Abstract
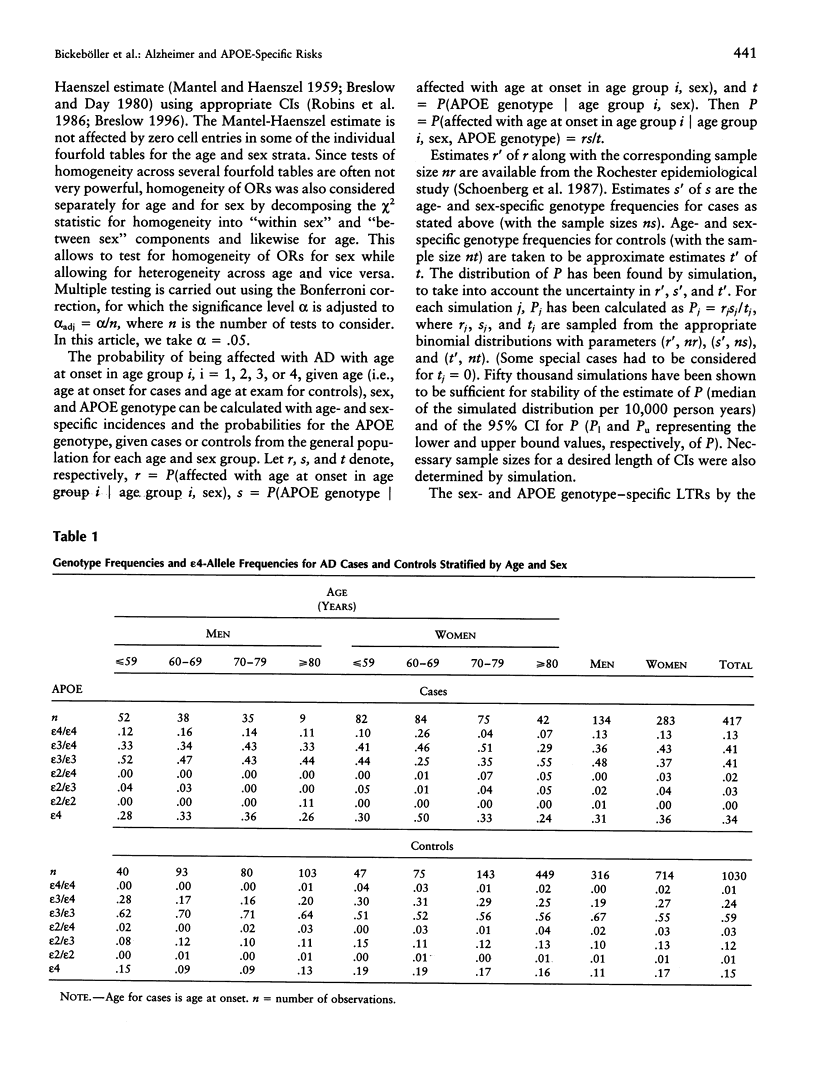
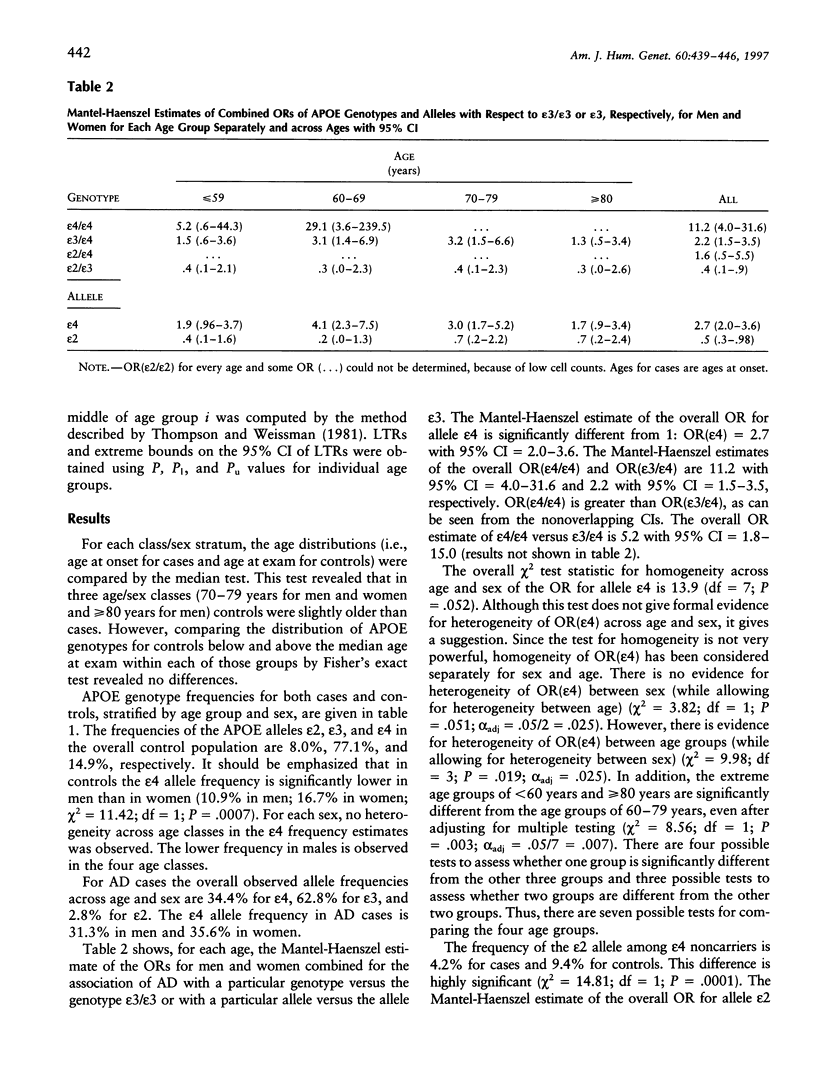
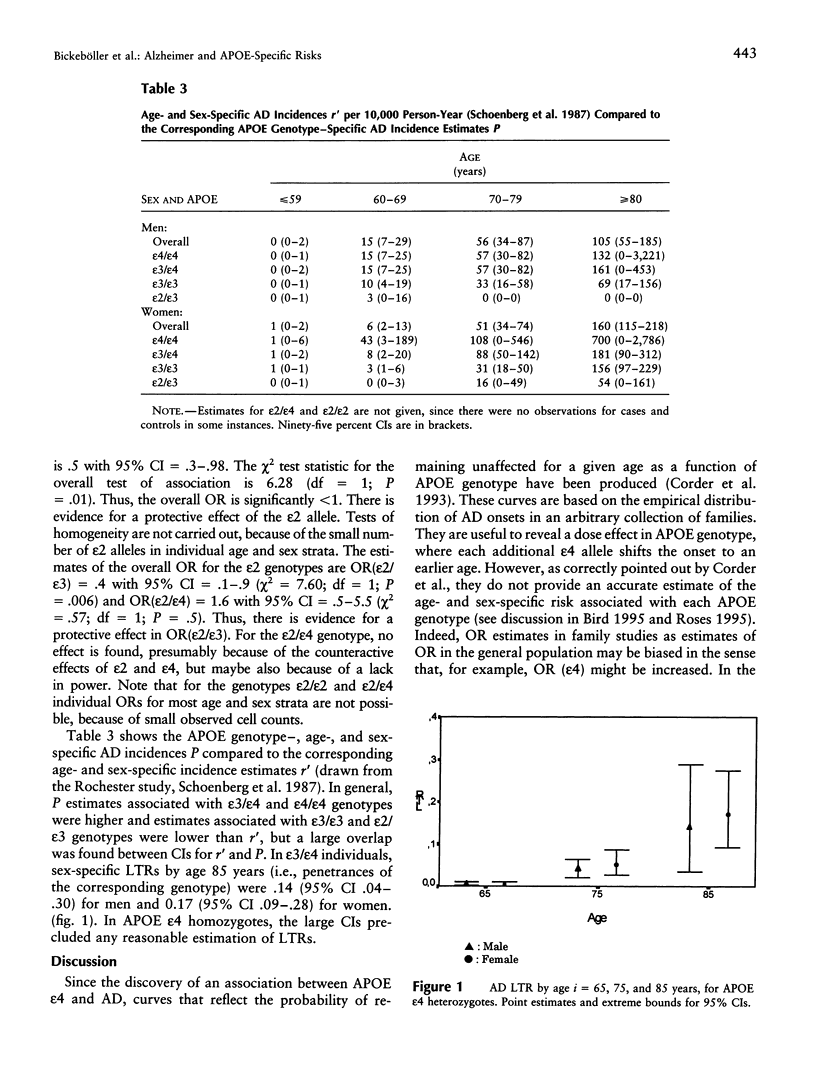
The distribution of apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotypes as a function of age and sex has been examined in a French population of 417 Alzheimer disease (AD) patients and 1,030 control subjects. When compared to the APOE epsilon3 allele, an increased risk associated with the APOE epsilon4 allele (odds ratio [OR] [epsilon4] = 2.7 with 95% confidence interval [CI] = 2.0-3.6; P < .001) and a protective effect of the APOE epsilon2 allele (OR[epsilon2] = 0.5 with 95% CI = 0.3-0.98; P = .012) were retrieved. An effect of the epsilon4 allele dosage on susceptibility was confirmed (OR[epsilon4/epsilon4] vs. the epsilon3/epsilon3 genotype = 11.2 [95% CI = 4.0-31.6]; OR[epsilon3/epsilon4] vs. the epsilon3/epsilon3 genotype = 2.2 [95% CI = 1.5-3.5]). The frequency of the epsilon4 allele was lower in male cases than in female cases, but, since a similar difference was found in controls, this does not lead to a difference in OR between sex. ORs for the epsilon4 allele versus the epsilon3 allele, OR(epsilon4), were not equal in all age classes: OR(epsilon4) in the extreme groups with onset at < 60 years or > 79 years were significantly lower than those from the age groups 60-79 years. In epsilon3/epsilon4 individuals, sex-specific lifetime risk estimates by age 85 years (i.e., sex-specific penetrances by age 85 years) were 0.14 (95% CI 0.04-0.30) for men and 0.17 (95% CI 0.09-0.28) for women.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird T. D. Apolipoprotein E genotyping in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: a cautionary view. Ann Neurol. 1995 Jul;38(1):2–4. doi: 10.1002/ana.410380103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow N. E. Statistics in epidemiology: the case-control study. J Am Stat Assoc. 1996 Mar;91(433):14–28. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1996.10476660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breteler M. M., Claus J. J., van Duijn C. M., Launer L. J., Hofman A. Epidemiology of Alzheimer's disease. Epidemiol Rev. 1992;14:59–82. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartier-Harlin M. C., Parfitt M., Legrain S., Pérez-Tur J., Brousseau T., Evans A., Berr C., Vidal O., Roques P., Gourlet V. Apolipoprotein E, epsilon 4 allele as a major risk factor for sporadic early and late-onset forms of Alzheimer's disease: analysis of the 19q13.2 chromosomal region. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Apr;3(4):569–574. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.4.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Risch N. J., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Rimmler J. B., Locke P. A., Conneally P. M., Schmader K. E. Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):180–184. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Rimmler J. B., Locke P. A., Conneally P. M., Schmader K. E., Tanzi R. E. Apolipoprotein E, survival in Alzheimer's disease patients, and the competing risks of death and Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1995 Jul;45(7):1323–1328. doi: 10.1212/wnl.45.7.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Roses A. D., Pericak-Vance M. A., Small G. W., Haines J. L. The apolipoprotein E E4 allele and sex-specific risk of Alzheimer's disease. JAMA. 1995 Feb 1;273(5):373–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming A. M., Robertson F. W. Polymorphism at the apoprotein-E locus in relation to risk of coronary disease. Clin Genet. 1984 Apr;25(4):310–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb01995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai X. Y., Nanko S., Hattori M., Fukuda R., Nagata K., Isse K., Ueki A., Kazamatsuri H. Association of apolipoprotein E4 with sporadic Alzheimer's disease is more pronounced in early onset type. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Jul 4;175(1-2):74–76. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)91081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisoni G. B., Govoni S., Geroldi C., Bianchetti A., Calabresi L., Franceschini G., Trabucchi M. Gene dose of the epsilon 4 allele of apolipoprotein E and disease progression in sporadic late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1995 May;37(5):596–604. doi: 10.1002/ana.410370509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Vernier D. T. Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res. 1990 Mar;31(3):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik G., Larson E. B., Goddard K., Schellenberg G. D., Wijsman E. M. Influence of apolipoprotein E genotype on the transmission of Alzheimer disease in a community-based sample. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jan;58(1):191–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusisto J., Koivisto K., Kervinen K., Mykkänen L., Helkala E. L., Vanhanen M., Hänninen T., Pyörälä K., Kesäniemi Y. A., Riekkinen P. Association of apolipoprotein E phenotypes with late onset Alzheimer's disease: population based study. BMJ. 1994 Sep 10;309(6955):636–638. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6955.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusisto J., Mykkänen L., Kervinen K., Kesäniemi Y. A., Laakso M. Apolipoprotein E4 phenotype is not an important risk factor for coronary heart disease or stroke in elderly subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995 Sep;15(9):1280–1286. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.9.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laakso M., Kesäniemi A., Kervinen K., Jauhiainen M., Pyörälä K. Relation of coronary heart disease and apolipoprotein E phenotype in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes. BMJ. 1991 Nov 9;303(6811):1159–1162. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6811.