Abstract
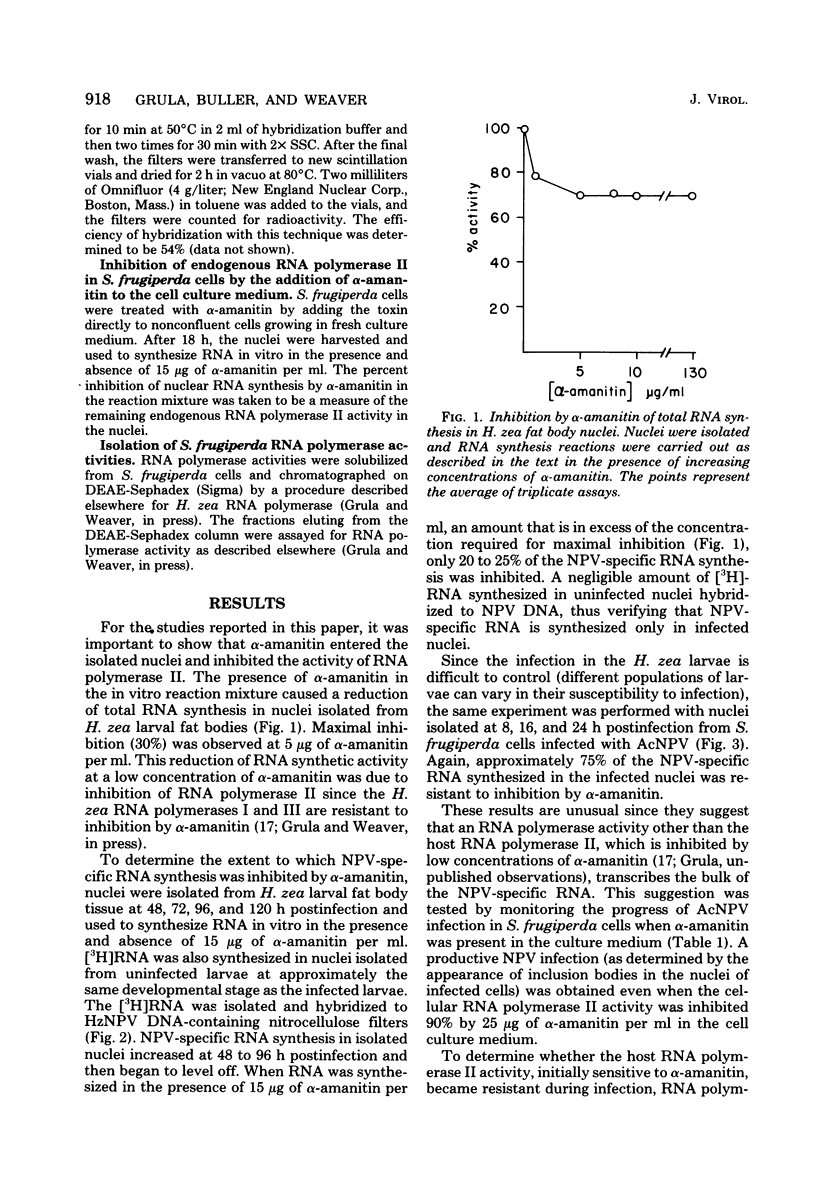
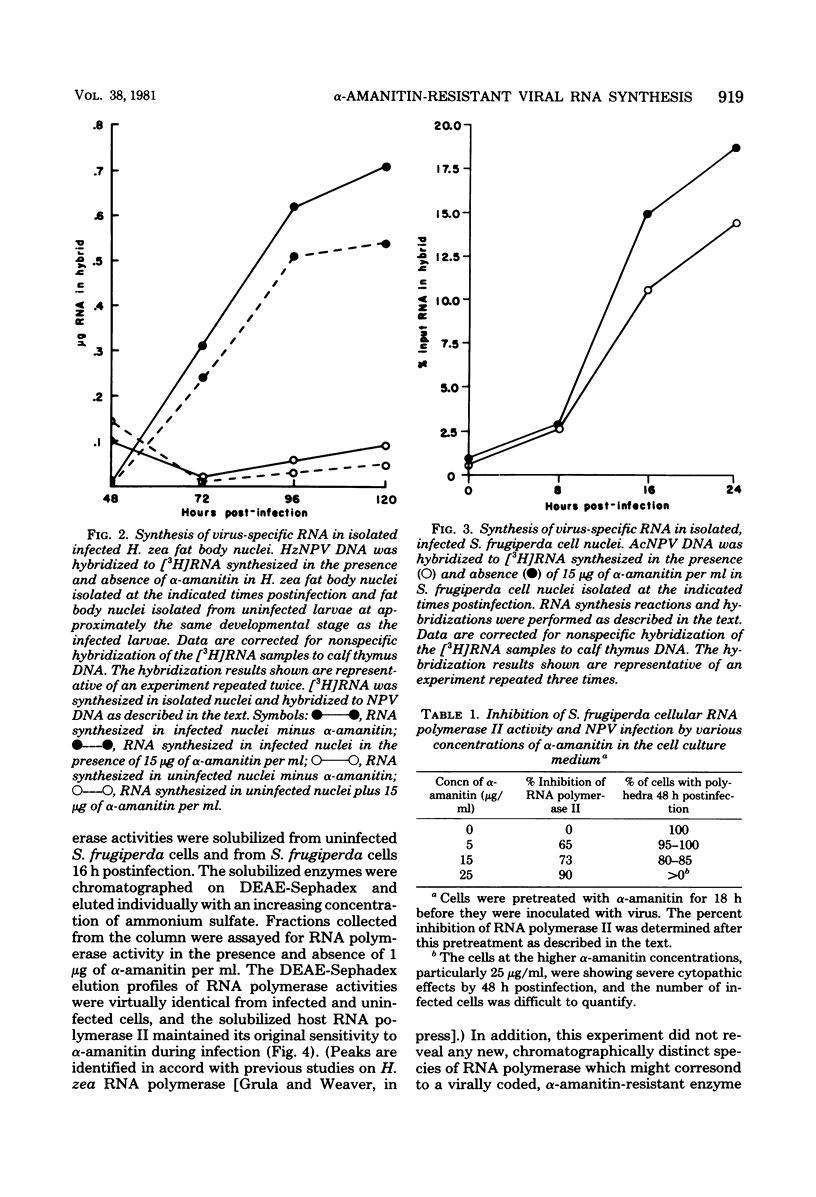
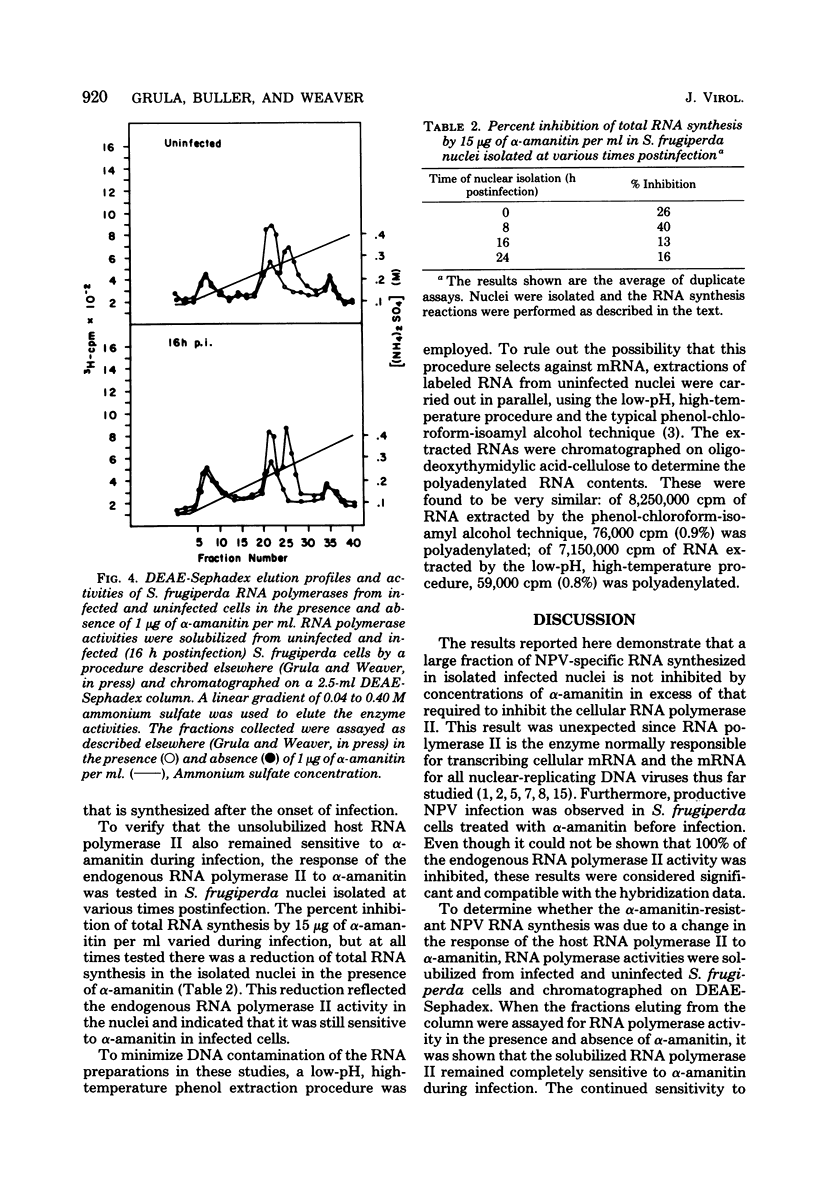
[3H]RNA was synthesized in nuclei isolated at various times postinfection from the fat bodies of Heliothis zea larvae infected with H. zea nuclear polyhedrosis virus and from cultured Spodoptera frugiperda cells infected with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. To detect virus-specific RNA synthesis, the [3H]RNA was hybridized to denatured viral DNA immobilized on nitrocellulose filters. Nuclear polyhedrosis virus-specific RNA synthesis in the infected nuclei isolated from H. zea larval fat bodies and S. frugiperda cells was only inhibited 20 to 25% by concentrations of α-amanitin sufficient to inhibit the host RNA polymerase II. In addition, a productive nuclear polyhedrosis virus infection was obtained in S. frugiperda cells grown in the presence of an α-amanitin concentration that inhibited 90% of the cellular RNA polymerase II activity. The cellular RNA polymerase II enzyme remained sensitive to α-amanitin during infection, and there was no evidence that a virus-coded, α-amanitin-resistant enzyme was synthesized after the onset of infection. The data suggest that the bulk of nuclear polyhedrosis virus-specific RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei is transcribed by an enzyme other than the host RNA polymerase II.