Abstract
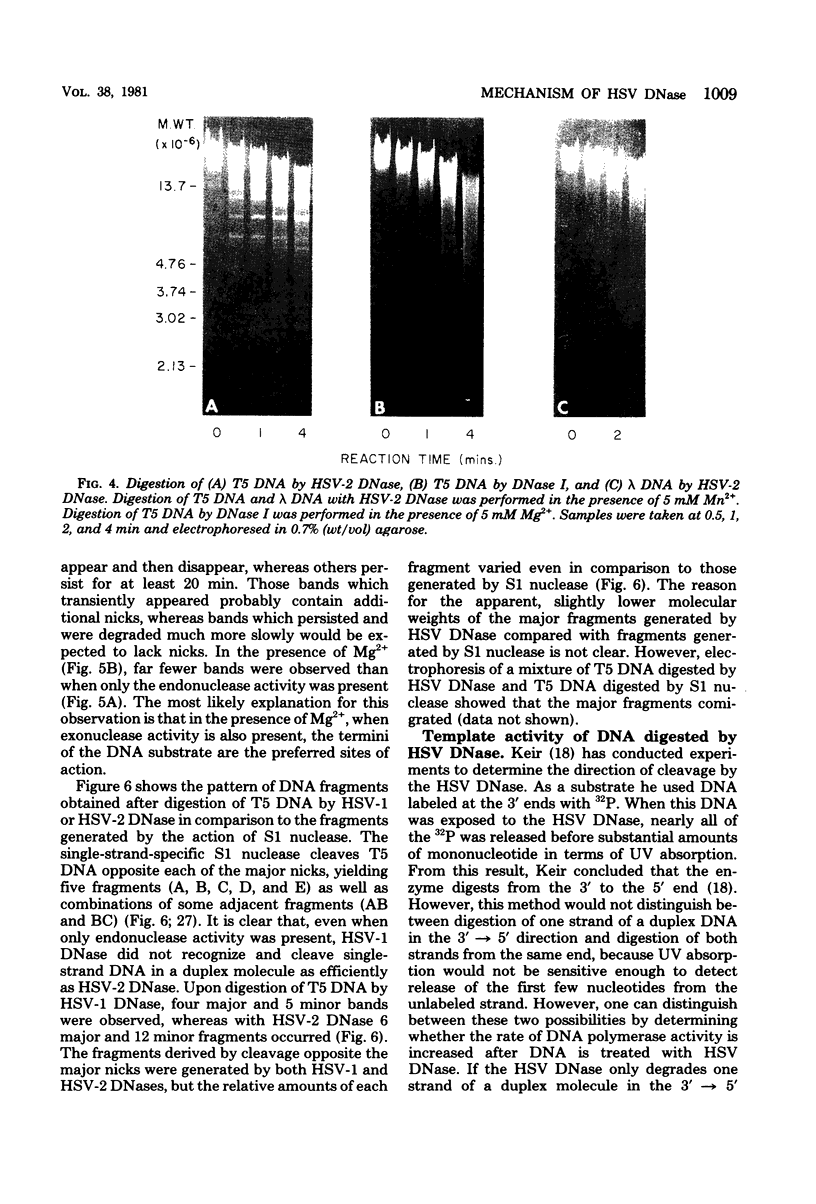
Reaction intermediates formed during the degradation of linear PM2, T5, and λ DNA by herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNase have been examined by agarose gel electrophoresis. Digestion of T5 DNA by HSV type 2 (HSV-2) DNase in the presence of Mn2+ (endonuclease only) gave rise to 6 major and 12 minor fragments. Some of the fragments produced correspond to those observed after cleavage of T5 DNA by the single-strand-specific S1 nuclease, indicating that the HSV DNase rapidly cleaves opposite a nick or gap in a duplex DNA molecule. In contrast, HSV DNase did not produce distinct fragments upon digestion of linear PM2 or λ DNA, which do not contain nicks. In the presence of Mg2+, when both endonuclease and exonuclease activities of the HSV DNase occur, most of the same distinct fragments from digestion of T5 DNA were observed. However, these fragments were then further degraded preferentially from the ends, presumably by the action of the exonuclease activity. Unit-length λ DNA, EcoRI restriction fragments of λ DNA, and linear PM2 DNA were also degraded from the ends by HSV DNase in the same manner. Previous studies have suggested that the HSV exonuclease degrades in the 3′ → 5′ direction. If this is correct, and since only 5′-monophosphate nucleosides are produced, then HSV DNase should “activate” DNA for DNA polymerase. However, unlike pancreatic DNase I, neither HSV-1 nor HSV-2 DNase, in the presence of Mg2+ or Mn2+, activated calf thymus DNA for HSV DNA polymerase. This suggests that HSV DNase degrades both strands of a linear double-stranded DNA molecule from the same end at about the same rate. That is, HSV DNase is apparently capable of degrading DNA strands in the 3′ → 5′ direction as well as in the 5′ → 3′ direction, yielding progressively smaller double-stranded molecules with flush ends. Except with minor differences, HSV-1 and HSV-2 DNases act in a similar manner.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Frey L. T4 bacteriophage gene 32: a structural protein in the replication and recombination of DNA. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1313–1318. doi: 10.1038/2271313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beerman T. A., Lebowitz J. Further analysis of the altered secondary structure of superhelical DNA. Sensitivity to methylmercuric hydroxide a chemical probe for unpaired bases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 25;79(3):451–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Timbury M. C., Hay J., Moss H. Mutant of herpes simplex virus type 2 with temperature-sensitive lesions affecting virion thermostability and DNase activity: identification of the lethal mutation and physical mapping of the nuc-lesion. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):140–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.140-146.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Hoffmann P. J., Ostrander M., Grill S., Caradonna S., Tsou J., Chen J. Y., Gallagher M. R., Flanagan T. D. Properties of herpesvirus-specific thymidine kinase, DNA polymerase and DNase and their implication in the development of specific antiherpes agents. Adv Ophthalmol. 1979;38:173–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G., McCorquodale D. J. Requirement of a phage-induced 5'-exonuclease for the expression of late genes of bacteriophage T5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3502–3505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. Toward a metabolic interpretation of genetic recombination of E. coli and its phages. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:437–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.002253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough W. An endonuclease isolated from Epstein-Barr virus-producing human lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6194–6198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Canelo E. S., Sinsheimer R. L. DNA of bacteriophage PM2: a closed circular double-stranded molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1164–1168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke B., Moss H., Timbury M. C., Hay J. Alkaline DNase activity in cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):209–213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.209-213.