Abstract
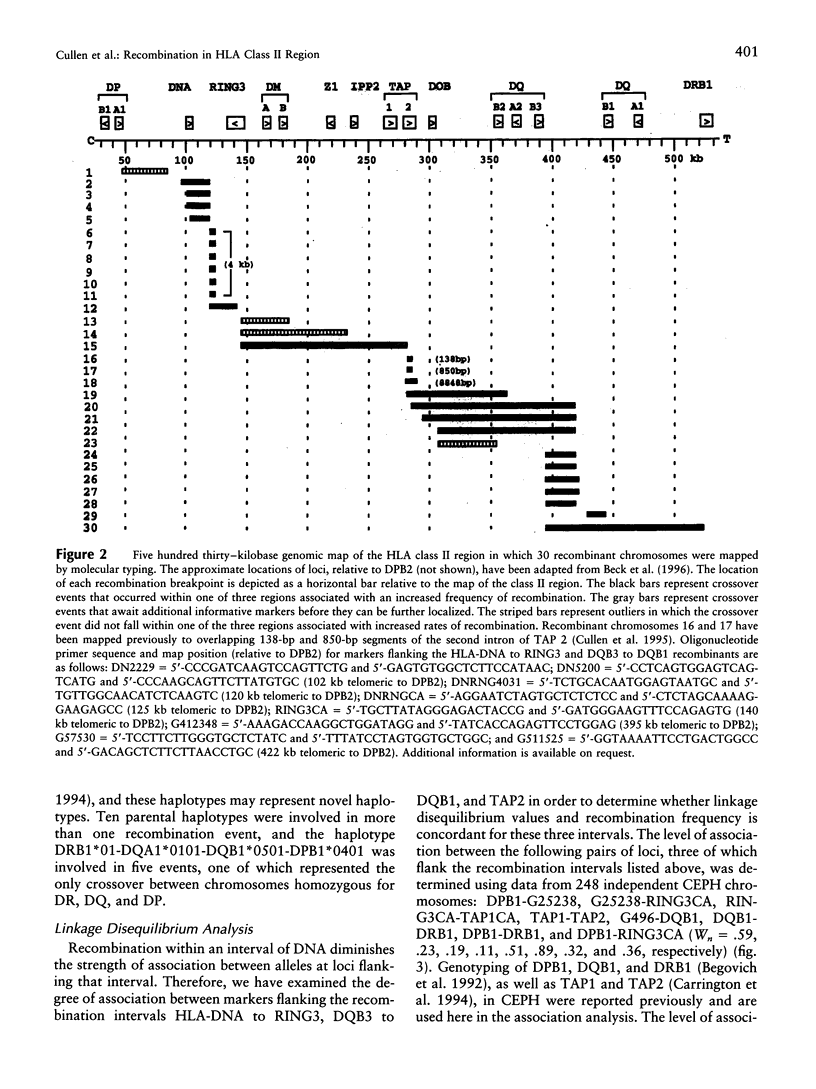
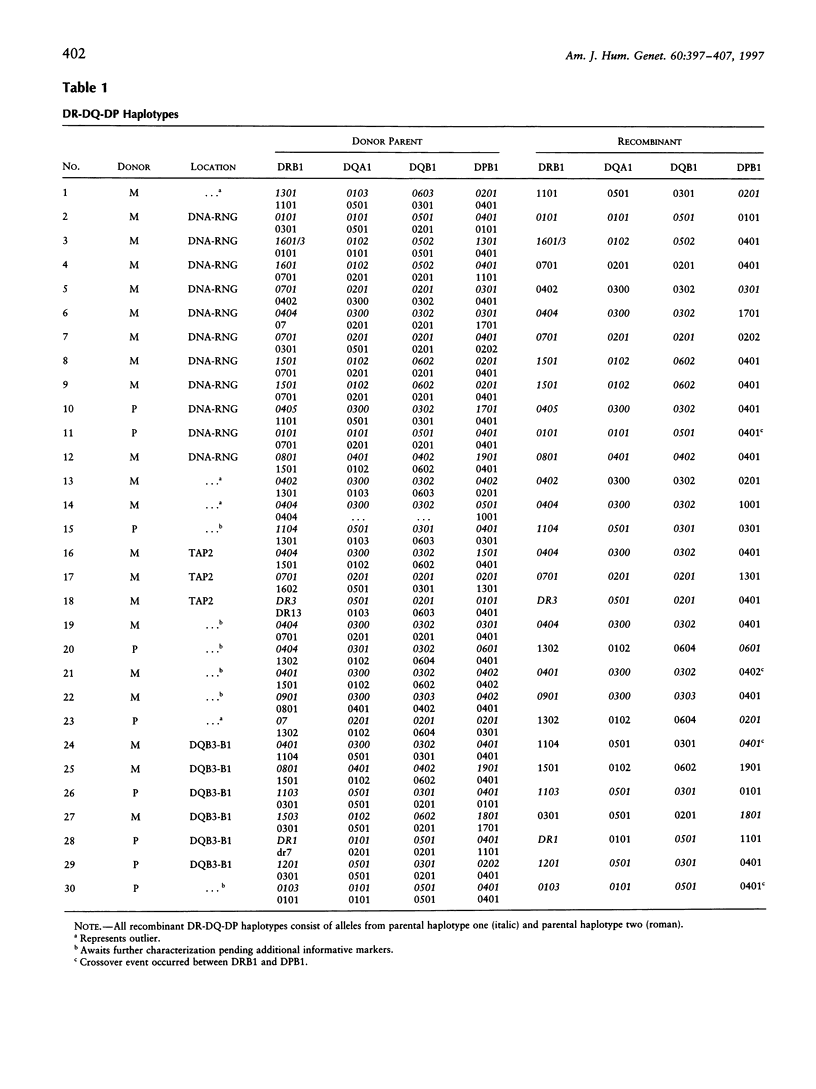
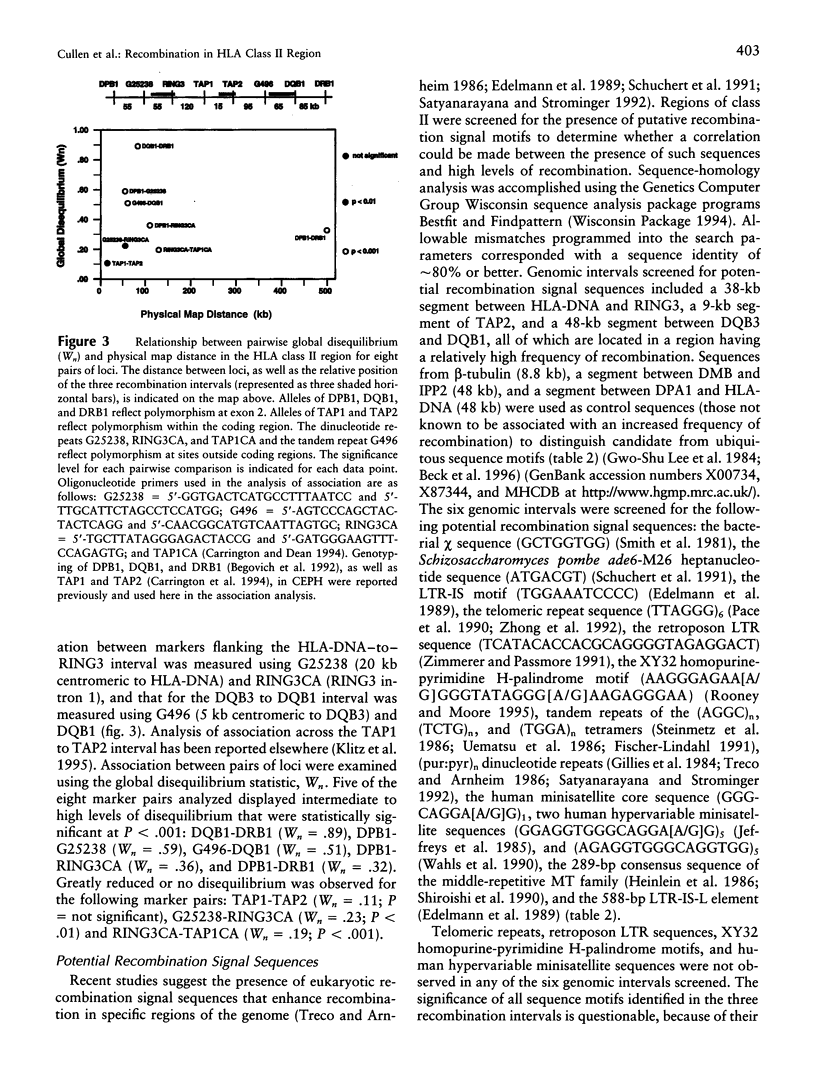
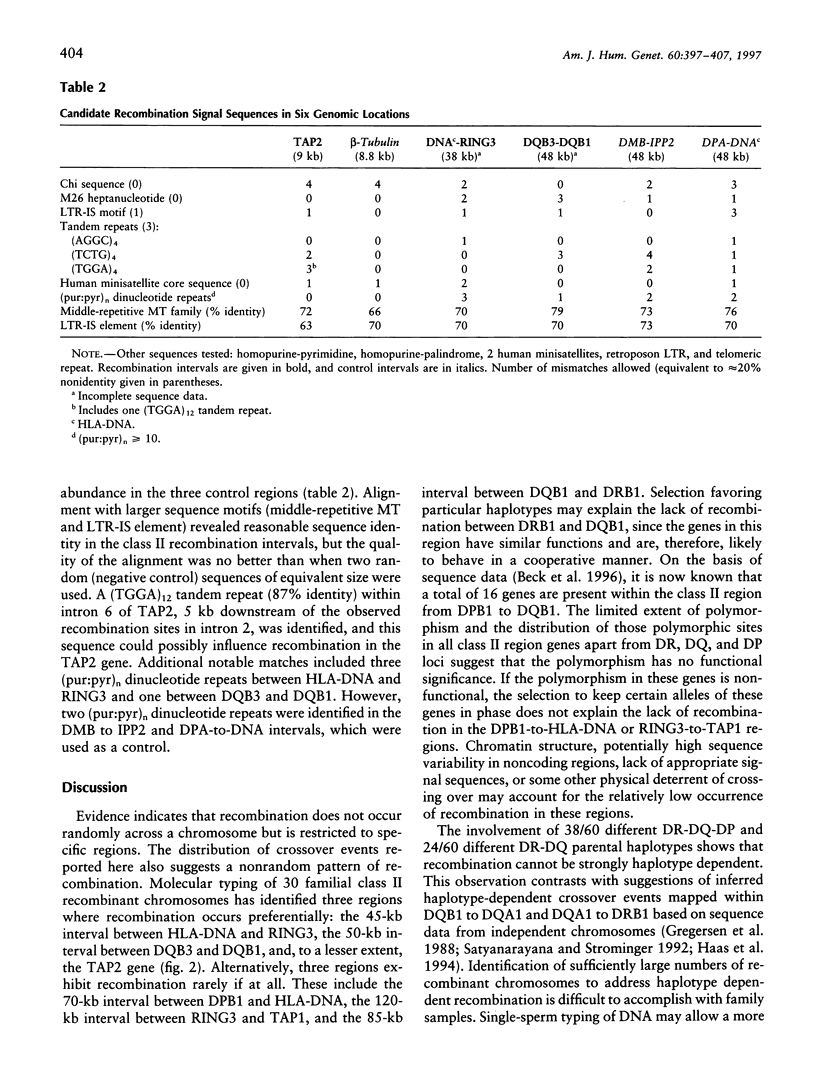
Studies of linkage disequilibrium across the HLA class II region have been useful in predicting where recombination is most likely to occur. The strong associations between genes within the 85-kb region from DQB1 to DRB1 are consistent with low frequency of recombination in this segment of DNA. Conversely, a lack of association between alleles of TAP1 and TAP2 (approximately 15 kb) has been observed, suggesting that recombination occurs here with relatively high frequency. Much of the HLA class II region has now been sequenced, providing the tools to undertake detailed analysis of recombination. Twenty-seven families containing one or two recombinant chromosomes within the 500-kb interval between the DPB1 and DRB1 genes were used to determine patterns of recombination across this region. SSCP analysis and microsatellite typing yielded identification of 127 novel polymorphic markers distributed throughout the class II region, allowing refinement of the site of crossover in 30 class II recombinant chromosomes. The three regions where recombination was observed most frequently are as follows: the 45-kb interval between HLA-DNA and RING3 (11 cases), the 50-kb interval between DQB3 and DQB1 (6 cases), and an 8.8-kb segment of the TAP2 gene (3 cases). Six of the 10 remaining recombinants await further characterization, pending identification of additional informative markers, while four recombinants were localized to other intervals (outliers). Analysis of association between markers flanking HLA-DNA to RING3 (45 kb), as well as TAP1 to TAP2 (15 kb), by use of independent CEPH haplotypes indicated little or no linkage disequilibrium, supporting the familial recombination data. A notable sequence motif located within a region associated with increased rates of recombination consisted of a (TGGA)12 tandem repeat within the TAP2 gene.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmann D. M., Sansom D., Marsh S. G. What is the basis for HLA-DQ associations with autoimmune disease? Immunol Today. 1991 Aug;12(8):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90124-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banchs I., Bosch A., Guimerà J., Lázaro C., Puig A., Estivill X. New alleles at microsatellite loci in CEPH families mainly arise from somatic mutations in the lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum Mutat. 1994;3(4):365–372. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380030407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck S., Abdulla S., Alderton R. P., Glynne R. J., Gut I. G., Hosking L. K., Jackson A., Kelly A., Newell W. R., Sanseau P. Evolutionary dynamics of non-coding sequences within the class II region of the human MHC. J Mol Biol. 1996 Jan 12;255(1):1–13. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begovich A. B., McClure G. R., Suraj V. C., Helmuth R. C., Fildes N., Bugawan T. L., Erlich H. A., Klitz W. Polymorphism, recombination, and linkage disequilibrium within the HLA class II region. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):249–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benger J. C., Teshima I., Walter M. A., Brubacher M. G., Daouk G. H., Cox D. W. Localization and genetic linkage of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes and the creatine kinase brain (CKB) gene: identification of a hot spot for recombination. