Abstract
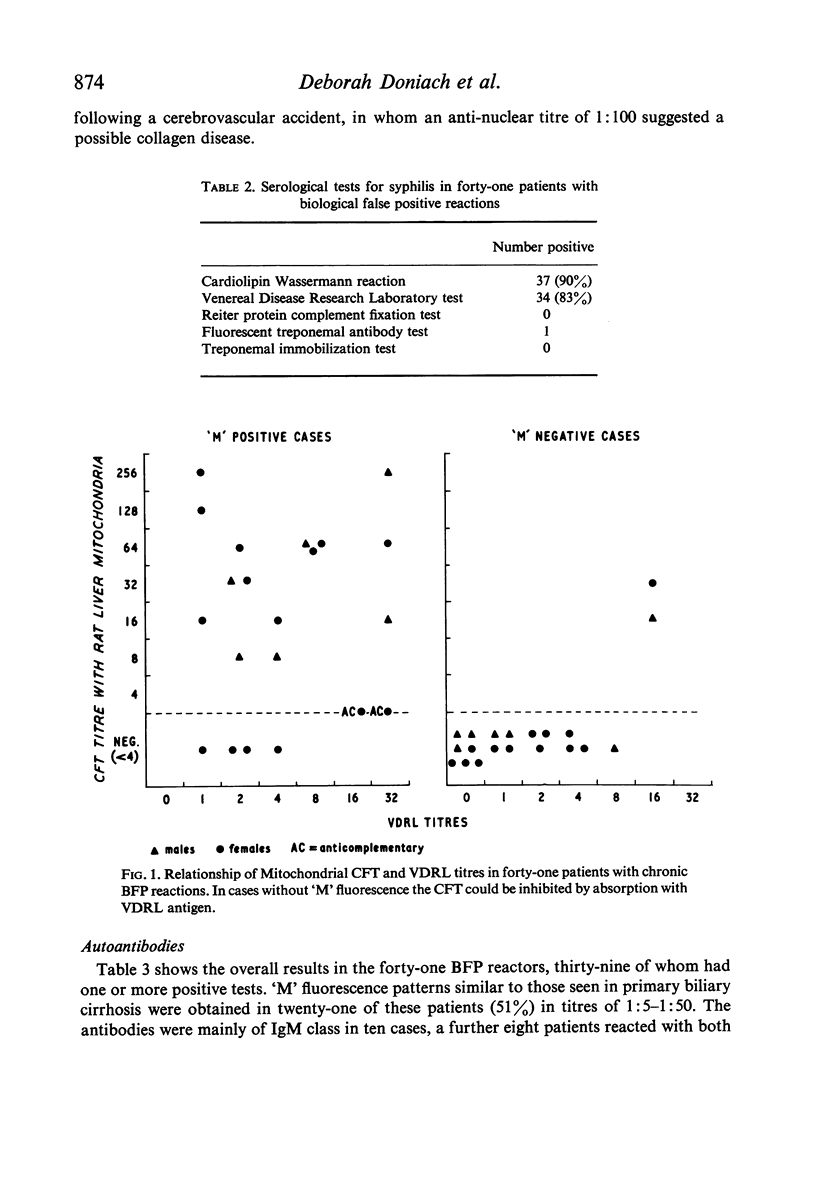
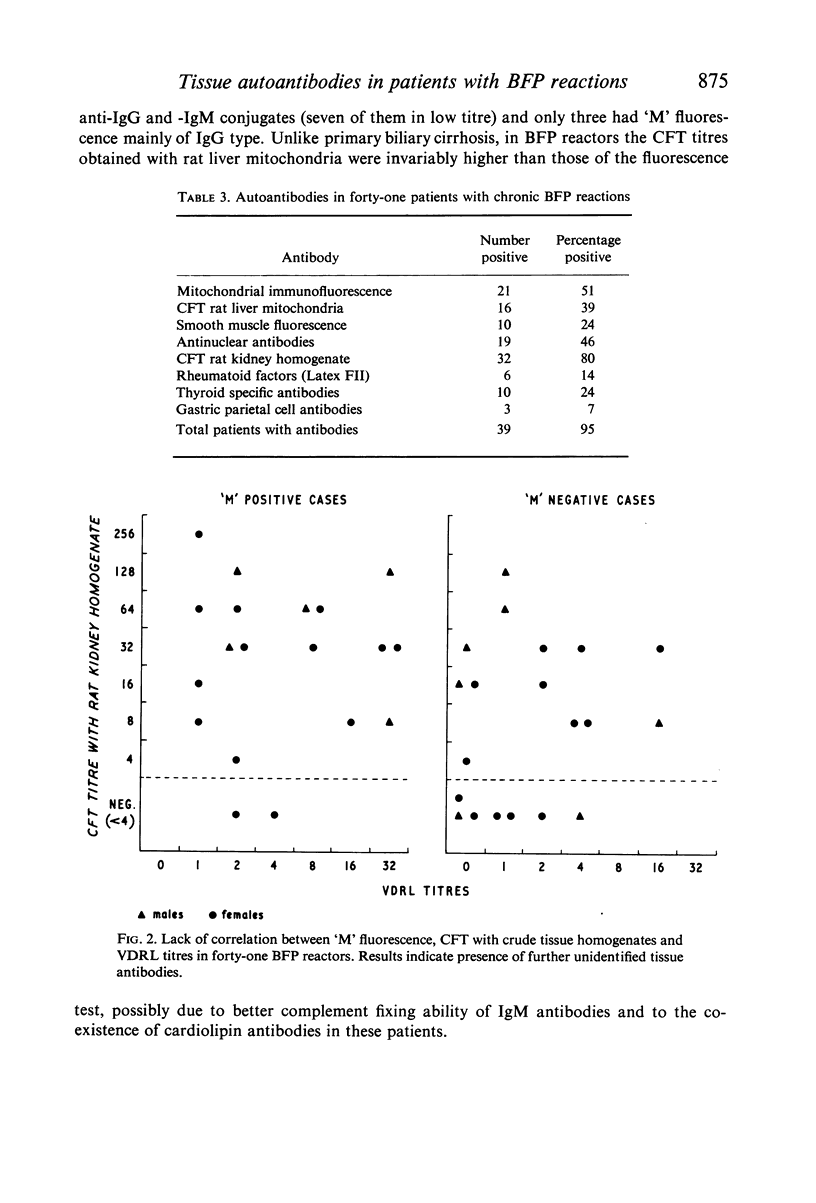
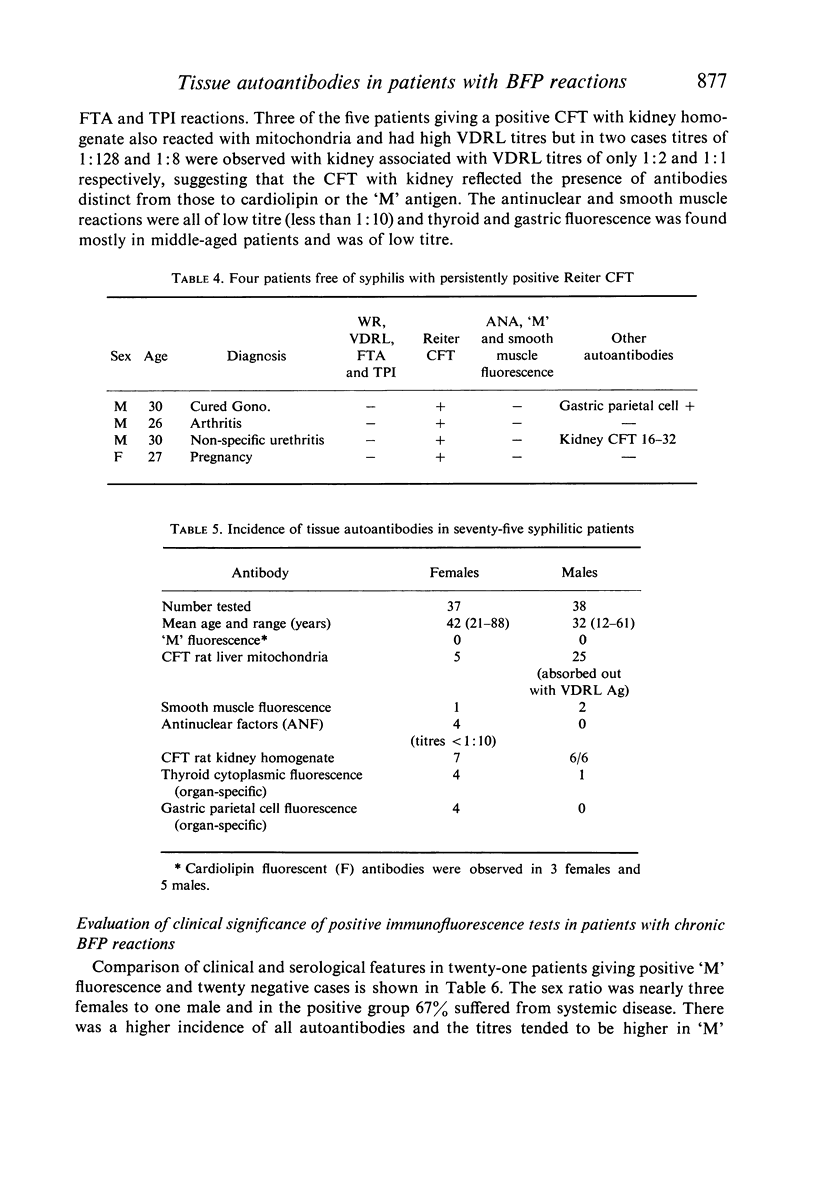
Mitochondrial antibodies (`M' fluorescence) similar to those seen in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis but of low titre and predominantly of IgM class were found in 51% of forty-one patients showing chronic false positive reactions for syphilis, in the absence of detectable liver abnormalities. The pathogenic significance of this association is not understood but the antigen of Wasserman reaction and Venereal Disease Research Laboratory tests, cardiolipin, is situated in close proximity to the distinct lipoprotein reactive in `M' fluorescence, both being components of the mitochondrial inner membranes. Since these two antibodies have a low incidence in the population, it is likely that their association in a highly selected group