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel G. D., Richardson C. C. The deoxyribonuclease induced after infection of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage T5. I. Characterization of the enzyme as a 5'-exonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4839–4847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel G. D., Richardson C. C. The deoxyribonuclease induced after infection of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage T5. II. Role of the enzyme in replication of the pahge deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4848–4852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Smith M. G. The chromosome of bacteriophage T5. I. Analysis of the single-stranded DNA fragments by agarose gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90435-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S. Unique double-stranded fragments of bacteriophage T5 DNA resulting from preferential shear-induced breakage at nicks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2108–2112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedgpeth J., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. DNA nucleotide sequence restricted by the RI endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann P. J., Cheng Y. C. DNase induced after infection of KB cells by herpes simplex virus type 1 or type 2. II. Characterization of an associated endonuclease activity. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):449–457. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.449-457.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann P. J., Cheng Y. C. The deoxyribonuclease induced after infection of KB cells by herpes simplex virus type 1 or type 2. I. Purification and characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3557–3562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. V., Nichols B. P., Donelson J. E. Distribution of "minor" nicks in bacteriophage T5 DNA. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):510–519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.510-519.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato A. C., Bartok K., Fraser M. J., Denhardt D. T. Sensitivity of superhelical DNA to a single-strand specific endonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 21;308(7):68–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay V., Linn S. The mechanism of degradation of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid by the recBC enzyme of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4286–4294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. M., Keir H. M. A new DNA-exonuclease in cells infected with herpes virus: partial purification and properties of the enzyme. J Gen Virol. 1968 Dec;3(3):337–347. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-3-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Rothe C. T. Role of the T5 gene D15 nuclease in the generation of nicked bacteriophage T5 DNA. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):177–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.177-193.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrander M., Cheng Y. C. Properties of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 DNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 19;609(2):232–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosamond J., Endlich B., Telander K. M., Linn S. Mechanisms of action of the type-I restriction endonuclease, ecoB, and the recBC DNase from Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1049–1057. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt M., Braunstein S. N., Camerini-Otero R. D., Franklin R. M. Structure and synthesis of a lipid-containing bacteriophage. X. Improved techniques for the purification of bacteriophage PM2. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shishido K., Ando T. Site-specific fragmentation of bacteriophage T5 DNA by single-strand-specific S1 endonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 16;390(1):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel-Fidler M., Francke B. Alkaline deoxyribonuclease induced by herpes simplex virus type 1: composition and properties of the purified enzyme. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):493–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90206-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A., Hong S. C., Aucker J., Muller R. Characterization of herpes simplex virus-induced deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6270–6277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