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):614–622. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90354-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouissou C., Pontarotti P., Crouau-Roy B. A precise meiotic map in the class I region of the human major histocompatibility complex. Genomics. 1995 Dec 10;30(3):486–492. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Hebert J. M., Wijsman E., Gadi I., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Boyd C. D. High recombination between two physically close human basement membrane collagen genes at the distal end of chromosome 13q. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryda E. C., DePari J. A., Sant'Angelo D. B., Murphy D. B., Passmore H. C. Multiple sites of crossing over within the Eb recombinational hotspot in the mouse. Mamm Genome. 1992;2(2):123–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00353860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington M., Colonna M., Spies T., Stephens J. C., Mann D. L. Haplotypic variation of the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) genes and their extension of HLA class II region haplotypes. Immunogenetics. 1993;37(4):266–273. doi: 10.1007/BF00187452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington M., Dean M. A polymorphic dinucleotide repeat in the third intron of TAP1. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):218–218. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington M., Miller T., White M., Gerrard B., Stewart C., Dean M., Mann D. Typing of HLA-DQA1 and DQB1 using DNA single-strand conformation polymorphism. Hum Immunol. 1992 Mar;33(3):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(92)90073-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington M., Stephens J. C., Klitz W., Begovich A. B., Erlich H. A., Mann D. Major histocompatibility complex class II haplotypes and linkage disequilibrium values observed in the CEPH families. Hum Immunol. 1994 Nov;41(3):234–240. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(94)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Buetow K. H., Antonarakis S. E., Waber P. G., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H. Nonuniform recombination within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1239–1258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Elbein S. C., Permutt M. A. Evidence for increased recombination near the human insulin gene: implication for disease association studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charmley P., Chao A., Concannon P., Hood L., Gatti R. A. Haplotyping the human T-cell receptor beta-chain gene complex by use of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4823–4827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouau-Roy B., Bouissou C., Sommer E., Pontarotti P., Thomsen M. Analysis of HLA-A/B recombinant families with new polymorphic markers. Hum Immunol. 1993 Oct;38(2):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(93)90530-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen M., Erlich H., Klitz W., Carrington M. Molecular mapping of a recombination hotspot located in the second intron of the human TAP2 locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1350–1358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Green P., Helms C., Cartinhour S., Weiffenbach B., Stephens K., Keith T. P., Bowden D. W., Smith D. R., Lander E. S. A genetic linkage map of the human genome. