Abstract
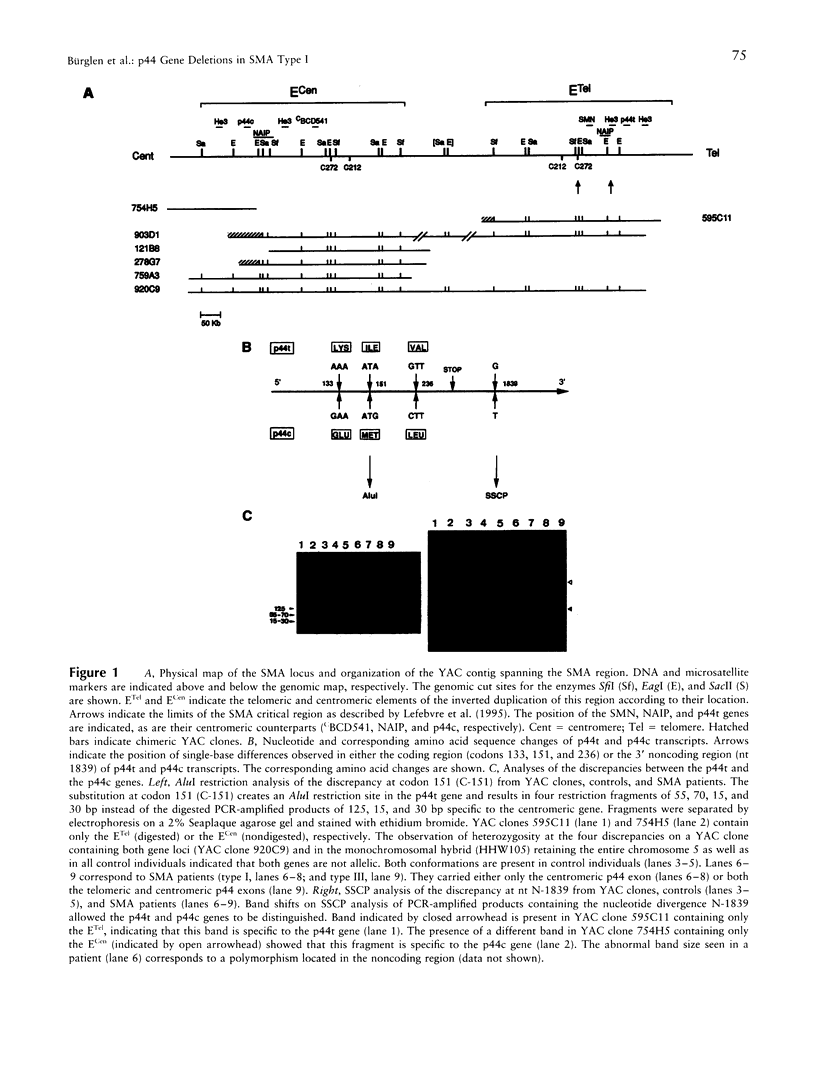
Mutations of the survival motor neurone gene (SMN) are associated with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a frequent lethal autosomal recessive disorder. In spite of this, no phenotype-genotype correlation was observed, since the SMN gene is lacking in the majority of patients affected with either the severe form (type I) or the milder forms (types II and III). Here, we show that the gene encoding p44, a subunit of the basal transcription factor TFIIH, is duplicated in the SMA region and that the p44 gene products (p44t and p44c) differ by three amino acid changes. Gene analysis of a total of 94 unrelated SMA patients revealed that the p44t gene is involved in large-scale deletions associated with Werdnig-Hoffmann disease (type I). The TFIIH polypeptide composition as well as transcription and DNA repair activities are normal in patients lacking the p44t gene on both mutant chromosomes, suggesting that the p44t gene is not critical for the development of SMA.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. DNA repair. Engagement with transcription. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):114–115. doi: 10.1038/363114a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzustowicz L. M., Lehner T., Castilla L. H., Penchaszadeh G. K., Wilhelmsen K. C., Daniels R., Davies K. E., Leppert M., Ziter F., Wood D. Genetic mapping of chronic childhood-onset spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q11.2-13.3. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):540–541. doi: 10.1038/344540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlet P., Bürglen L., Clermont O., Lefebvre S., Viollet L., Munnich A., Melki J. Large scale deletions of the 5q13 region are specific to Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. J Med Genet. 1996 Apr;33(4):281–283. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.4.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussaglia E., Clermont O., Tizzano E., Lefebvre S., Bürglen L., Cruaud C., Urtizberea J. A., Colomer J., Munnich A., Baiget M. A frame-shift deletion in the survival motor neuron gene in Spanish spinal muscular atrophy patients. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):335–337. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Skarecky D., Dana S. L., Wasmuth J. J. Deletion mapping of human chromosome 5 using chromosome-specific DNA probes. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Sep;37(5):839–852. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czeizel A., Hamula J. A hungarian study on Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. J Med Genet. 1989 Dec;26(12):761–763. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.12.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard M., Fischer L., Moncollin V., Chipoulet J. M., Chambon P., Egly J. M. Purification and interaction properties of the human RNA polymerase B(II) general transcription factor BTF2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20940–20945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Brzustowicz L. M., Castilla L. H., Lehner T., Penchaszadeh G. K., Daniels R. J., Byth B. C., Knowles J., Hislop J. E., Shapira Y. Genetic homogeneity between acute and chronic forms of spinal muscular atrophy. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):823–825. doi: 10.1038/345823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H., Egly J. M., Vermeulen W. TFIIH: a key component in multiple DNA transactions. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996 Feb;6(1):26–33. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert S., van Vuuren H., Lutz Y., Hoeijmakers J. H., Egly J. M., Moncollin V. p44 and p34 subunits of the BTF2/TFIIH transcription factor have homologies with SSL1, a yeast protein involved in DNA repair. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2393–2398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre S., Bürglen L., Reboullet S., Clermont O., Burlet P., Viollet L., Benichou B., Cruaud C., Millasseau P., Zeviani M. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Abdelhak S., Sheth P., Bachelot M. F., Burlet P., Marcadet A., Aicardi J., Barois A., Carriere J. P., Fardeau M. Gene for chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophies maps to chromosome 5q. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):767–768. doi: 10.1038/344767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Lefebvre S., Burglen L., Burlet P., Clermont O., Millasseau P., Reboullet S., Bénichou B., Zeviani M., Le Paslier D. De novo and inherited deletions of the 5q13 region in spinal muscular atrophies. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1474–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.7910982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Sheth P., Abdelhak S., Burlet P., Bachelot M. F., Lathrop M. G., Frezal J., Munnich A. Mapping of acute (type I) spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q12-q14. The French Spinal Muscular Atrophy Investigators. Lancet. 1990 Aug 4;336(8710):271–273. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91803-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearn J. H. The gene frequency of acute Werdnig-Hoffmann disease (SMA type 1). A total population survey in North-East England. J Med Genet. 1973 Sep;10(3):260–265. doi: 10.1136/jmg.10.3.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Owen N., Talbot K., Patel S., Muntoni F., Ignatius J., Dubowitz V., Davies K. E. Gene deletions in spinal muscular atrophy. J Med Genet. 1996 Feb;33(2):93–96. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.2.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy N., Mahadevan M. S., McLean M., Shutler G., Yaraghi Z., Farahani R., Baird S., Besner-Johnston A., Lefebvre C., Kang X. The gene for neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein is partially deleted in individuals with spinal muscular atrophy. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90461-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Roy R., Humbert S., Moncollin V., Vermeulen W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Chambon P., Egly J. M. DNA repair helicase: a component of BTF2 (TFIIH) basic transcription factor. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):58–63. doi: 10.1126/science.8465201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D., Robins P., Lindahl T. Complementation of the xeroderma pigmentosum DNA repair defect in cell-free extracts. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Steege G., Draaijers T. G., Grootscholten P. M., Osinga J., Anzevino R., Velonà I., Den Dunnen J. T., Scheffer H., Brahe C., van Ommen G. J. A provisional transcript map of the spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) critical region. Eur J Hum Genet. 1995;3(2):87–95. doi: 10.1159/000472281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]