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtovirta M., Helisalmi S., Mannermaa A., Soininen H., Koivisto K., Ryynänen M., Riekkinen P., Sr Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease in eastern Finland. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Feb 6;185(1):13–15. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)11213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenzen H. J., Assmann G., Buchwalsky R., Schulte H. Association of apolipoprotein E polymorphism, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and coronary artery disease. Clin Chem. 1986 May;32(5):778–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locke P. A., Conneally P. M., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Haines J. L. Apolipoprotein E4 allele and Alzheimer disease: examination of allelic association and effect on age at onset in both early- and late-onset cases. Genet Epidemiol. 1995;12(1):83–92. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370120108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEL N., HAENSZEL W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Apr;22(4):719–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez M., Campion D., Babron M. C., Hannequin D., Agid Y., Bellis M., Brice A., Mallet J., Michon A., Thomas-Anterion C. Segregation analysis of Alzheimer pedigrees: rare Mendelian dominant mutation(s) explain a minority of early-onset cases. French Alzheimer Collaborative Group. Am J Med Genet. 1996 Feb 16;67(1):9–12. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320670102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Ottman R., Tatemichi T. K., Tang M. X., Maestre G., Ngai C., Tycko B., Ginsberg H. The apolipoprotein epsilon 4 allele in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1993 Nov;34(5):752–754. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. H., Schaefer E. J., Wilson P. W., D'Agostino R., Ordovas J. M., Espino A., Au R., White R. F., Knoefel J. E., Cobb J. L. Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 association with dementia in a population-based study: The Framingham study. Neurology. 1996 Mar;46(3):673–677. doi: 10.1212/wnl.46.3.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrman J., Brookes A. J., Yates C., St Clair D. Apolipoprotein E genotype and its effect on duration and severity of early and late onset Alzheimer's disease. Br J Psychiatry. 1995 Oct;167(4):533–536. doi: 10.1192/bjp.167.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payami H., Montee K. R., Kaye J. A., Bird T. D., Yu C. E., Wijsman E. M., Schellenberg G. D. Alzheimer's disease, apolipoprotein E4, and gender. JAMA. 1994 May 4;271(17):1316–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payami H., Zareparsi S., Montee K. R., Sexton G. J., Kaye J. A., Bird T. D., Yu C. E., Wijsman E. M., Heston L. L., Litt M. Gender difference in apolipoprotein E-associated risk for familial Alzheimer disease: a possible clue to the higher incidence of Alzheimer disease in women. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Apr;58(4):803–811. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J., Davignon J., Bouthillier D., Kogan S., Bertrand P., Gauthier S. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):697–699. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91705-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Tur J., Campion D., Martinez M., Brice A., Tardieu S., Hannequin D., Agid Y., Delacourte A., Clerget-Darpoux F., Chartier-Harlin M. C. Evidence for apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 association in early-onset Alzheimer's patients with late-onset relatives. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Dec 18;60(6):550–553. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320600613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins J., Breslow N., Greenland S. Estimators of the Mantel-Haenszel variance consistent in both sparse data and large-strata limiting models. Biometrics. 1986 Jun;42(2):311–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocca W. A., Hofman A., Brayne C., Breteler M. M., Clarke M., Copeland J. R., Dartigues J. F., Engedal K., Hagnell O., Heeren T. J. Frequency and distribution of Alzheimer's disease in Europe: a collaborative study of 1980-1990 prevalence findings. The EURODEM-Prevalence Research Group. Ann Neurol. 1991 Sep;30(3):381–390. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E genotyping in the differential diagnosis, not prediction, of Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1995 Jul;38(1):6–14. doi: 10.1002/ana.410380105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D., George-Hyslop P. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Joo S. H., Rosi B. L., Gusella J. F., Crapper-MacLachlan D. R., Alberts M. J. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993 Aug;43(8):1467–1472. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.8.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg B. S., Kokmen E., Okazaki H. Alzheimer's disease and other dementing illnesses in a defined United States population: incidence rates and clinical features. Ann Neurol. 1987 Dec;22(6):724–729. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Johnston C., Sim E., Nagy Z., Jobst K. A., Hindley N., King E. Protective effect of apo epsilon 2 in Alzheimer's disease. Oxford Project to Investigate Memory and Ageing (OPTIMA) Lancet. 1994 Aug 13;344(8920):473–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorbi S., Nacmias B., Forleo P., Latorraca S., Gobbini I., Bracco L., Piacentini S., Amaducci L. ApoE allele frequencies in Italian sporadic and familial Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Aug 15;177(1-2):100–102. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair D., Rennie M., Slorach E., Norrman J., Yates C., Carothers A. Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele is a risk factor for familial and sporadic presenile Alzheimer's disease in both homozygote and heterozygote carriers. J Med Genet. 