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelmann W., Kröger B., Goller M., Horak I. A recombination hotspot in the LTR of a mouse retrotransposon identified in an in vitro system. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):937–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiermann T. H., Fakler J., Goldmann S. F., Böhm B. O. TAP2 gene polymorphism segregates with DR-DQ in DR/DP recombinant siblings. Hum Immunol. 1993 Nov;38(3):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(93)90544-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Folsom V., Tonegawa S. Cell type-specific enhancer element associated with a mouse MHC gene, E beta. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):594–597. doi: 10.1038/310594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen P. K., Kao H., Nunez-Roldan A., Hurley C. K., Karr R. W., Silver J. Recombination sites in the HLA class II region are haplotype dependent. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1365–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm T., Müller B., Dreier M., Kind E., Bettecken T., Meng G., Müller C. R. Hot spot of recombination within DXS164 in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Sep;45(3):368–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas J. P., Kimura A., Andreas A., Hochberger M., Keller E., Brünnler G., Bettinotti M. P., Nevinny-Stickel C., Hildebrandt B., Sierp G. Polymorphism in the upstream regulatory region of DQA1 genes and DRB1, QAP, DQA1, and DQB1 haplotypes in the German population. Hum Immunol. 1994 Jan;39(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(94)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinlein U. A., Lange-Sablitzky R., Schaal H., Wille W. Molecular characterization of the MT-family of dispersed middle-repetitive DNA in rodent genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6403–6416. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klitz W., Stephens J. C., Grote M., Carrington M. Discordant patterns of linkage disequilibrium of the peptide-transporter loci within the HLA class II region. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;57(6):1436–1444. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobori J. A., Strauss E., Minard K., Hood L. Molecular analysis of the hotspot of recombination in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):173–179. doi: 10.1126/science.3018929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobori J. A., Winoto A., McNicholas J., Hood L. Molecular characterization of the recombination region of six murine major histocompatibility complex (MHC) I-region recombinants. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1984;1(2):125–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok W. W., Kovats S., Thurtle P., Nepom G. T. HLA-DQ allelic polymorphisms constrain patterns of class II heterodimer formation. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2263–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafuse W. P., David C. S. Recombination hot spots within the I region of the mouse H-2 complex map to the E beta and E alpha genes. Immunogenetics. 