts with demonstration of protein synthesis early in viral replication. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):991–997. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.991-997.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen J. L., Walig C., Wertheim P., van der Noordaa J. Human cytomegalovirus DNA. I. Molecular weight and infectivity. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):813–816. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.813-816.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Jacob R. J., Wadsworth S. C., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA: evidence for four populations of molecules that differ in the relative orientations of their long and short components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Stringer J. R., Wagner E. K. Isolation and localization of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA abundant before viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):447–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.447-462.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA VII. alpha-RNA is homologous to noncontiguous sites in both the L and S components of viral DNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.268-276.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick B. A., Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus genome: partial denaturation map and organization of genome sequences. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):261–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.261-276.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. J. Cytomegalovirus infections in organ transplantation and post transfusion. An hypothesis. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;37(4):365–377. doi: 10.1007/BF01241460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Stinski M. F. Persistence of the cytomegalovirus genome in human cells. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):761–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.761-775.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes B. E., Stark G. R. Nucleic acid hybridization using DNA covalently coupled to cellulose. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer G. Cytomegaloviruses of man and animals. Prog Med Virol. 1973;15:92–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp F., Geder L., Murasko D., Lausch R., Ladda R., Huang E. S., Webber M. M. Long-term persistence of cytomegalovirus genome in cultured human cells of prostatic origin. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):982–990. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.982-990.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick P., Berthelot N. Inverted repetitions in the chromosome of herpes simplex virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):667–678. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Jeor S. C., Hutt R. Cell DNA replication as a function in the synthesis of human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):65–73. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Mocarski E. S., Thomsen D. R. DNA of human cytomegalovirus: size heterogeneity and defectiveness resulting from serial undiluted passage. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):231–239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.231-239.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Synthesis of proteins and glycoproteins in cells infected with human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):751–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.751-767.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Mapping early transcripts of herpes simplex virus type 1 by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):56–73. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.56-73.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C., Siegel R. B. Transcription of late phage RNA by T7 RNA polymerase. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1160–1162. doi: 10.1038/2281160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of cytomegalovirus strains of human origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):253–258. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weststrate M. W., Geelen J. L., van der Noordaa J. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: physical maps for restriction endonucleases BglII, hindIII and XbaI. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]