Abstract
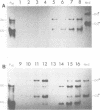
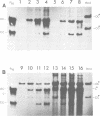
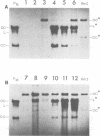
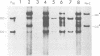
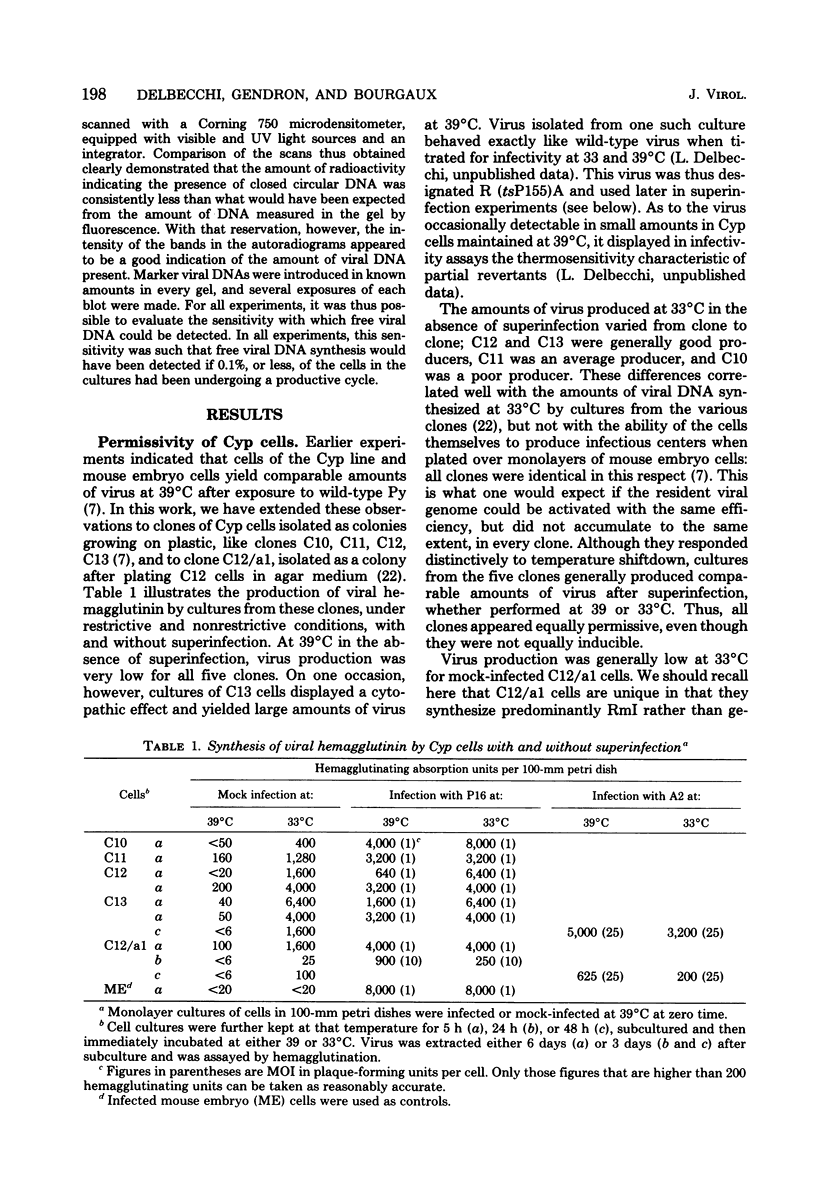
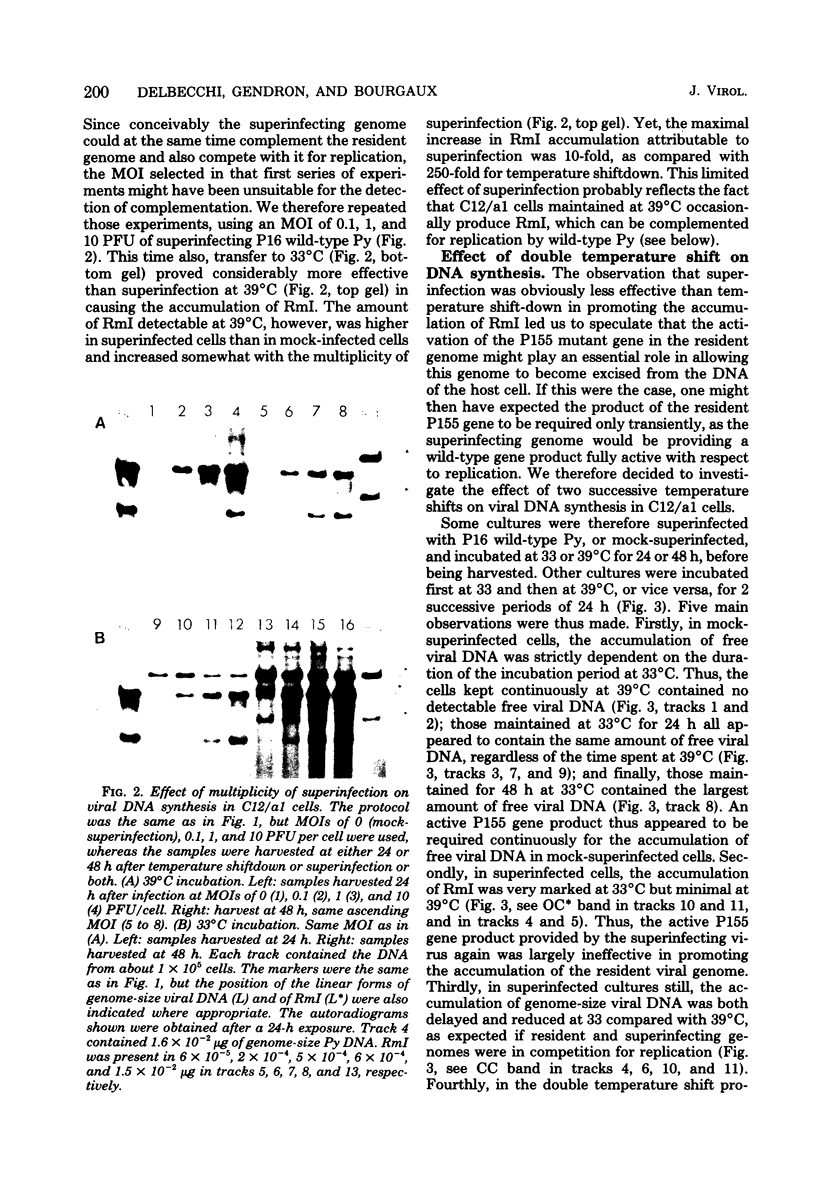
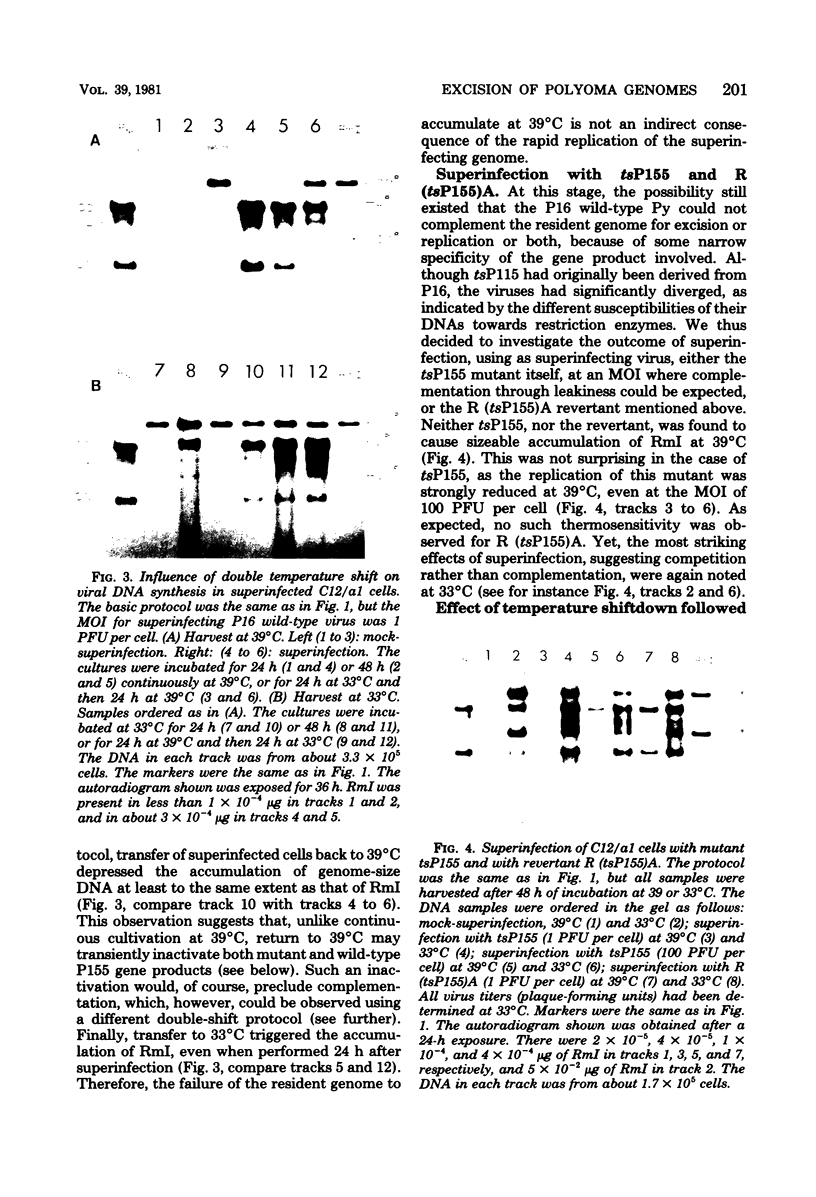
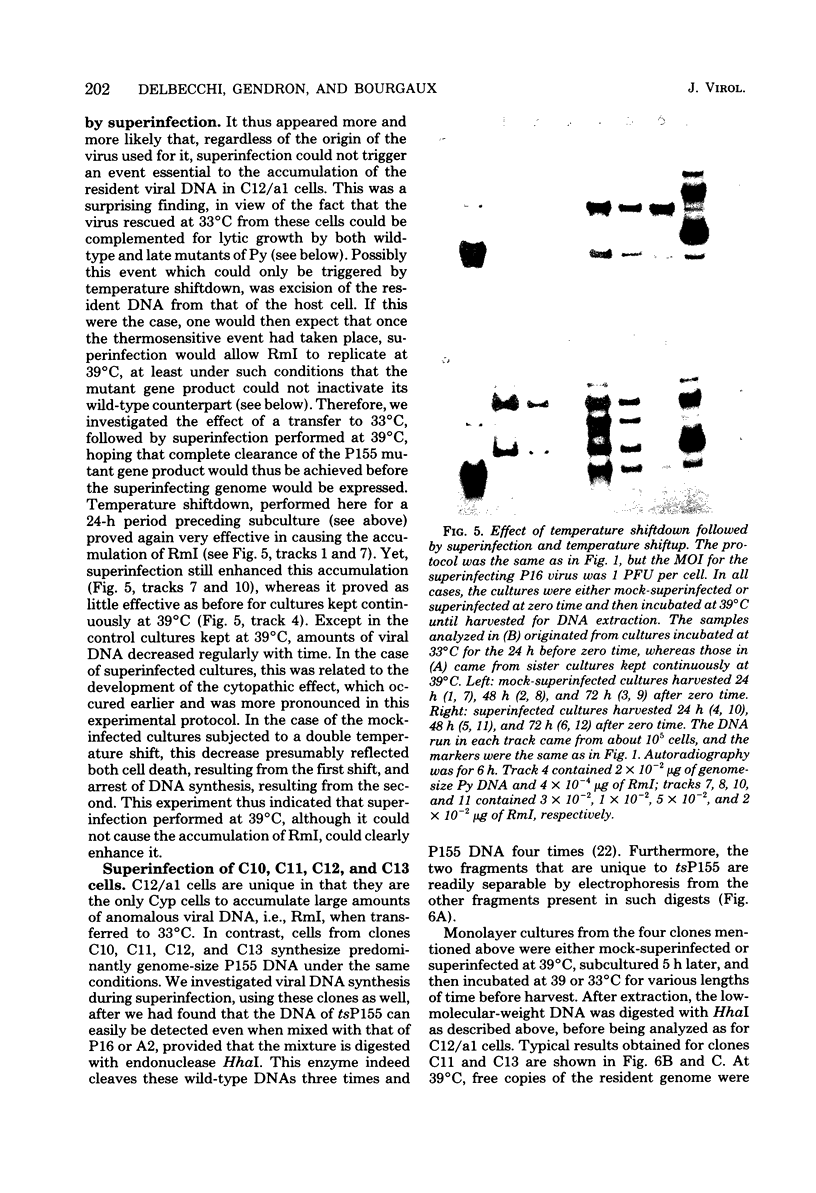
After exposure of mouse embryo cells to the early temperature-sensitive mutant tsP155 of polyoma virus (Py), a transformed cell line (Cyp line) that can be readily induced to synthesize Py by transfer to 33 degrees C was isolated at 39 degrees C (7). Virus production and synthesis of free viral DNA occurring after temperature shiftdown or superinfection with wild-type Py or both were studied in several clonal isolates of the Cyp cell line. Measurements of virus yields indicated that, although some could be induced more effectively than others, all cell clones behaved as highly permissive when subjected to superinfection. We analyzed the origin of free viral DNA accumulating in the superinfected cultures, taking advantage of (i) the unique physical properties of the low-molecular-weight DNA which, in the case of one of the Cyp clones, accumulates during temperature shiftdown, and (ii) the differences between resident and superinfecting viral genomes in their susceptibilities towards restriction endonucleases. At 33 degrees C, both viral genomes were found to accumulate in all clones studied whereas in the case of the clones with lower inducibility, the replication of the resident genome appeared to be enhanced by superinfection. At 39 degrees C, however, accumulation of the superinfecting genome was not accompanied by that of the resident genome, unless it had already