Abstract
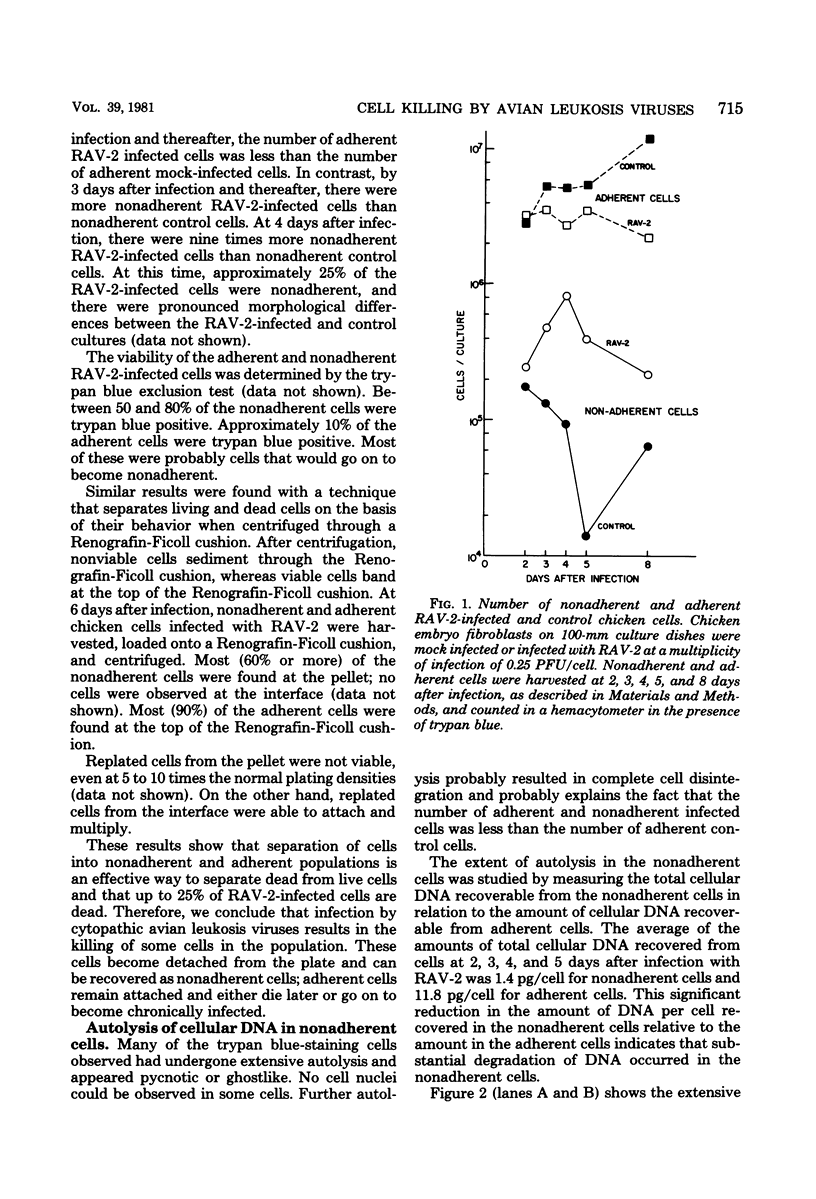
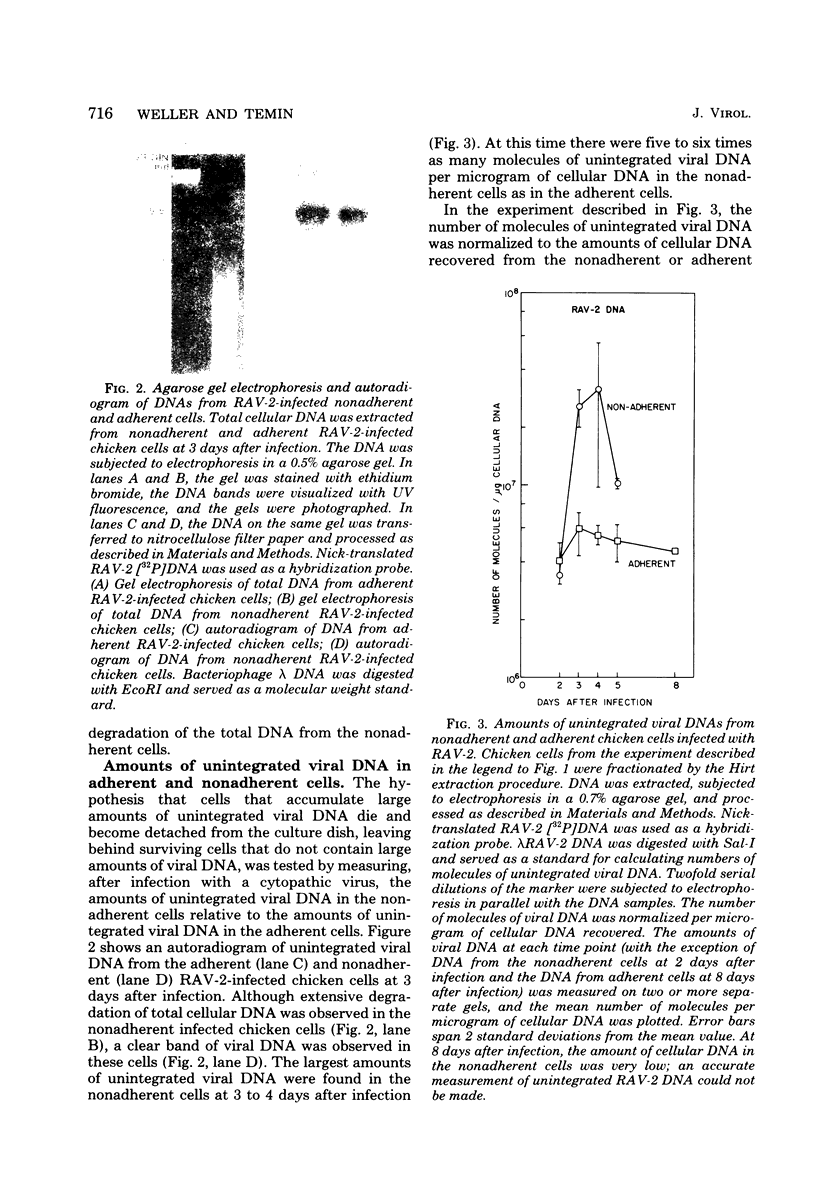
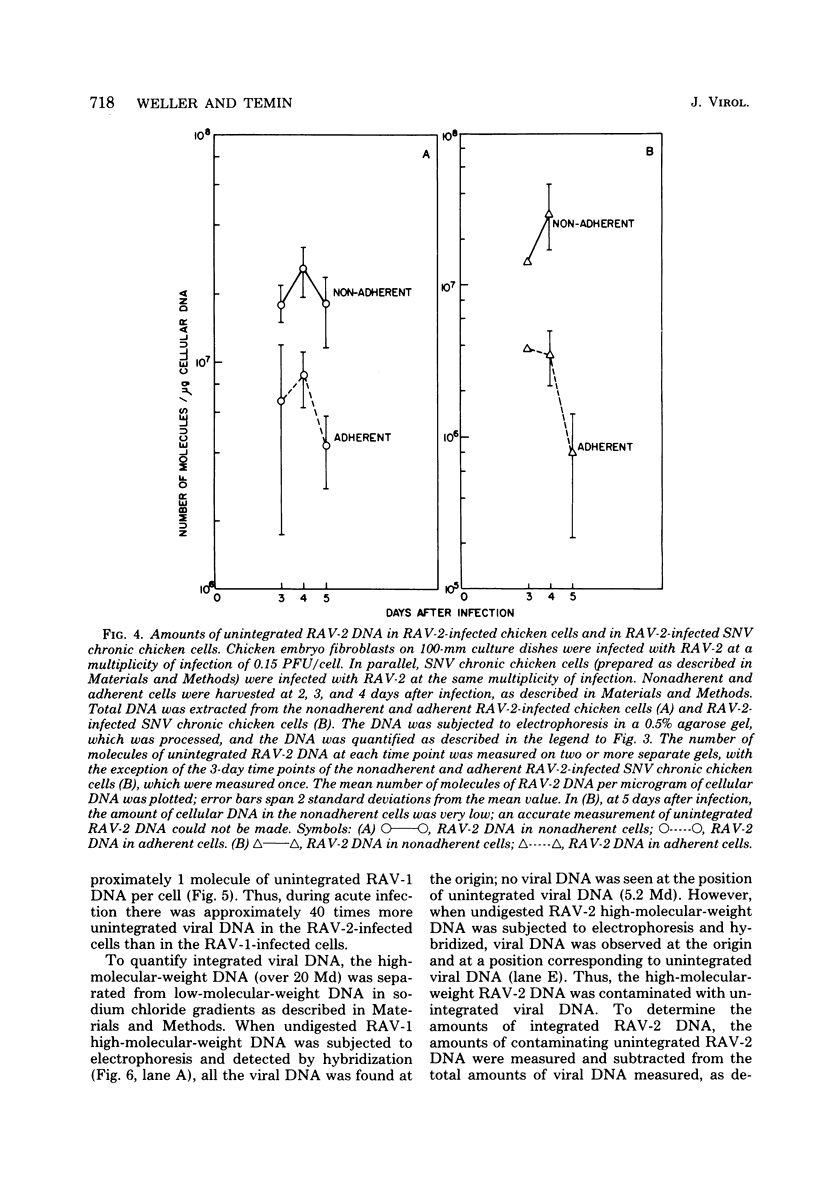
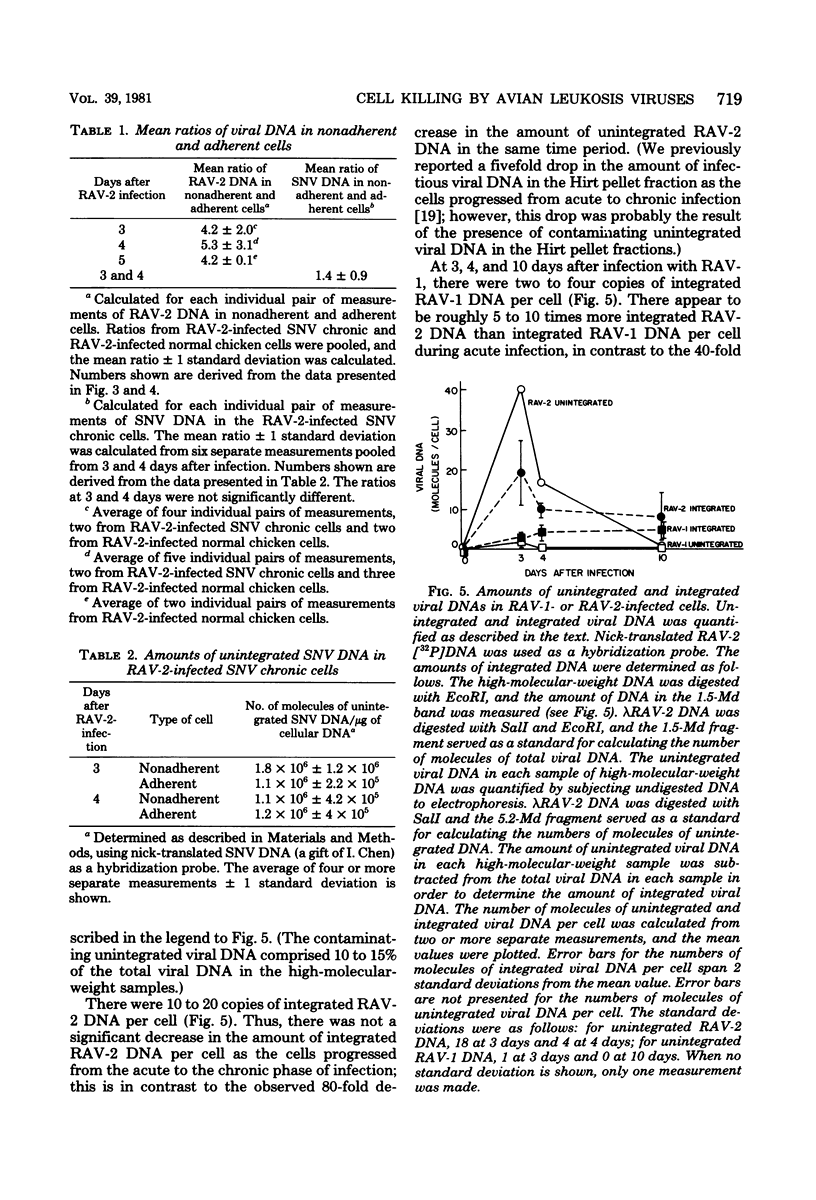
Infection of chicken cells with a cytopathic avian leukosis virus resulted in the detachment of killed cells from the culture dish. The detached, dead cells contained more unintegrated viral DNA than the attached cells. These results confirm the hypothesis that cell killing after infection with a cytopathic avian leukosis virus is associated with accumulation of large amounts of unintegrated viral DNA. No accumulation of large amounts of integrated viral DNA was found in cells infected with cytopathic avian leukosis viruses.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battula N., Temin H. M. Sites of integration of infectious DNA of avian reticuloendotheliosis viruses in different avian cellular DNAs. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T. A plaque assay for avian RNA tumor viruses. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju G., Boone L., Skalka A. M. Isolation and characterization of recombinant DNA clones of avian retroviruses: size heterogeneity and instability of the direct repeat. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1026–1033. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1026-1033.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. Plaque assay for some strains of avian leukosis virus. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):126–135. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., Temin H. M. Cell killing by spleen necrosis virus is correlated with a transient accumulation of spleen necrosis virus DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):376–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.376-388.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Chi D., Gazzolo L., Moscovici M. G. A study of plaque formation with avian RNA tumor viruses. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rear J. J., Mizutani S., Hoffman G., Fiandt M., Temin H. M. Infectious and noninfectious recombinant clones of the provirus of SNV differ in cellular DNA and are apparently the same in viral DNA. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):423–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90628-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Kassner V. K. Avian leukosis viruses of different subgroups and types isolated after passage of Rous sarcoma virus-Rous-associated virus-0 in cells from different ring-necked pheasant embryos. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):302–312. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.302-312.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Kassner V. K. Replication of reticuloendotheliosis viruses in cell culture: acute infection. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):291–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.291-297.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Keshet E., Weller S. K. Correlation of transient accumulation of linear unintegrated viral DNA and transient cell killing by avian leukosis and reticuloendotheliosis viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):773–778. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Studies on carcinogenesis by avian sarcoma viruses. 8. Glycolysis and cell multiplication. Int J Cancer. 1968 Mar 15;3(2):273–282. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Joy A. E., Temin H. M. Correlation between cell killing and massive second-round superinfection by members of some subgroups of avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):494–506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.494-506.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]