Abstract
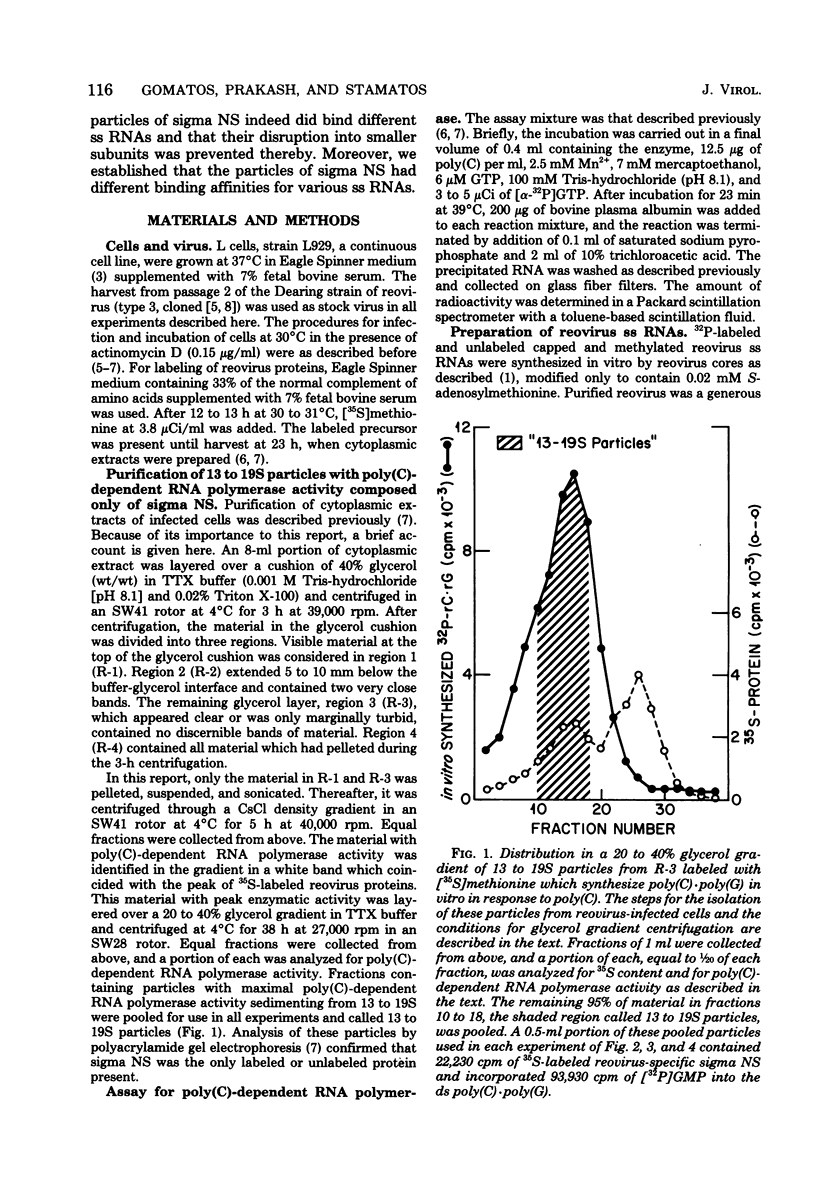
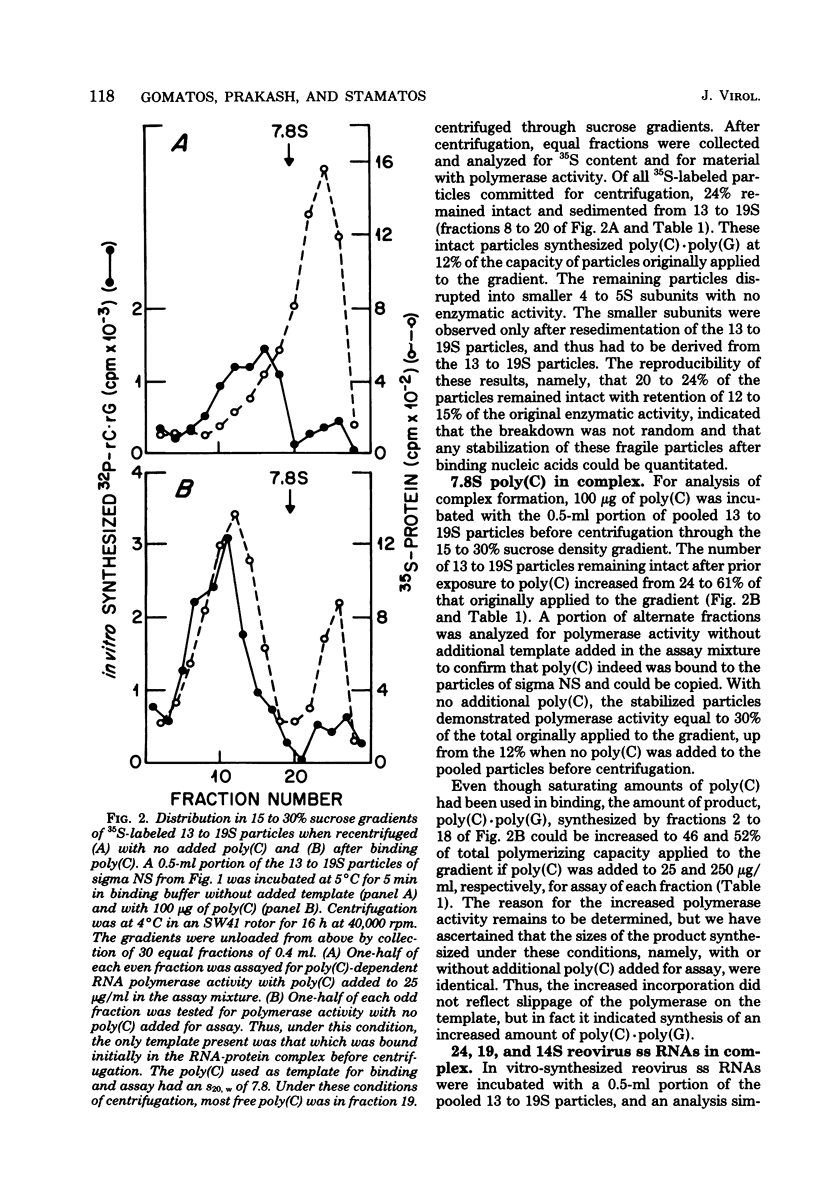
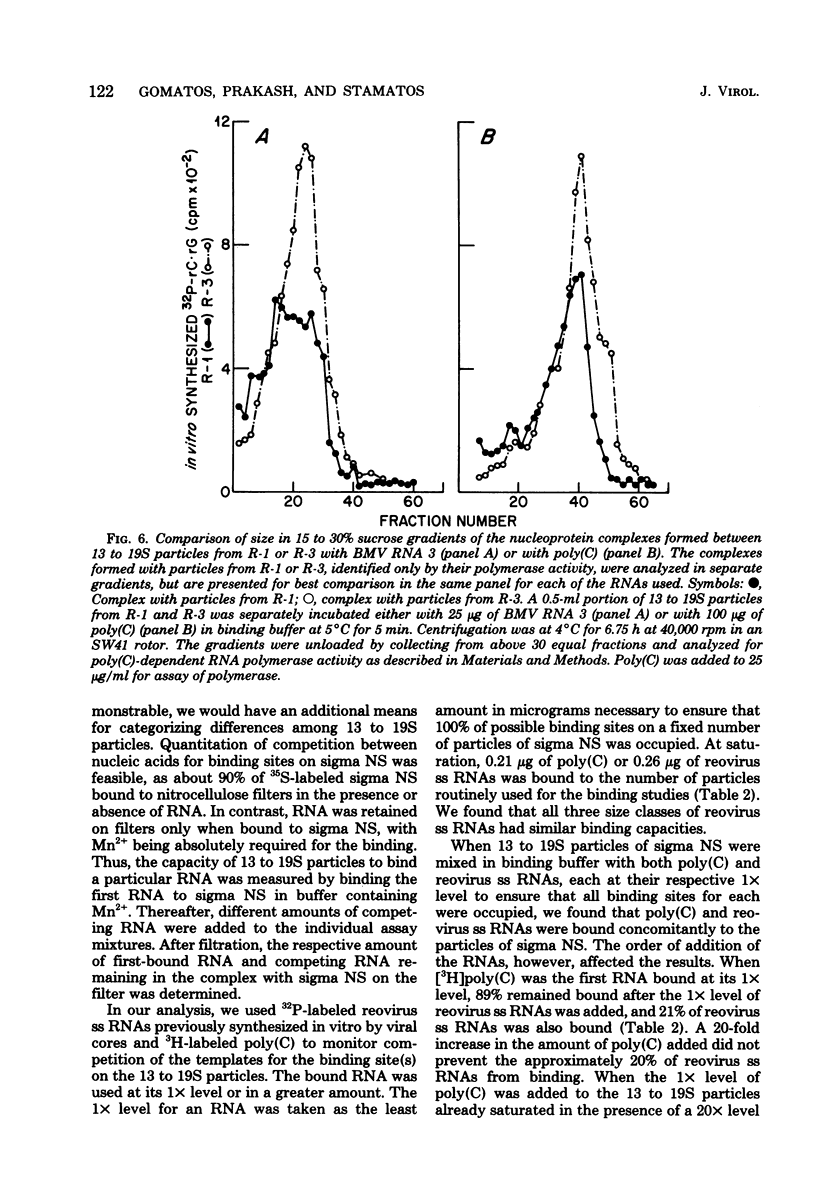
We reported previously that polycytidylate [poly(C)]-dependent RNA polymerase activity was a property of small spherical or triangular reovirus-specific particles which sedimented at 13 to 19S and were composed solely of the reovirus protein, sigma NS. Depending on the fraction of cellular extracts from which they were obtained, these particles exhibited marked differences in stability. Most 13 to 19S particles from a particular fraction repeatedly disaggregated into smaller 4 to 5S subunits with no enzymatic activity. Disruption of many particles could be prevented and polymerase activity retained after these particles had bound different single-stranded (ss) RNAs. Our previous results indicated that there was heterogeneity among the 13 to 19S particles in that possession of poly(C)-dependent RNA polymerase activity was a property of only some. Support for this heterogeneity was derived from the demonstration in this report that there were at least three types of binding sites present within particles in any purified preparation: (i) those binding only poly(C); (ii) those binding only reovirus ss RNAs; and (iii) those binding one or the other, but not both at the same time. It is suggested that only those particles able to bind either poly(C) or reovirus ss RNAs had poly(C)-dependent RNA polymerase activity, as reovirus ss RNAs markedly inhibited the polymerase activity. All three size classes of reovirus ss RNAs were equally effective in binding, but once bound, they were not copied. It is possible that heterogeneity in binding capacity of different particles comprised of only one protein, sigma NS, could result from the ability of subunits containing this protein to assemble into slightly different 13 to 19S particles with specificity of