Abstract
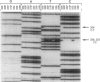
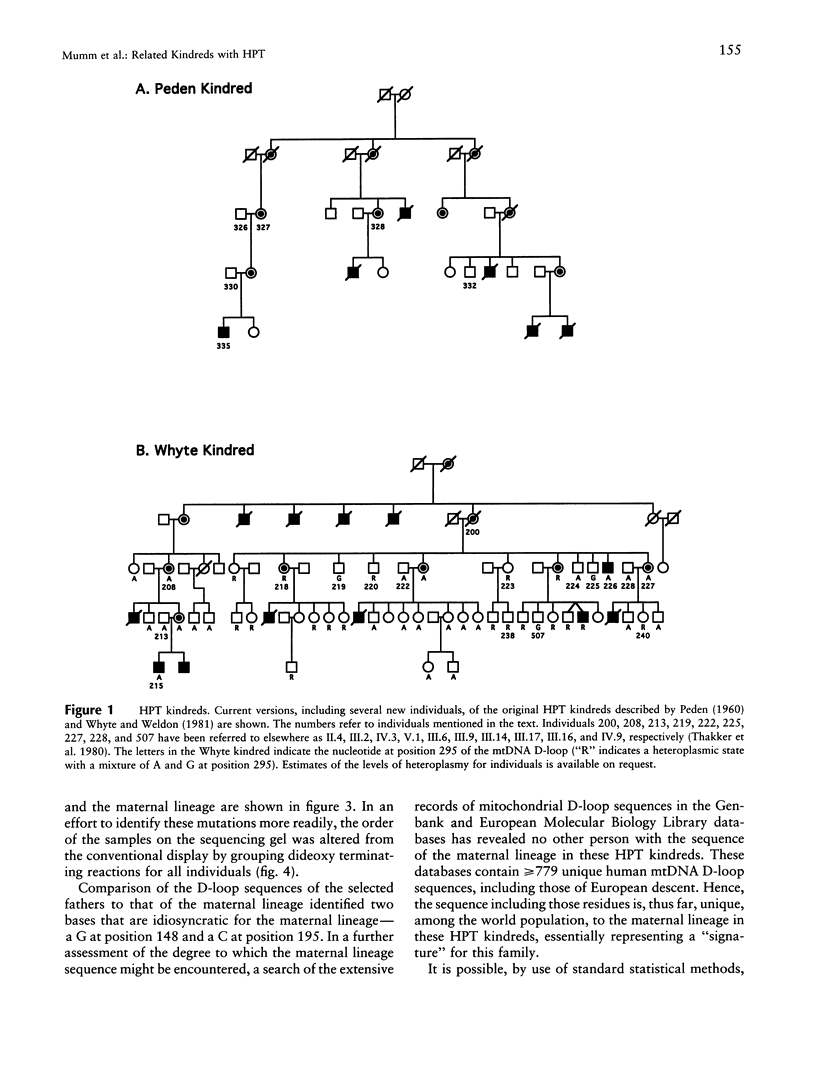
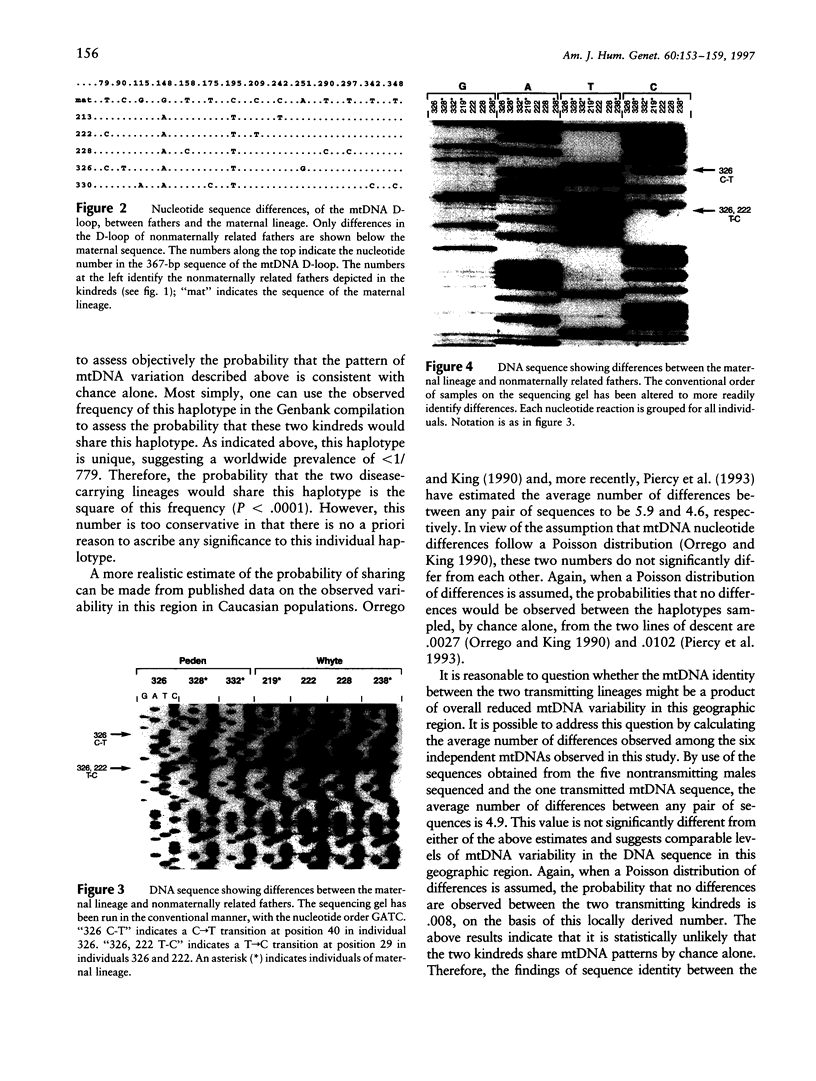
Two kindreds residing in eastern Missouri and exhibiting X-linked recessive idiopathic hypoparathyroidism have been described. Genealogical records extending back five generations revealed no common ancestor. To investigate the possibility of relatedness, the DNA sequence of the mitochondrial D-loop was compared among several individuals in both kindreds. The mtDNA D-loop was amplified from the total DNA of individuals by use of nested PCR reactions, and the resulting 430-bp fragment was sequenced. The mtDNA sequence was identical among affected males and their maternal lineage for individuals in both kindreds. Conversely, the mtDNA sequence of the fathers of the affected males differed from that of the maternal lineage at three to six positions. These results demonstrate that the two kindreds exhibiting X-linked recessive hypoparathyroidism are indeed related and that an identical gene defect is responsible for the disease. A further feature of the inheritance pattern was examined when a unique point mutation was identified in the mtDNA of one branch of one of the kindreds. This mutation appears to be de novo and segregates in subsequent generations without obscuring relatedness. In addition, the results of our study of mtDNA analysis indicate that this approach may be of importance in investigating common ancestry in other X-linked disorders.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanchard M. M., Taillon-Miller P., Nowotny P., Nowotny V. PCR buffer optimization with uniform temperature regimen to facilitate automation. PCR Methods Appl. 1993 Feb;2(3):234–240. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.3.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. M., George M., Jr, Wilson A. C. Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1967–1971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rienzo A., Wilson A. C. Branching pattern in the evolutionary tree for human mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1597–1601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles R. E., Blanc H., Cann H. M., Wallace D. C. Maternal inheritance of human mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6715–6719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginther C., Issel-Tarver L., King M. C. Identifying individuals by sequencing mitochondrial DNA from teeth. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):135–138. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEDEN V. H. True idiopathic hypoparathyroidism as a sexlinked recessive trait. Am J Hum Genet. 1960 Sep;12:323–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piercy R., Sullivan K. M., Benson N., Gill P. The application of mitochondrial DNA typing to the study of white Caucasian genetic identification. Int J Legal Med. 1993;106(2):85–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01225046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulton J. Transmission of mtDNA: cracks in the bottleneck. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Aug;57(2):224–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A. K., Montanaro V., Kere J. Simplified template preparation and improved direct sequencing using Taq polymerase. PCR Methods Appl. 1992 May;1(4):255–256. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.4.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V., Davies K. E., Whyte M. P., Wooding C., O'Riordan J. L. Mapping the gene causing X-linked recessive idiopathic hypoparathyroidism to Xq26-Xq27 by linkage studies. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):40–45. doi: 10.1172/JCI114712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte M. P., Kim G. S., Kosanovich M. Absence of parathyroid tissue in sex-linked recessive hypoparathyroidism. J Pediatr. 1986 Nov;109(5):915–915. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80741-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte M. P., Weldon V. V. Idiopathic hypoparathyroidism presenting with seizures during infancy: X-linked recessive inheritance in a large Missouri kindred. J Pediatr. 1981 Oct;99(4):608–611. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucchi I., Mumm S., Pilia G., Macmillan S., Reinbold R., Susani L., Weissenbach J., Schlessinger D. YAC/STS map across 12 Mb of Xq27 at 25-kb resolution, merging Xq26-qter. Genomics. 1996 May 15;34(1):42–54. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]