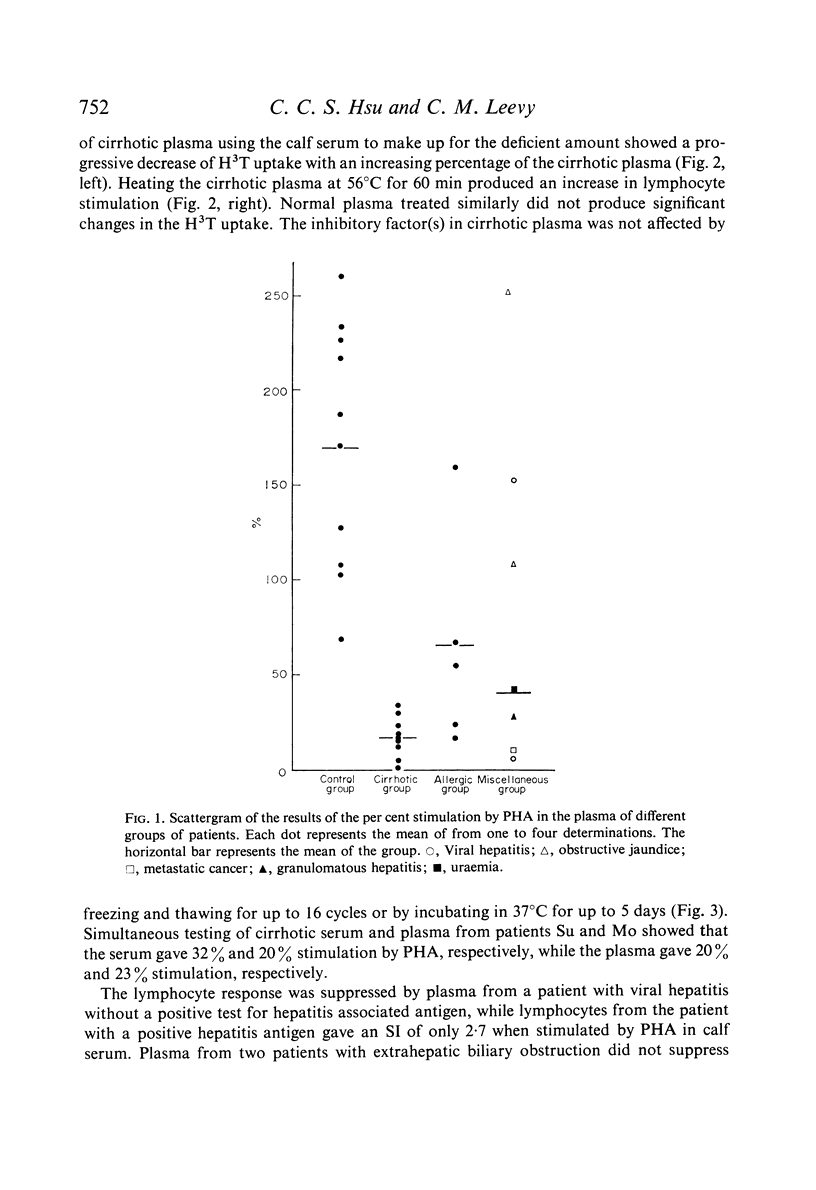
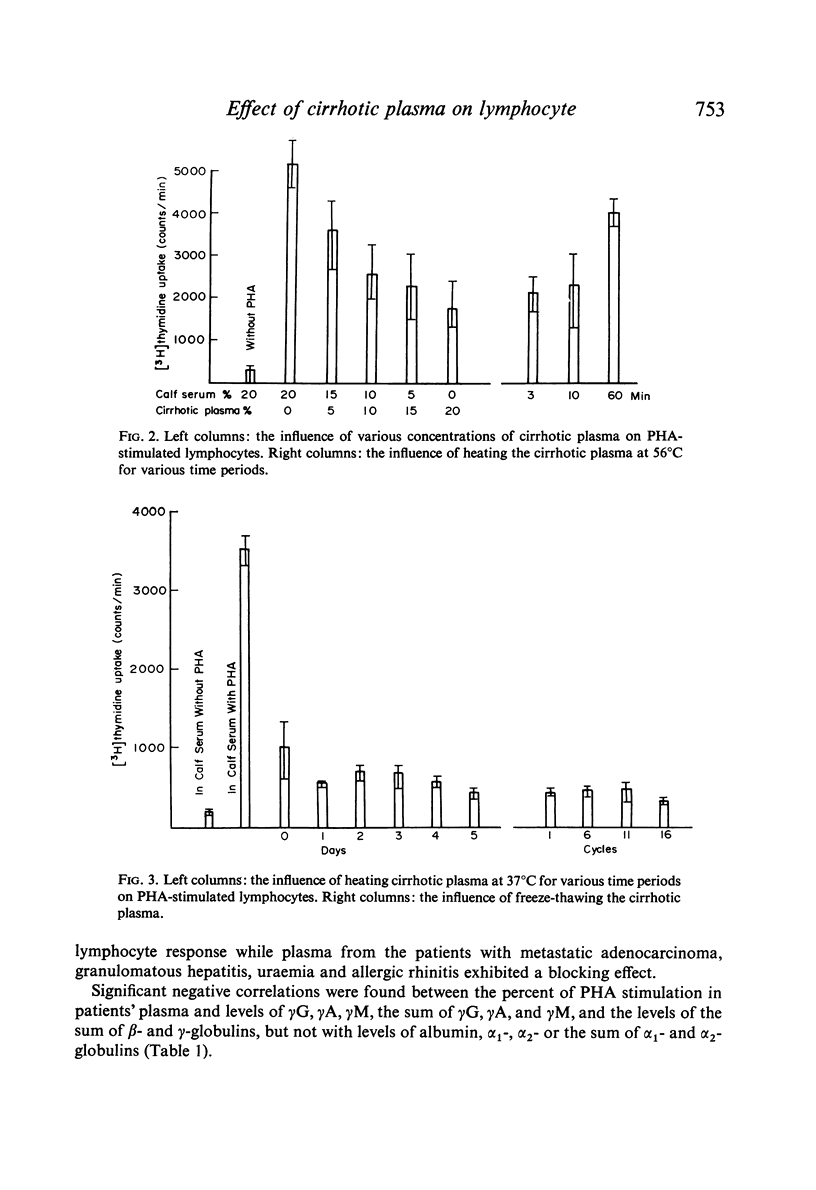
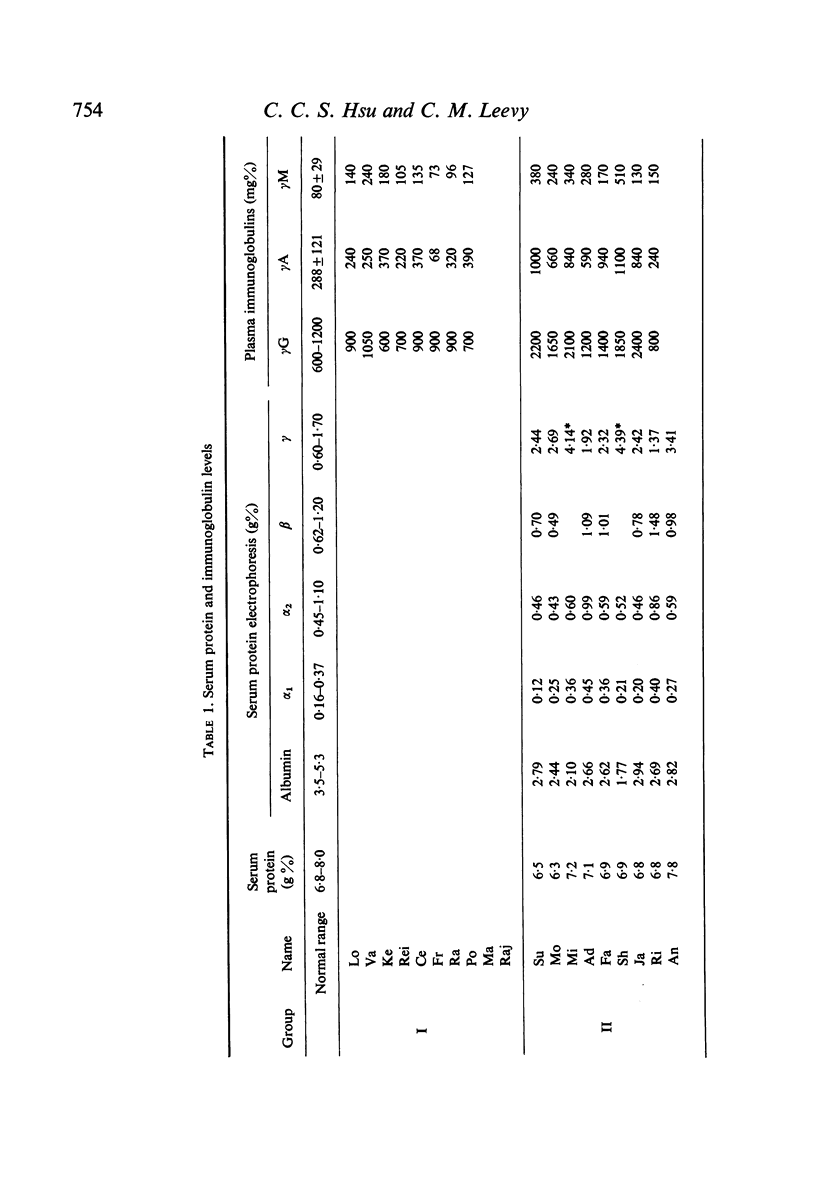
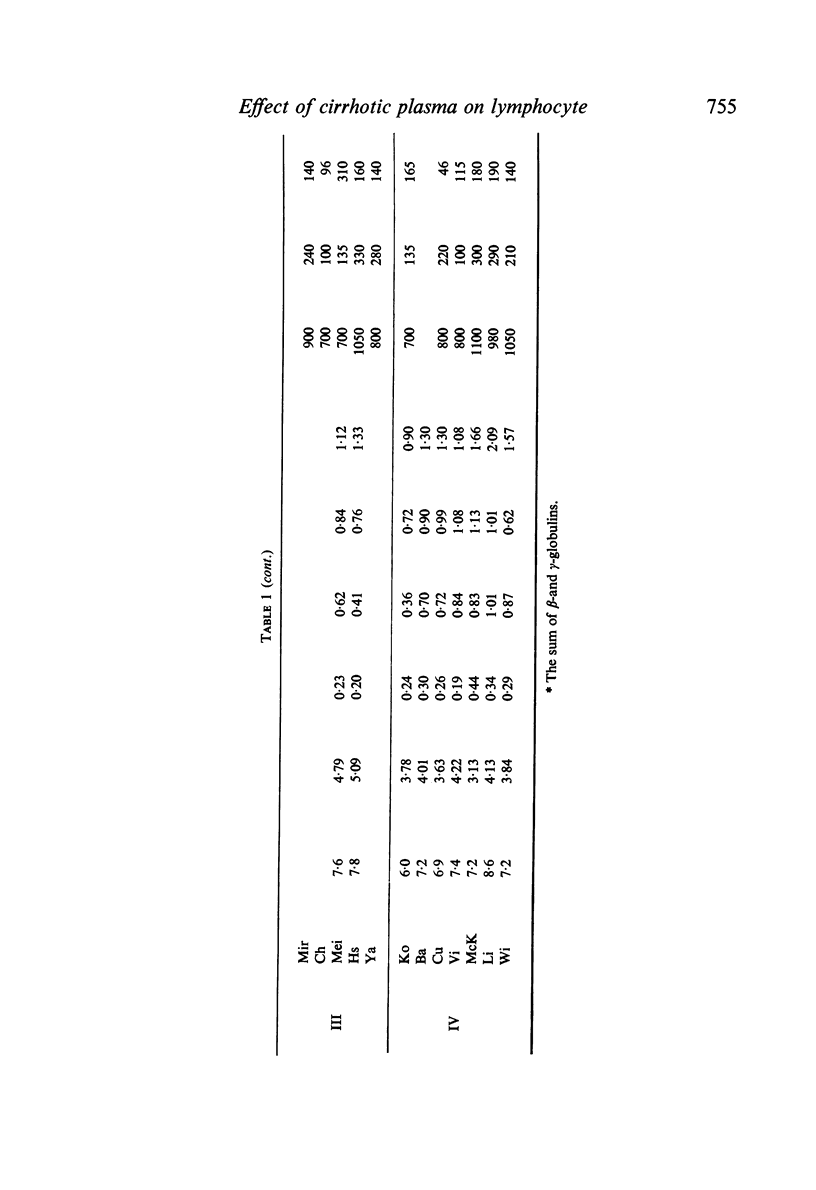
Abstract
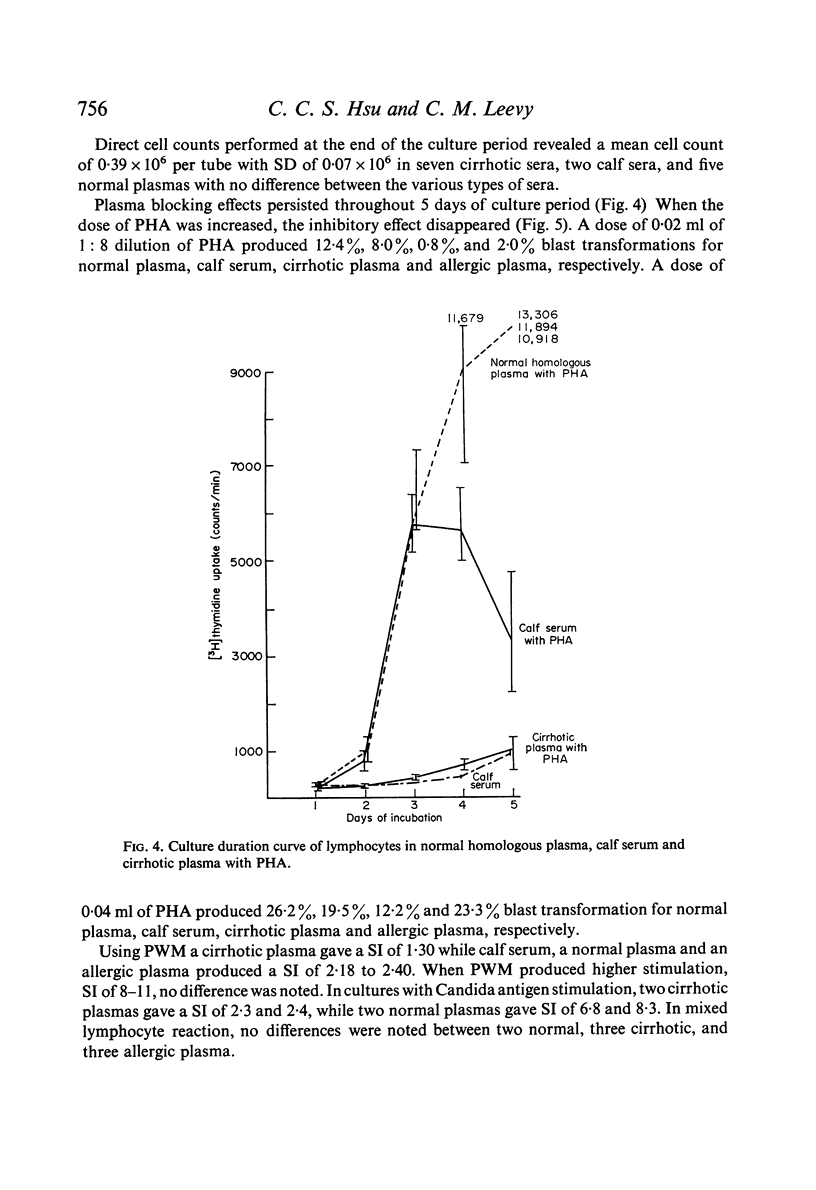
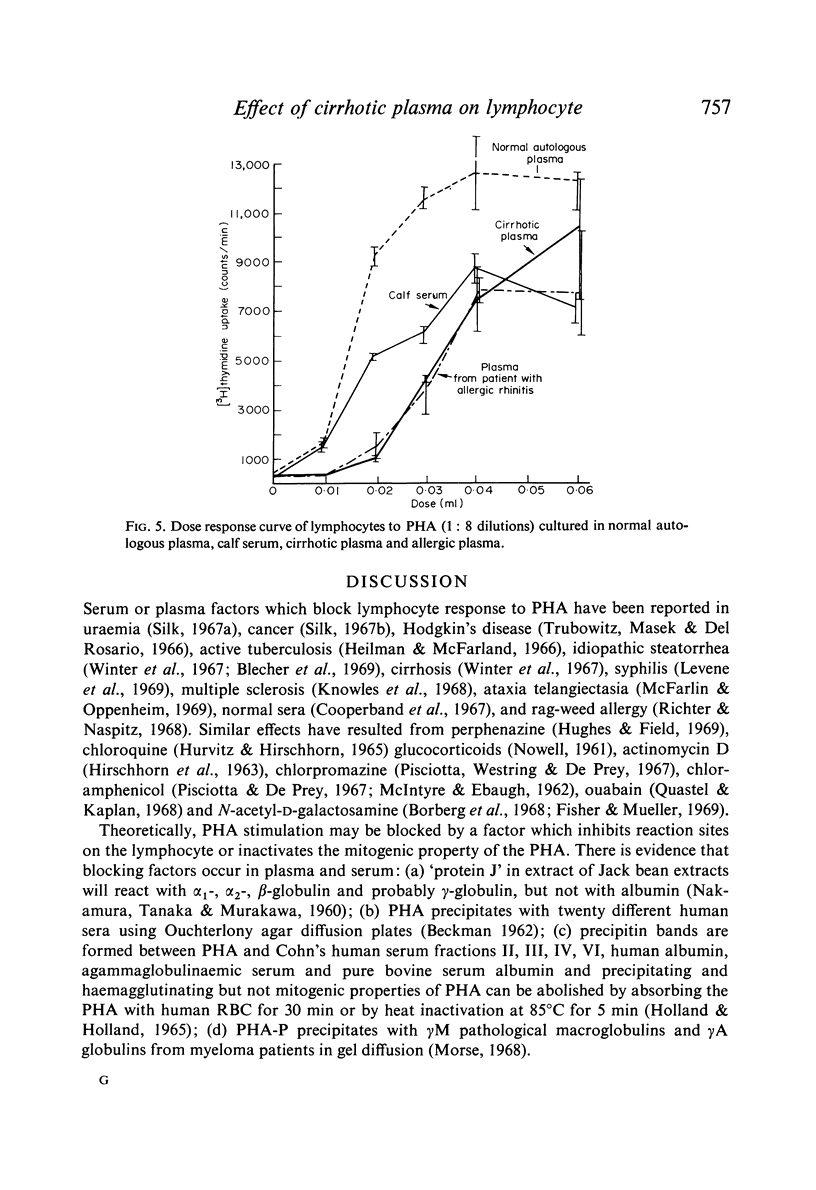
Studies of lymphocyte transformation in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver indicate lymphocytes of such patients respond normally to PHA stimulation; however, their plasma or serum contains factors which block expected response to PHA. This effect was diminished by heating at 56°C for 60 minutes but was not affected by freezing and thawing. It could be overcome by increasing the dose of PHA. Blocking was also encountered in the response to pokeweed mitogen and Candida antigen stimulation but was not seen in the mixed lymphocyte reaction. Indentical results were obtained with plasma from patients with allergic rhinitis, uraemia, carcinomatosis, and granulomatous hepatitis. The magnitude of blocking effects in all of these conditions was negatively correlated with the serum γ-globulin levels.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKMAN L. Effect of phytohaemagglutinin on human serum and cell proteins. Nature. 1962 Aug 11;195:582–583. doi: 10.1038/195582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blecher T. E., Brzechwa-Ajdukiewicz A., McCarthy C. F., Read A. E. Serum immunoglobulins and lymphocyte transformation studies in coeliac disease. Gut. 1969 Jan;10(1):57–62. