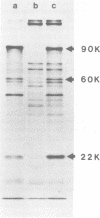
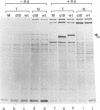
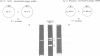
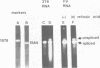
Abstract
The mouse teratocarcinoma stem cell line, F9, becomes permissive for productive polyoma infection upon treatment with retinoic acid. Through the use of M13-polyoma recombinant single-stranded DNA probes, spliced and unspliced early viral RNA were detected after polyoma infection of retinoic acid-treated and untreated F9 cultures.
Full text
PDF
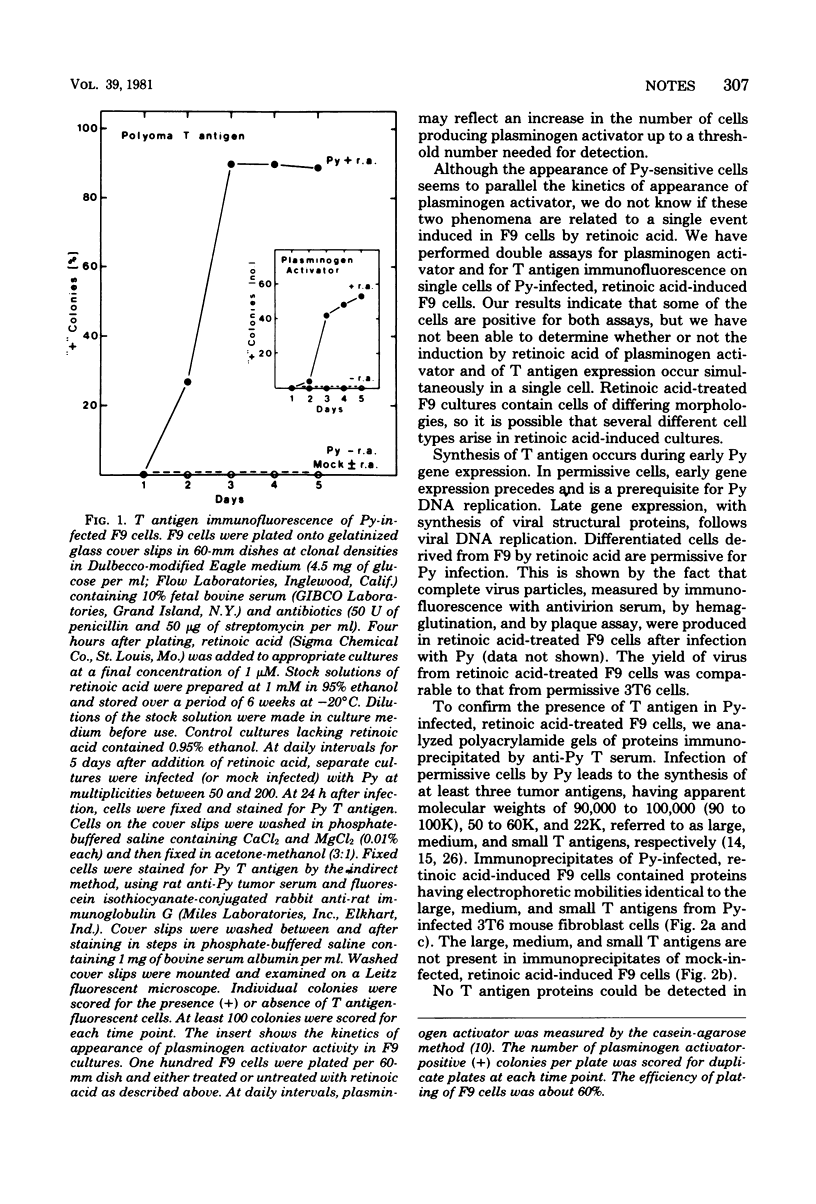

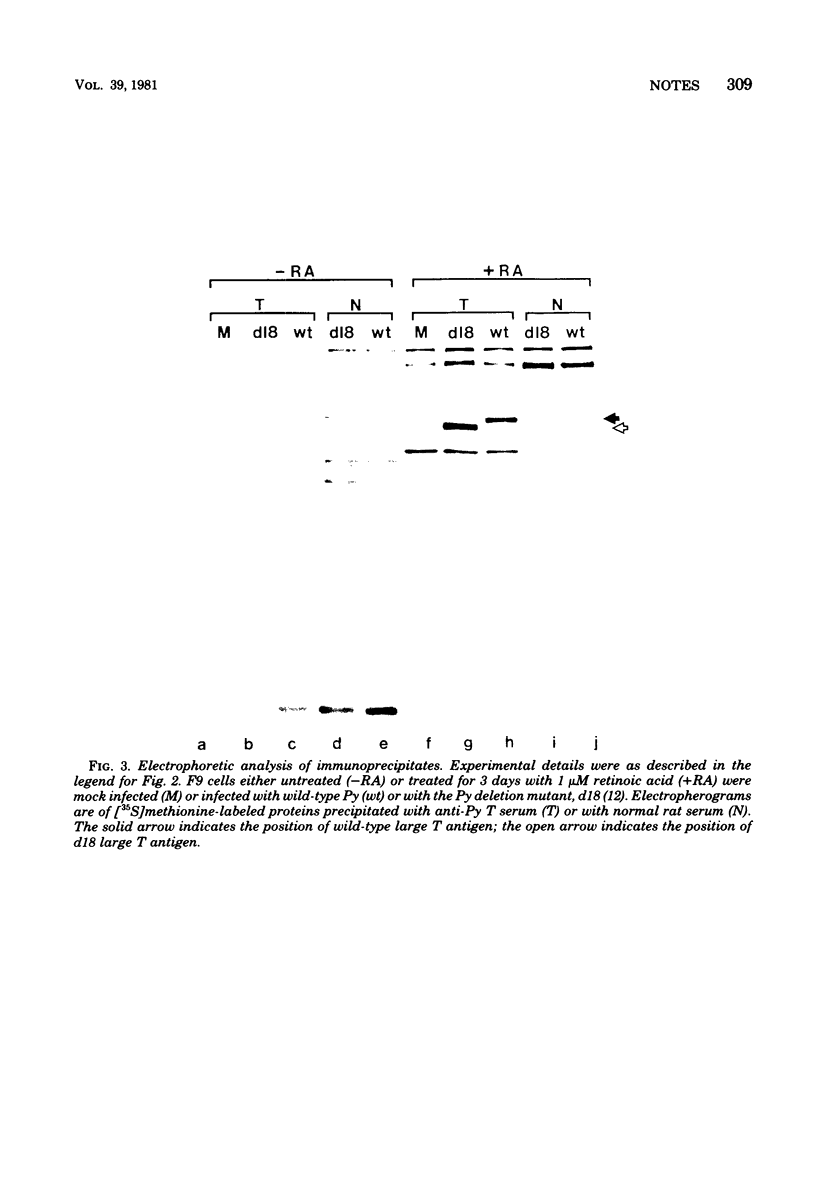
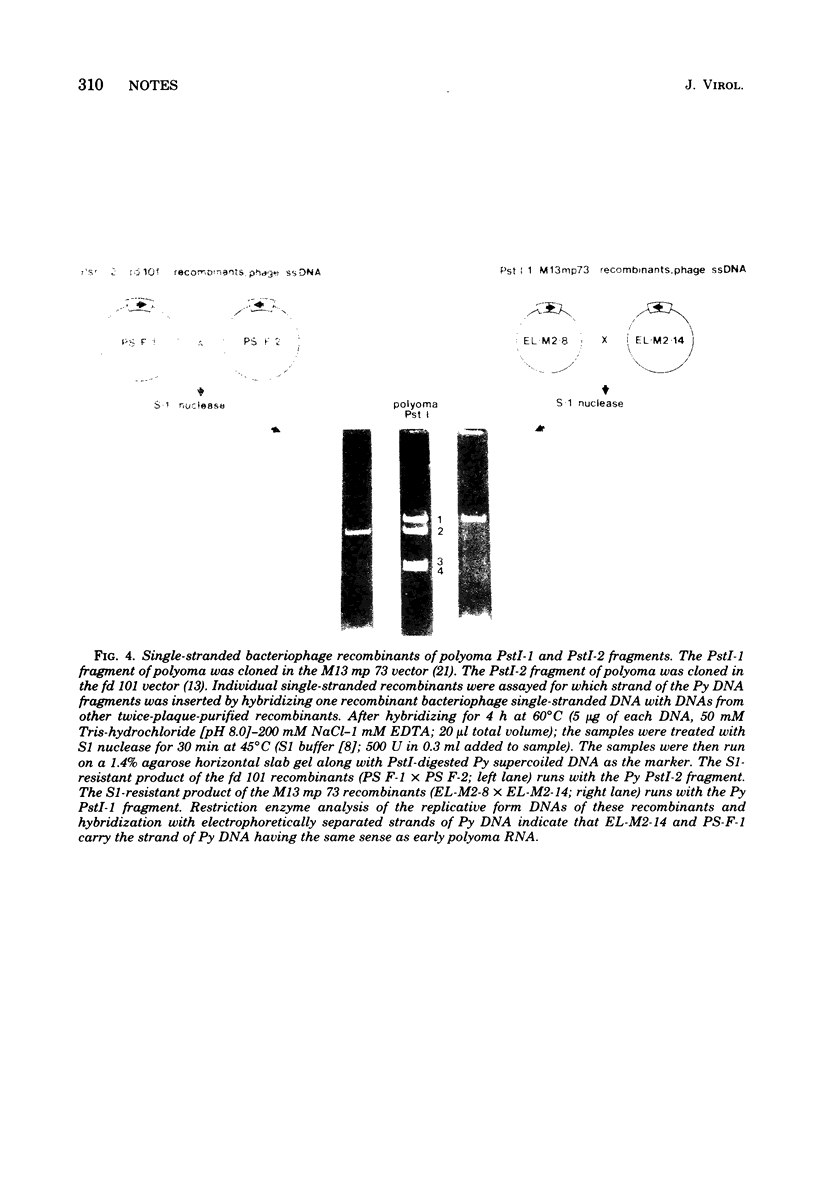


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloni Y., Dhar R., Laub O., Horowitz M., Khoury G. Novel mechanism for RNA maturation: the leader sequences of simian virus 40 mRNA are not transcribed adjacent to the coding sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstine E. G., Hooper M. L., Grandchamp S., Ephrussi B. Alkaline phosphatase activity in mouse teratoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3899–3903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogen B. Virus-specific early RNA in 3T6 cells infected by a tsA mutant of polyoma virus. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90426-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Cole C. N., Smith A. E., Paucha E., Tegtmeyer P., Rundell K., Berg P. Organization and expression of early genes of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):117–121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deninger P. L., Esty A., LaPorte P., Hsu H., Friedmann T. The nucleotide sequence and restriction enzyme sites of the polyoma genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 25;8(4):855–860. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T., Esty A., LaPorte P., Deininger P. The nucleotide sequence and genome organization of the polyoma early region: extensive nucleotide and amino acid homology with SV40. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R. Increased protease levels in transformed cells: a casein overlay assay for the detection of plasminogen activator production. Cell. 1974 Jun;2(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Maddock C. New classes of viable deletion mutants in the early region of polyoma virus. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):645–656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.645-656.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann R., Neugebauer K., Pirkl E., Zentgraf H., Schaller H. Conversion of bacteriophage fd into an efficient single-stranded DNA vector system. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):231–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00267434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M. A., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Characterization of T antigens in polyoma-infected and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Brocklehurst J. R., Dulbecco R. Virus-specific proteins in the plasma membrane of cells lytically infected or transformed by pol-oma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4666–4670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Spurr N., Griffin B. E. Middle T antigen as primary inducer of full expression of the phenotype of transformation by polyoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):219–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.219-232.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Favaloro J., Parker J., Treisman R., Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Legon S. Structure of polyoma virus mRNAs synthesized in productively infected mouse cells. Differentiation. 1979;13(1):45–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S., Groner Y. 5'-Terminal sequences and coding region of late simian virus 40 mRNAs are derived from noncontiguous segments of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5323–5327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Levinson B. B. Teratocarcinoma differentiation: plasminogen activator activity associated with embryoid body formation. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Teratocarcinomas as a model system for the study of embryogenesis and neoplasia. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Ward D. C., Ruddle F. H. Embryonal carcinoma cells (and their somatic cell hybrids) are resistant to infection by the murine parvovirus MVM, which does infect other teratocarcinoma-derived cell lines. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):393–401. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R., Linney E. Identification of murine extra-embryonic endodermal cells by reaction with teratocarcinoma basement membrane antiserum. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Apr;126(2):485–490. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90294-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. B. Teratocarcinoma: model for a developmental concept of cancer. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1967;2:223–246. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Silver J. E., Benjamin T. L. Tumor antigen(s) in cell productively infected by wild-type polyoma virus and mutant NG-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal S., Khoury G. Differentiation as a requirement for simian virus 40 gene expression in F-9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5611–5615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal S., Levine A. J., Khoury G. Evidence for non-spliced SV40 RNA in undifferentiated murine teratocarcinoma stem cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):335–338. doi: 10.1038/280335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. I., Strickland S., Reich E. Differentiation of early mouse embryonic and teratocarcinoma cells in vitro: plasminogen activator production. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4208–4216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Griffin B. E. Sequence from early region of polyoma virus DNA containing viral replication origin and encoding small, middle and (part of) large T antigens. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):357–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens L. C. The biology of teratomas. Adv Morphog. 1967;6:1–31. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9953-5.50005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Reich E., Sherman M. I. Plasminogen activator in early embryogenesis: enzyme production by trophoblast and parietal endoderm. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzendruber D. E., Friedrich T. D., Lehman J. M. Resistance of teratocarcinoma stem cells to infection with simian virus 40: early events. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Oct;93(1):25–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040930105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzendruber D. E., Lehman J. M. Neoplastic differentiation: interaction of simian virus 40 and polyoma virus with murine teratocarcinoma cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Apr;85(2 Pt 1):179–187. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teich N. M., Weiss R. A., Martin G. R., Lowy D. R. Virus infection of murine teratocarcinoma stem cell lines. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W., Hall J. D., Rifkin D., Levine A. J., Pollack R. The characterization of SV40-transformed cell lines derived from mouse teratocarcinoma: growth properties and differentiated characteristics. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Nov;93(2):269–276. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040930212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]