of patients represents a particular immunological abnormality in the context of the collagenoses. Thus four of the cases presented with unusual neurological features.
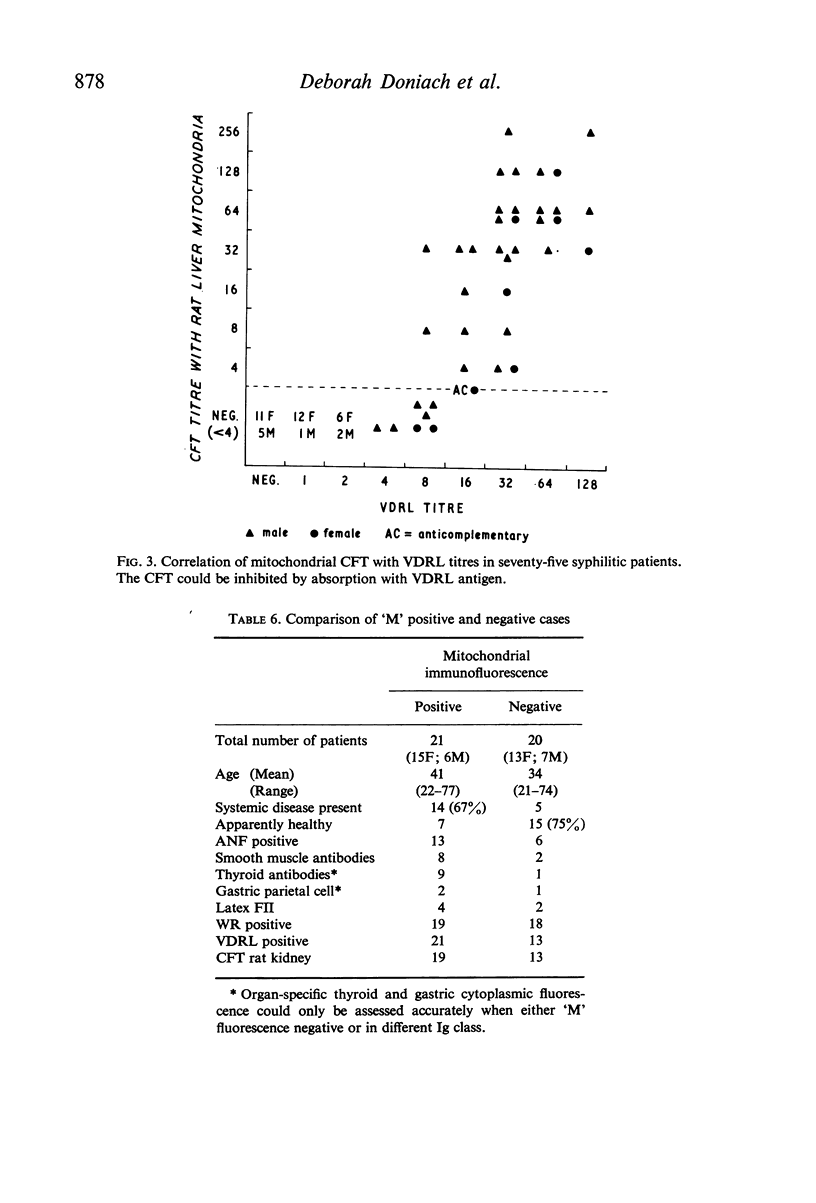
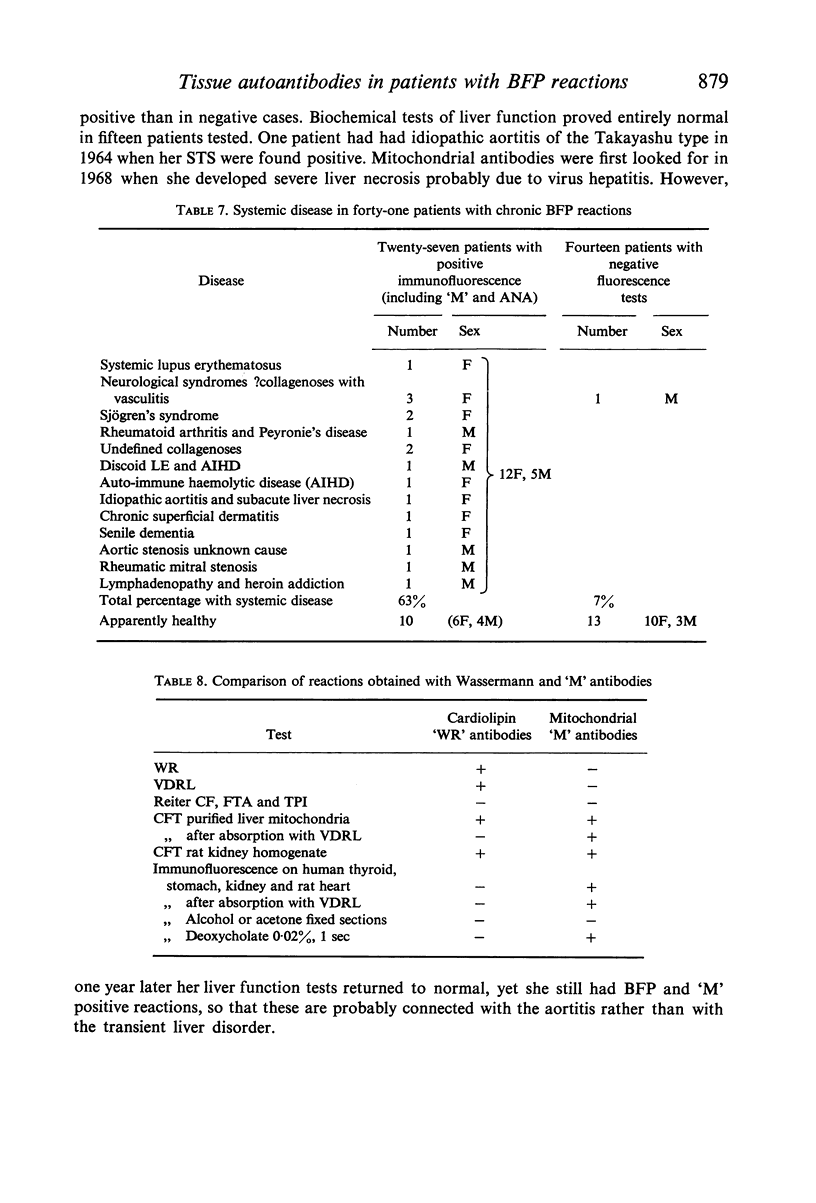
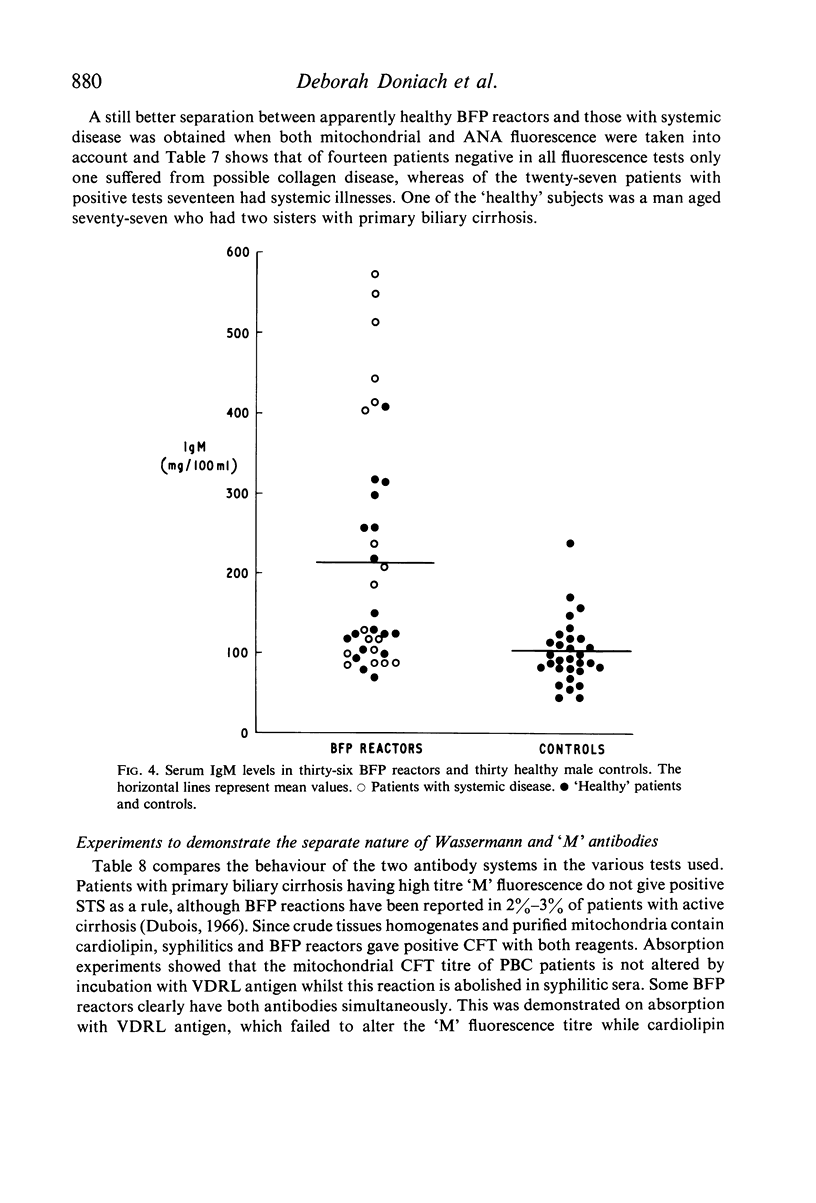
The presence of `M' fluorescence in biological false positive reactors was strongly correlated with systemic disease. This test, together with those for antinuclear and other tissue antibodies may prove of help in differentiating unusual variants of connective tissue disorders and in the follow-up of symptomless patients who are liable to develop these diseases in later life.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K. Studies of syphilitic antibodies. II. Substances responsible for biological false positive sero-reactions. Br J Vener Dis. 1968 Mar;44(1):49–54. doi: 10.1136/sti.44.