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Steinhart W. L., Hill C. W. Transcription of herpes simplex type 1 DNA in nuclei isolated from infected HEp-2 and KB cells. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):302–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90390-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Rose J. A. Transcription of adenovirus-associated virus RNA in isolated KB cell nuclei. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. H., Sugden B. Inhibition by -amanitin of simian virus 40-specific ribonucleic acid synthesis in nuclei of infected monkey cells. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1086–1089. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1086-1089.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K., Dawes K. P. Physical Map of the DNA Genome of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1044–1055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1044-1055.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. T., Stout E. R., Bates R. C. Transcription of the bovine parvovirus genome in isolated nuclei. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):917–922. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.917-922.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R., Penman S. Transcription of the adenovirus genome by an -amanitine-sensitive ribonucleic acid polymerase in HeLa cells. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):621–626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.621-626.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharnhorst D. W., Saving K. L., Vuturo S. B., Cooke P. H., Weaver R. F. Structural studies on the polyhedral inclusion bodies, virions, and DNA of the nuclear polyhedrosis virus of the cotton bollworm Heliothis zea. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):292–300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.292-300.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. D., Smith G. E. Baculovirus structural polypeptides. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):390–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90257-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. D., Kates J. State of adenovirus 2 deoxyribonucleic acid in the nucleus and its mode of transcription: studies with isolated viral deoxyribonucleic acid-protein complexes and isolated nuclei. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):627–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.627-635.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Brendler T. G., Raskas H. J., Roeder R. G. Low molecular weight viral RNAs transcribed by RNA polymerase III during adenovirus 2 infection. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):557–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90206-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


