Abstract
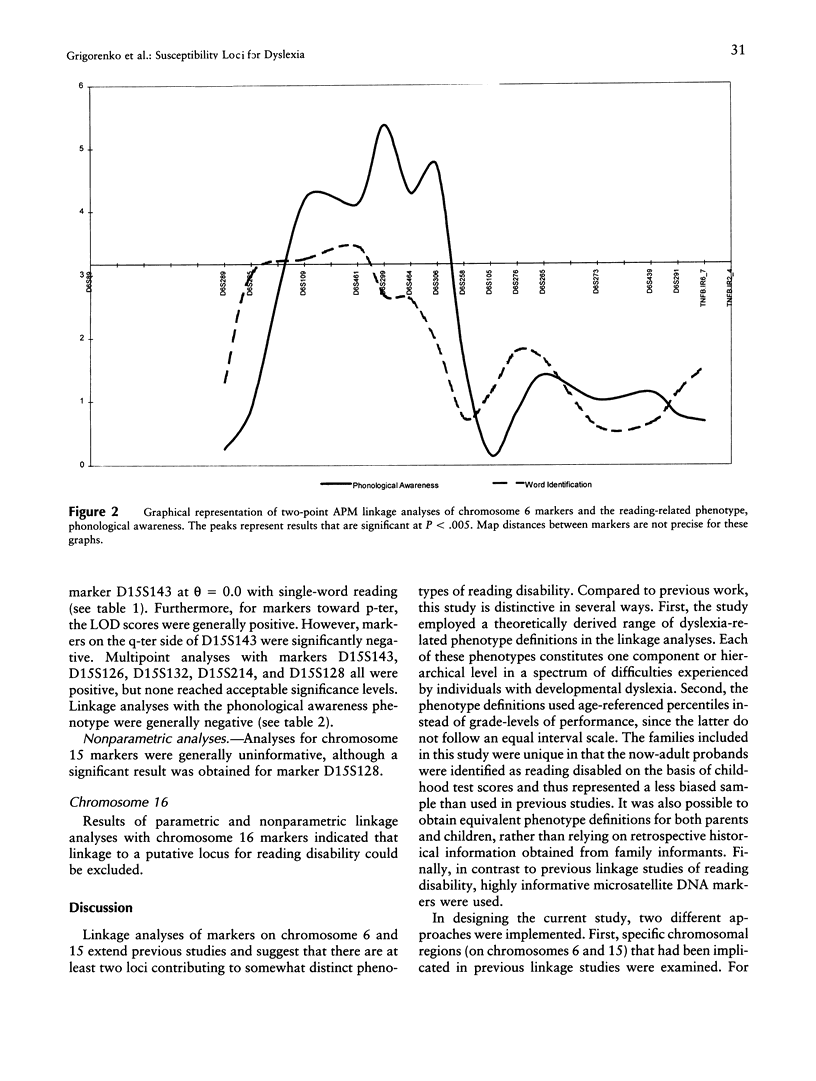
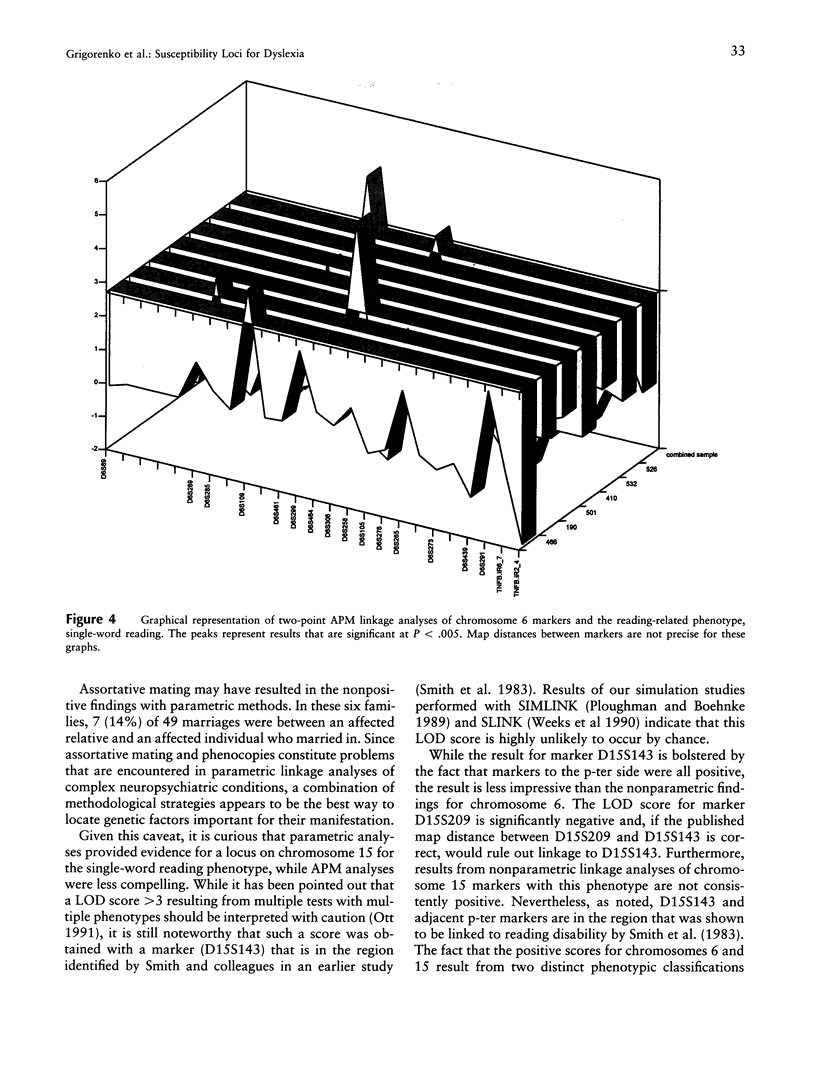
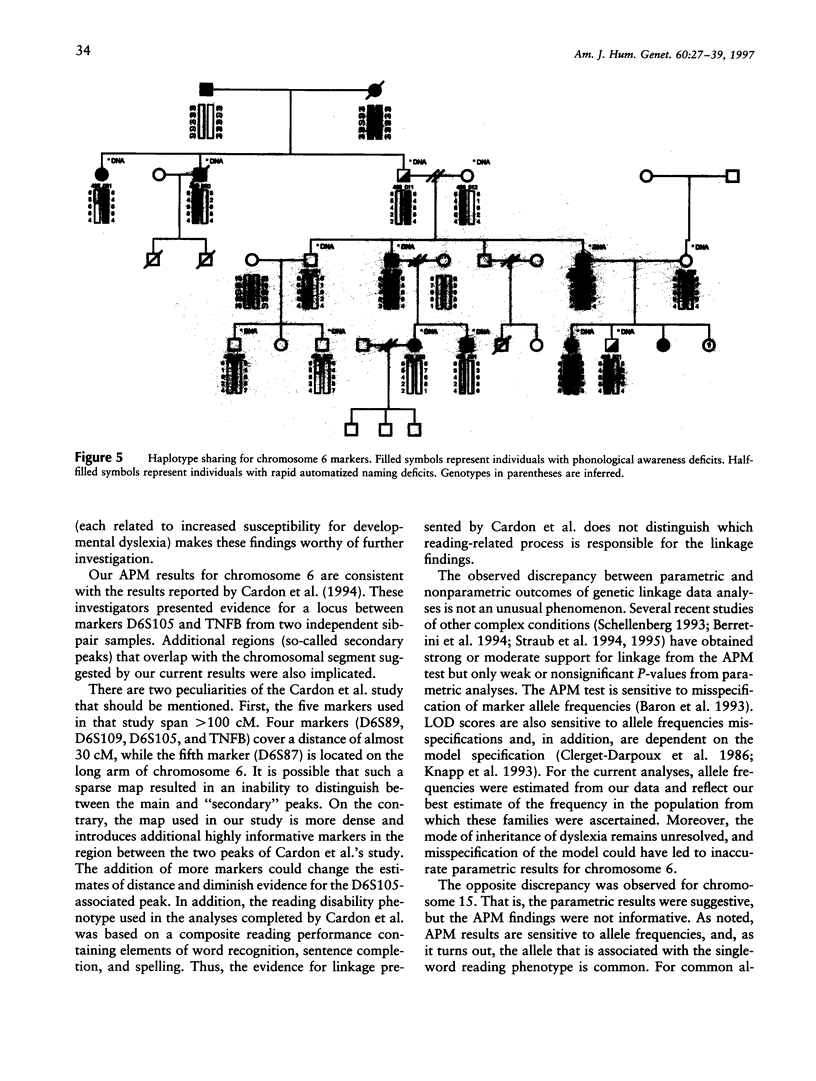
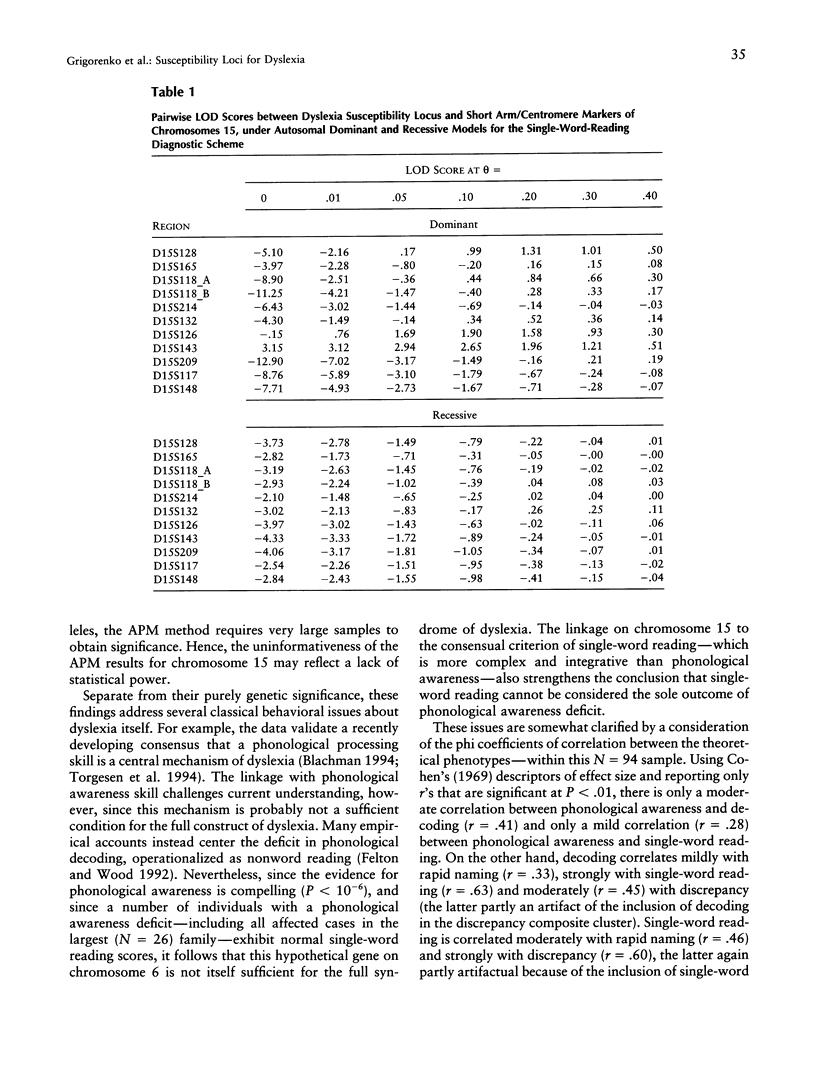
Six extended dyslexic families with at least four affected individuals were genotyped with markers in three chromosomal regions: 6p23-p21.3, 15pter-qter, and 16pter-qter. Five theoretically derived phenotypes were used in the linkage analyses: (1) phonological awareness; (2) phonological decoding; (3) rapid automatized naming; (4) single-word reading; and (5) discrepancy between intelligence and reading performance, an empirically derived, commonly used phenotype. Two-point and multipoint allele-sharing analyses of chromosome 6 markers revealed significant evidence (P < 10(-6)) for linkage of the phonological awareness phenotype to five adjacent markers (D6S109, D6S461, D6S299, D6S464, and D6S306). The least compelling results were obtained with single-word reading. In contrast, with chromosome 15 markers, a LOD score of 3.15 was obtained for marker D15S143 at theta = 0.0 with single-word reading. Multipoint analyses with markers adjacent to D15S143 (D15S126, D15S132, D15S214, and D15S128) were positive, but none reached acceptable significance levels. Chromosome 15 analyses with the phonological awareness phenotype were negative. Parametric and nonparametric linkage analyses with chromosome 16 markers were negative. The most intriguing aspect of the current findings is that two very distinct reading-related phenotypes, reflecting different levels in the hierarchy of reading-related skills, each contributing to different processes, appear to be linked to two different chromosomal regions.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babron M. C., Martinez M., Bonaïti-Pellié C., Clerget-Darpoux F. Linkage detection by the Affected-Pedigree-Member method: what is really tested? Genet Epidemiol. 1993;10(6):389–394. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370100610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrettini W. H., Ferraro T. N., Goldin L. R., Weeks D. E., Detera-Wadleigh S., Nurnberger J. I., Jr, Gershon E. S. Chromosome 18 DNA markers and manic-depressive illness: evidence for a susceptibility gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5918–5921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaard M. L., Eiberg H., Møller N., Niebuhr E., Mohr J. Dyslexia and chromosome 15 heteromorphism: negative lod score in a Danish material. Clin Genet. 1987 Aug;32(2):118–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boder E. Developmental dyslexia: a diagnostic approach based on three atypical reading-spelling patterns. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1973 Oct;15(5):663–687. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1973.tb05180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardon L. R., Smith S. D., Fulker D. W., Kimberling W. J., Pennington B. F., DeFries J. C. Quantitative trait locus for reading disability on chromosome 6. Science. 1994 Oct 14;266(5183):276–279. doi: 10.1126/science.7939663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerget-Darpoux F., Bonaïti-Pellié C., Hochez J. Effects of misspecifying genetic parameters in lod score analysis. Biometrics. 1986 Jun;42(2):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFries J. C., Fulker D. W., LaBuda M. C. Evidence for a genetic aetiology in reading disability of twins. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):537–539. doi: 10.1038/329537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. N., Bender B. G. Converging evidence for multiple genetic forms of reading disability. Brain Lang. 1988 Mar;33(2):197–215. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(88)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denckla M. B., Rudel R. G. Naming of object-drawings by dyslexic and other learning disabled children. Brain Lang. 1976 Jan;3(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(76)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felton R. H., Naylor C. E., Wood F. B. Neuropsychological profile of adult dyslexics. Brain Lang. 1990 Nov;39(4):485–497. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(90)90157-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felton R. H., Wood F. B. Cognitive deficits in reading disability and attention deficit disorder. J Learn Disabil. 1989 Jan;22(1):3-13, 22. doi: 10.1177/002221948902200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorm A. F. Specific reading retardation and working memory: a review. Br J Psychol. 1983 Aug;74(Pt 3):311–342. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1983.tb01865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp M., Seuchter S. A., Baur M. P. The effect of misspecifying allele frequencies in incompletely typed families. Genet Epidemiol. 1993;10(6):413–418. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370100614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Rao D. C., Morton N. E., Elston R. C. A unified model for complex segregation analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Sep;35(5):816–826. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Matthysse S. Simulation of pedigree genotypes by random walks. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):959–970. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewitter F. I., DeFries J. C., Elston R. C. Genetic models of reading disability. Behav Genet. 1980 Jan;10(1):9–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01067316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Luty J. A. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D6S89 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4301–4301. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedospasov S. A., Udalova I. A., Kuprash D. V., Turetskaya R. L. DNA sequence polymorphism at the human tumor necrosis factor (TNF) locus. Numerous TNF/lymphotoxin alleles tagged by two closely linked microsatellites in the upstream region of the lymphotoxin (TNF-beta) gene. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):1053–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell J. R., Weeks D. E. The VITESSE algorithm for rapid exact multilocus linkage analysis via genotype set-recoding and fuzzy inheritance. Nat Genet. 