1986;24(6):352–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00377952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafuse W. P., Lanning D., Spies T., David C. S. PFGE mapping and RFLP analysis of the S/D region of the mouse H-2 complex. Immunogenetics. 1992;36(2):110–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00215287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebo R. V., Chakravarti A., Buetow K. H., Cheung M. C., Cann H., Cordell B., Goodman H. Recombination within and between the human insulin and beta-globin gene loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4808–4812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Loomis C., Cowan N. J. Sequence of an expressed human beta-tubulin gene containing ten Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5823–5836. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl K. F. His and hers recombinational hotspots. Trends Genet. 1991 Sep;7(9):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90306-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M., Mann D., Carrington M. Recombination rates across the HLA complex: use of microsatellites as a rapid screen for recombinant chromosomes. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Mar;4(3):423–428. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.3.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Krystal M., Arnheim N. A member of a new repeated sequence family which is conserved throughout eucaryotic evolution is found between the human delta and beta globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5931–5947. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom G. T., Erlich H. MHC class-II molecules and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:493–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet C., Hanauer A., Clemens P., Caskey T., Mandel J. L. Two hot spots of recombination in the DMD gene correlate with the deletion prone regions. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Nov;1(8):599–603. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.8.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace T., Ponzi M., Dore E., Janse C., Mons B., Frontali C. Long insertions within telomeres contribute to chromosome size polymorphism in Plasmodium berghei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6759–6764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett K. A., Shreffler D. C., Saha B. K. Molecular mapping of murine I region recombinants. III. Crossing over at two discrete sites within the beta 1-beta 2 intron of the E beta gene. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2764–2770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore H. C., Kobori J. A., Zimmerer E. J., Spinella D. G., Hood L. Molecular characterization of meiotic recombination within the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse: mapping of crossover sites within the I region. Biochem Genet. 1987 Aug;25(7-8):513–526. doi: 10.1007/BF00554353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powis S. H., Tonks S., Mockridge I., Kelly A. P., Bodmer J. G., Trowsdale J. Alleles and haplotypes of the MHC-encoded ABC transporters TAP1 and TAP2. Immunogenetics. 1993;37(5):373–380. doi: 10.1007/BF00216802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney S. M., Moore P. D. Antiparallel, intramolecular triplex DNA stimulates homologous recombination in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2141–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha B. K., Cullen S. E. Molecular mapping of murine I region recombinants: crossing over in the E beta gene. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1112–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha B. K., Raziuddin, Cullen S. E. Molecular mapping of murine I region recombinants. II. Crossing over in the E beta gene is restricted to a 4.5 kb stretch of DNA that excludes the beta 1 exon. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):4004–4009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant'Angelo D. B., Lafuse W. P., Passmore H. C. Evidence that nucleotide sequence identity is a requirement for meiotic crossing over within the mouse Eb recombinational hot spot. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1334–1336. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90061-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satyanarayana K., Strominger J. L. DNA sequences near a meiotic recombinational breakpoint within the human HLA-DQ region. Immunogenetics. 1992;35(4):235–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00166828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Griffith R. L., Erlich H. A. Rapid typing of DNA sequence polymorphism at the HLA-DRB1 locus using the polymerase chain reaction and nonradioactive oligonucleotide probes. Hum Immunol. 1991 Mar;30(3):190–201. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(91)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchert P., Langsford M., Käslin E., Kohli J. A specific DNA sequence is required for high frequency of recombination in the ade6 gene of fission yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2157–2163. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07750.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Hanzawa N., Sagai T., Ishiura M., Gojobori T., Steinmetz M., Moriwaki K. Recombinational hotspot specific to female meiosis in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Immunogenetics. 1990;31(2):79–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00661217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Sagai T., Hanzawa N., Gotoh H., Moriwaki K. Genetic control of sex-dependent meiotic recombination in the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):681–686. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Sagai T., Moriwaki K. A new wild-derived H-2 haplotype enhancing K-IA recombination. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):370–372. doi: 10.1038/300370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Sagai T., Moriwaki K. Hotspots of meiotic recombination in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Genetica. 1993;88(2-3):187–196. doi: 10.1007/BF02424475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Sagai T., Moriwaki K. Sexual preference of meiotic recombination within the H-2 complex. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(4):258–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00404696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Kunes S. M., Schultz D. W., Taylor A., Triman K. L. Structure of chi hotspots of generalized recombination. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Minard K., Horvath S., McNicholas J., Srelinger J., Wake C., Long E., Mach B., Hood L. A molecular map of the immune response region from the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):35–42. doi: 10.1038/300035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Stephan D., Fischer Lindahl K. Gene organization and recombinational hotspots in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara N., Haber J. E. Characterization of double-strand break-induced recombination: homology requirements and single-stranded DNA formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):563–575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Rothstein R. Sex, maps, and imprinting. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90199-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen M., Abbal M., Neugebauer M., Cambon-Thomsen A. Recombinations in the HLA system. Tissue Antigens. 1989 Jan;33(1):38–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1989.tb01675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treco D., Arnheim N. The evolutionarily conserved repetitive sequence d(TG.AC)n promotes reciprocal exchange and generates unusual recombinant tetrads during yeast meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3934–3947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uematsu Y., Kiefer H., Schulze R., Fischer-Lindahl K., Steinmetz M. Molecular characterization of a meiotic recombinational hotspot enhancing homologous equal crossing-over. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2123–2129. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahls W. P., Wallace L. J., Moore P. D. Hypervariable minisatellite DNA is a hotspot for homologous recombination in human cells. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90719-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino M., Sagai T., Lindahl K. F., Toyoda Y., Moriwaki K., Shiroishi T. Allele-dependent recombination frequency: homology requirement in meiotic recombination at the hot spot in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Genomics. 1995 May 20;27(2):298–305. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino M., Sagai T., Lindahl K. F., Toyoda Y., Shirayoshi Y., Matsumoto K., Sugaya K., Ikemura T., Moriwaki K., Shiroishi T. Recombination in the class III region of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Immunogenetics. 1994;40(4):280–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00189973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino M., Sagai T., Lindahl K. F., Toyoda Y., Shiroishi T., Moriwaki K. No dosage effect of recombinational hotspots in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Immunogenetics. 1994;39(6):381–389. doi: 10.1007/BF00176154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Shiue L., Kaplan S., de Lange T. A mammalian factor that binds telomeric TTAGGG repeats in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4834–4843. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerer E. J., Passmore H. C. Structural and genetic properties of the Eb recombinational hotspot in the mouse. Immunogenetics. 1991;33(2):132–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00210827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Endert P. M., Lopez M. T., Patel S. D., Monaco J. J., McDevitt H. O. Genomic polymorphism, recombination, and linkage disequilibrium in human major histocompatibility complex-encoded antigen-processing genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11594–11597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