1995 Aug;32(8):642–644. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.8.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):4725–4727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.4725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot C., Lendon C., Craddock N., Shears S., Morris J. C., Goate A. Protection against Alzheimer's disease with apoE epsilon 2. Lancet. 1994 Jun 4;343(8910):1432–1433. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang M. X., Maestre G., Tsai W. Y., Liu X. H., Feng L., Chung W. Y., Chun M., Schofield P., Stern Y., Tycko B. Relative risk of Alzheimer disease and age-at-onset distributions, based on APOE genotypes among elderly African Americans, Caucasians, and Hispanics in New York City. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Mar;58(3):574–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. D., Weissman M. M. Quantifying lifetime risk of psychiatric disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 1981;16(2):113–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(81)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. S., Tangalos E. G., Petersen R. C., Smith G. E., Schaid D. J., Kokmen E., Ivnik R. J., Thibodeau S. N. Apolipoprotein E: risk factor for Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):643–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Lopez R., Rogaeva E. A., Freedman M., Rogaev E., Drachman D., Pollen D., Haines J., Liang Y., McLachlan D. R. Are the associations between Alzheimer's disease and polymorphisms in the apolipoprotein E and the apolipoprotein CII genes due to linkage disequilibrium? Ann Neurol. 1994 Jul;36(1):97–100. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Yamakawa-Kobayashi K., Komatsuzaki Y., Arinami T., Oguni E., Mizusawa H., Shoji S., Hamaguchi H. Dose-dependent association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset, sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1994 Oct;36(4):656–659. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bockxmeer F. M., Mamotte C. D. Apolipoprotein epsilon 4 homozygosity in young men with coronary heart disease. Lancet. 1992 Oct 10;340(8824):879–880. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., de Knijff P., Cruts M., Wehnert A., Havekes L. M., Hofman A., Van Broeckhoven C. Apolipoprotein E4 allele in a population-based study of early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet. 1994 May;7(1):74–78. doi: 10.1038/ng0594-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., de Knijff P., Wehnert A., De Voecht J., Bronzova J. B., Havekes L. M., Hofman A., Van Broeckhoven C. The apolipoprotein E epsilon 2 allele is associated with an increased risk of early-onset Alzheimer's disease and a reduced survival. Ann Neurol. 1995 May;37(5):605–610. doi: 10.1002/ana.410370510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