been initiated before superinfection. These findings demonstrate that, when routinely cultivated at 39 degrees C, Cyp cells contain few viral DNA molecules readily available for autonomous replication and that, upon transfer to 33 degrees C, therefore, excision must first take place before the resident genome can accumulate as free viral DNA. Our findings also suggest that, unlike the P155 gene product provided by the resident viral genome upon induction, the allelic gene product supplied by the superinfecting genome may be less effective in triggering excision than in promoting replication.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad-Zadeh C., Allet B., Greenblatt J., Weil R. Two forms of simian-virus-40-specific T-antigen in abortive and lytic infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1097–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURGAUX P. THE FATE OF POLYOMA VIRUS IN HAMSTER, MOUSE, AND HUMAN CELLS. Virology. 1964 May;23:46–55. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(64)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basilico C., Gattoni S., Zouzias D., Valle G. D. Loss of integrated viral DNA sequences in polyomatransformed cells is associated with an active viral A function. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):645–659. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastin M., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D., Bourgaux P. Biological properties of polyoma DNA fragments cloned in plasmid pBR322. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):179–184. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Stringer J., Mitchison T., Sambrook J. Integration and excision of SV40 DNA from the chromosome of a transformed cell. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgaux P., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D., Seiler P. The replication of the ring-shaped DNA of polyoma virus. II. Identification of molecules at various stages of replication. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):195–206. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90421-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgaux P., Delbecchi L., Yu K. K., Herring E., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D. A mouse embryo cell line carrying an inducible, temperature-sensitive, polyoma virus genome. Virology. 1978 Jul 15;88(2):348–360. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD L. V. The adsorption of polyoma virus. Virology. 1962 Oct;18:177–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Hager L., Dulbecco R. Simian virus 40 T antigen binds to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3754–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Gusew-Chartrand N., Bourgaux P. Integrated polyoma genomes in inducible permissive transformed cells. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):185–195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.185-195.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W. Complementation and transformation by temperature-sensitive mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):120–125. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W. Properties of temperature-sensitive mutants of polyoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):37–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke B., Eckhart W. Polyoma gene function required for viral DNA synthesis. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Griffin B. E., Lund E., Robberson D. L. Polyoma virus--a study of wild-type, mutant and defective DNAs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):45–52. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Davison J., Oren M., Winocour E. Properties of permissive monkey cells transformed by UV-irradiated simian virus 40. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):256–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.256-266.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Kuff E. L., Winocour E. Recombination between endogenous and exogenous simian virus 40 genes. I. Rescue of a simian virus 40 temperature-sensitive mutant by passage in permissive transformed monkey lines. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):534–540. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.534-540.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler M. P., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. Phenotypic complementation of the SV40 tsA mutant defect in viral DNA synthesis following microinjection of SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):983–994. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90352-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. SV40: T antigen, the A function and transformation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):267–276. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylla B. S., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D., Bourgaux P. Induction of viral DNA synthesis in clonal derivatives of a permissive cell line transformed by a temperature-sensitive polyoma virus. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]