binding or polymerase activity conferred by the configuration of the assembled particles. The high capacity of sigma NS to bind many different nucleic acids with some specificity suggests that these particles may act during infection as condensing agents to bring together 10 reovirus ss RNA templates in preparation for double-stranded RNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Both G. W., Lavi S., Shatkin A. J. Synthesis of all the gene products of the reovirus genome in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouloy M., Plotch S. J., Krug R. M. Both the 7-methyl and the 2'-O-methyl groups in the cap of mRNA strongly influence its ability to act as primer for influenza virus RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. N., Raine C. S., Baum S. G. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus type 3: defects in viral maturation as studied by immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. Virology. 1971 Mar;43(3):569–578. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMATOS P. J., TAMM I., DALES S., FRANKLIN R. M. Reovirus type 3: physical characteristics and interaction with L cells. Virology. 1962 Jul;17:441–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J., Kuechenthal I. Reovirus-specific enzyme(s) associated with subviral particles responds in vitro to polyribocytidylate to yield double-stranded polyribocytidylate-polyriboguanylate. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):80–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.80-90.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J. Reovirus-specific, single-stranded RNA's synthesized in vitro with enzyme purified from reovirus-infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):423–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J., Stamatos N. M., Sarkar N. H. Small reovirus-specific particle with polycytidylate-dependent RNA polymerase activity. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):556–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.556-565.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H., Joklik W. K. Reovirus-coded polypeptides in infected cells: isolation of two native monomeric polypeptides with affinity for single-stranded and double-stranded RNA, respectively. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. I. Patterns of gene expression by mutants of groups C, D, and E. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau R. Y., Van Alstyne D., Berckmans R., Graham A. F. Synthesis of reovirus-specific polypeptides in cells pretreated with cycloheximide. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):470–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.470-478.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Joklik W. K. The nature of the polypeptide encoded by each of the 10 double-stranded RNA segments of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):578–593. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustoe T. A., Ramig R. F., Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. Genetics of reovirus: identification of the ds RNA segments encoding the polypeptides of the mu and sigma size classes. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):594–604. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus. II. Assignment of the double-stranded RNA-negative mutant groups C, D, and E to genome segments. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):531–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Graham A. F. Nonpermissive infection of L cells by an avian reovirus: restricted transcription of the viral genome. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):977–984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.977-984.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