1995 Dec;11(4):402–408. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington B. F., Gilger J. W., Pauls D., Smith S. A., Smith S. D., DeFries J. C. Evidence for major gene transmission of developmental dyslexia. JAMA. 1991 Sep 18;266(11):1527–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploughman L. M., Boehnke M. Estimating the power of a proposed linkage study for a complex genetic trait. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):543–551. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin M., Wen X. L., Hepburn M., Lubs H. A., Feldman E., Duara R. Suggestive linkage of developmental dyslexia to chromosome 1p34-p36. Lancet. 1993 Jul 17;342(8864):178–178. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91384-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranum L. P., Chung M. Y., Duvick L. A., Zoghbi H. Y., Orr H. T. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D6S109 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1171–1171. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1171-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter M., Yule W. The concept of specific reading retardation. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1975 Jul;16(3):181–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1975.tb01269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Payami H., Wijsman E. M., Orr H. T., Goddard K. A., Anderson L., Nemens E., White J. A., Alonso M. E., Ball M. J. Chromosome 14 and late-onset familial Alzheimer disease (FAD). Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Sep;53(3):619–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaywitz S. E., Shaywitz B. A., Fletcher J. M., Escobar M. D. Prevalence of reading disability in boys and girls. Results of the Connecticut Longitudinal Study. JAMA. 1990 Aug 22;264(8):998–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. S. IQ is irrelevant to the definition of learning disabilities. J Learn Disabil. 