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borberg H., Yesner I., Gesner B., Silber R. The effect of N acetyl C-galactosamine and other sugars on the mitogenic activity and attachment of PHA to tonsil cells. Blood. 1968 Jun;31(6):747–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperband S. R., Bondevik H., Schmid K., Mannick J. A. Transformation of human lymphocytes: inhibition by homologous alpha globulin. Science. 1968 Mar 15;159(3820):1243–1244. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3820.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperband S. R., Green J. A., Kennedy M. A., Grant M. M. Dissociation and inhibition of the stimulatory effect of phytohaemagglutinin on protein and DNA synthesis in human lymphocyte cultures. Nature. 1967 Jun 17;214(5094):1240–1241. doi: 10.1038/2141240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. B., Mueller G. C. N-acetyl-D-galactosamine inhibits the early phospholipid response by lymphocytes to phytohaemagglutinin. Nature. 1969 Feb 8;221(5180):566–567. doi: 10.1038/221566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsdyke D. R. Quantitiative nucleic acid changes during phytohaemagglutinin-induced lymphocyte transformation in vitro. Dependence of the response on phytohaemagglutinin-serum rati. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):679–684. doi: 10.1042/bj1050679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHHORN K., BACH F., KOLODNY R. L., FIRSCHEIN I. L., HASHEM N. IMMUNE RESPONSE AND MITOSIS OF HUMAN PERIPHERAL BLOOD LYMPHOCYTES IN VITRO. Science. 1963 Nov 29;142(3596):1185–1187. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3596.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHHORN K., SCHREIBMAN R. R., BACH F. H., SILTZBACH L. E. IN-VITRO STUDIES OF LYMPHOCYTES FROM PATIENTS WITH SARCOIDOSIS AND LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASES. Lancet. 1964 Oct 17;2(7364):842–843. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90691-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURVITZ D., HIRSCHHORN K. SUPPRESSION OF IN VITRO LYMPHOCYTE RESPONSES BY CHLOROQUINE. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jul 1;273:23–26. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196507012730105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman D. H., McFarland W. Inhibition of tuberculin-induced mitogenesis in cultures of lymphocytes from tuberculous donors. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;30(1):58–66. doi: 10.1159/000229793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh E. M., Oppenheim J. J. Impaired in vitro lymphocyte transformation in Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1965 Nov 4;273(19):1006–1012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196511042731903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland N. H., Holland P. Haemagglutinating, precipitating and lymphocyte-stimulating factors of phytohaemagglutinin. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1307–1308. doi: 10.1038/2071307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M., Hughes D., Caspary E. A., Field E. J. Lymphocyte transformation in multiple sclerosis. Inhibition of unstimulated thymidine uptake by a serum factor. Lancet. 1968 Dec 7;2(7580):1207–1209. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer R., Say B., Brown D., Rosen F. S. Congenital aplasia of the thymus gland (DiGeorge's syndrome). N Engl J Med. 1968 Dec 12;279(24):1295–1301. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196812122792401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene G. M., Turk J. L., Wright D. J., Grimble A. G. Reduced lymphocyte transformation due to a plasma factor in patients with active syphilis. Lancet. 1969 Aug 2;2(7614):246–247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal B. G., Waldorf D. S., Talal N. Impaired Lymphocyte Transformation and Delayed Hypersensitivity in Sjögren's Syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1338–1345. doi: 10.1172/JCI105626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlin D. E., Oppenheim J. J. Impaired lymphocyte transformation in ataxia-telangiectasia in part due to a plasma inhibitory factor. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1212–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse J. H. Immunological studies of phytohaemagglutinin. I. Reaction between phytohaemagglutinin and normal sera. Immunology. 1968 May;14(5):713–724. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAMURA S., TANAKA K., MURAKAWA S. Specific protein of legumes which reacts with animal proteins. Nature. 1960 Oct 8;188:144–145. doi: 10.1038/188144b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOWELL P. C. Inhibition of human leukocyte mitosis by prednisolone in vitro. Cancer Res. 1961 Dec;21:1518–1521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naspitz C. K., Eisen A. H., Richter M. DN synthesis in vitro in leukocytes from patients with ataxia telangiectasia. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;33(3):217–226. doi: 10.1159/000230041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisciotta A. V., DePrey C. Inhibition of mitosis by chloramphenicol in phytohemagglutinin stimulated lymphocytes. Blood. 1967 Oct;30(4):457–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisciotta A. V., Westring D. W., DePrey C. Studies on agranulocytosis. 8. Inhibition of mitosis in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocytes by chlorpromazine. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Aug;70(2):229–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quastel M. R., Kaplan J. G. Inhibition by ouabain of human lymphocyte transformation induced by phytohaemagglutinin in vitro. Nature. 