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg P. A., Roitt I. M., Doniach D., Cooper H. M. Mitochondrial antibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis. IV. Significance of membrane structure for the complement-fixing antigen. Immunology. 1969 Aug;17(2):281–293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglund S., Carlsson M. Clinical significance of chronic biologic false positive Wassermann reaction and "antinuclear factors". Acta Med Scand. 1966 Oct;180(4):407–412. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb02852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATTERALL R. D. Collagen disease and the chronic biological false positive phenomenon. Q J Med. 1961 Jan;30:41–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr R. D., Becker S. W., Carpenter C. M. The biological false-positive phenomenon in elderly men. Arch Dermatol. 1966 Apr;93(4):393–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniach D., Walker J. G. A unified concept of autoimmune hepatitis. Lancet. 1969 Apr 19;1(7599):813–815. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAURE M., COULON-MORELEC [Relations between the chemical structure of cardiolipid and its serologic activity. Preservation of the cardiolipid]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Feb;104:246–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T. Immunoglobulins in chronic liver disease. Gut. 1968 Apr;9(2):193–198. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.2.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey A. M., Shulman L. E. Connective tissue disease and the chronic biologic false-positive test for syphilis (BFP reaction). Med Clin North Am. 1966 Sep;50(5):1271–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE J. E., MOHR C. F. Biologically false positive serologic tests for syphilis; type, incidence, and cause. J Am Med Assoc. 1952 Oct 4;150(5):467–473. doi: 10.1001/jama.1952.03680050033010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustakallio K. K., Lassus A., Putkonen T., Wager O. Cryoglobulins and rheumatoid factor in sera from chronic false positive seroreactors for syphilis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1967;47(4):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strejcek J., Malina L., Bielický T. Antinuclear factors, rheumatoid factors and Bordet-Wassermann reaction in chronic and systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Derm Venereol. 1968;48(3):198–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuffanelli D. L., Wuepper K. D., Bradford L. L., Wood R. M. Fluorescent treponemal-antibody absorption tests. Studies of false-positive reactions to tests for syphilis. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 2;276(5):258–262. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702022760503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER J. G., DONIACH D., ROITT I. M., SHERLOCK S. SEROLOGICAL TESTS IN DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS. Lancet. 1965 Apr 17;1(7390):827–831. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. G., Doniach D., Doniach I. Mitochondrial antibodies and subclinical liver disease. Q J Med. 1970 Jan;39(153):31–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. J., Doniach D., Lessof M. H., Turk J. L., Grimble A. S., Catterall R. D. New antibody in early syphilis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 11;1(7650):740–743. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90972-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