1989 Oct;22(8):469-78, 486. doi: 10.1177/002221948902200803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Kimberling W. J., Pennington B. F., Lubs H. A. Specific reading disability: identification of an inherited form through linkage analysis. Science. 1983 Mar 18;219(4590):1345–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.6828864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanovich K. E. Explaining the differences between the dyslexic and the garden-variety poor reader: the phonological-core variable-difference model. J Learn Disabil. 1988 Dec;21(10):590–604. doi: 10.1177/002221948802101003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., Lehner T., Luo Y., Loth J. E., Shao W., Sharpe L., Alexander J. R., Das K., Simon R., Fieve R. R. A possible vulnerability locus for bipolar affective disorder on chromosome 21q22.3. Nat Genet. 1994 Nov;8(3):291–296. doi: 10.1038/ng1194-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., MacLean C. J., O'Neill F. A., Burke J., Murphy B., Duke F., Shinkwin R., Webb B. T., Zhang J., Walsh D. A potential vulnerability locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 6p24-22: evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):287–293. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torgesen J. K., Wagner R. K., Rashotte C. A. Longitudinal studies of phonological processing and reading. J Learn Disabil. 1994 May;27(5):276–291. doi: 10.1177/002221949402700503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Kwitek A. E., May P. E., Zoghbi H. Y. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D6S105 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):968–968. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Lange K. The affected-pedigree-member method of linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):315–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Sobel E., O'Connell J. R., Lange K. Computer programs for multilocus haplotyping of general pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1506–1507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