1968 Jul 13;219(5150):198–200. doi: 10.1038/219198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter M., Naspitz C. K. The in vitro blastogenic response of lymphocytes of ragweed-sensitive individuals. J Allergy. 1968 Mar;41(3):140–151. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(68)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rössler R., Havemann K., Dölle W. Unterschiedliche Reaktion von Lymphocyten auf Phythämagglutinin (PHA) bei Lebererkrankungen. Klin Wochenschr. 1969 Aug 1;47(15):803–806. doi: 10.1007/BF01882306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S., Fox R. A., James D. G., Scheuer P. J., Sharma O. Impaired delayed hypersensitivity in primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet. 1969 May 10;1(7602):959–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91860-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk M. R. The effect of uremic plasma on lymphocyte transformation. Invest Urol. 1967 Sep;5(2):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk M. Effect of plasma from patients with carcinoma on in vitro lymphocyte transformation. Cancer. 1967 Dec;20(12):2088–2089. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196712)20:12<2088::aid-cncr2820201205>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M. J., Fowler R., Fitzgerald M. G. Mechanism of lymphocyte transformation induced by phytohaemagglutinin. Nature. 1968 Sep 7;219(5158):1021–1025. doi: 10.1038/2191021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias H., Safran A. P., Schaffner F. Lymphocyte stimulation and chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1967 Jan 28;1(7483):193–195. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91830-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trubowitz S., Masek B., Del Rosario A. Lymphocyte response to phytohemagglutinin in Hodgkin's disease, lymphatic leukemia and lymphosarcoma. Cancer. 1966 Dec;19(12):2019–2023. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196612)19:12<2019::aid-cncr2820191228>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems F. T., Melnick J. L., Rawls W. E. Viral inhibition of the phytohemagglutinin response of human lymphocytes and application to viral hepatitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Feb;130(2):652–661. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. D., Onstad G., Williams R. C., Jr Serum immunoglobulin concentrations in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jul;57(1):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G. C., McCarthy C. F., Read A. E., Yoffey J. M. Development of macrophages in phytohaemagglutinin cultures of blood from patients with idiopathic steatorrhoea and with cirrhosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Feb;48(1):66–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


