Abstract
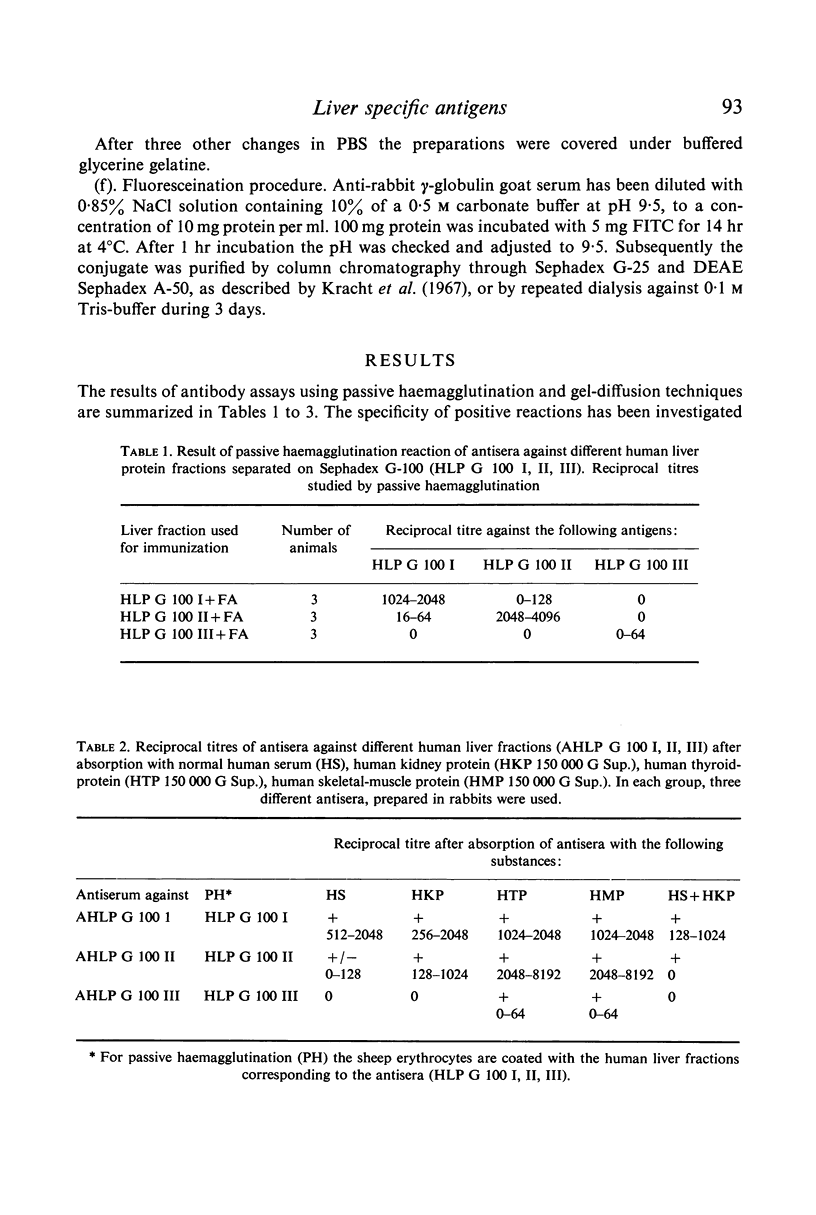
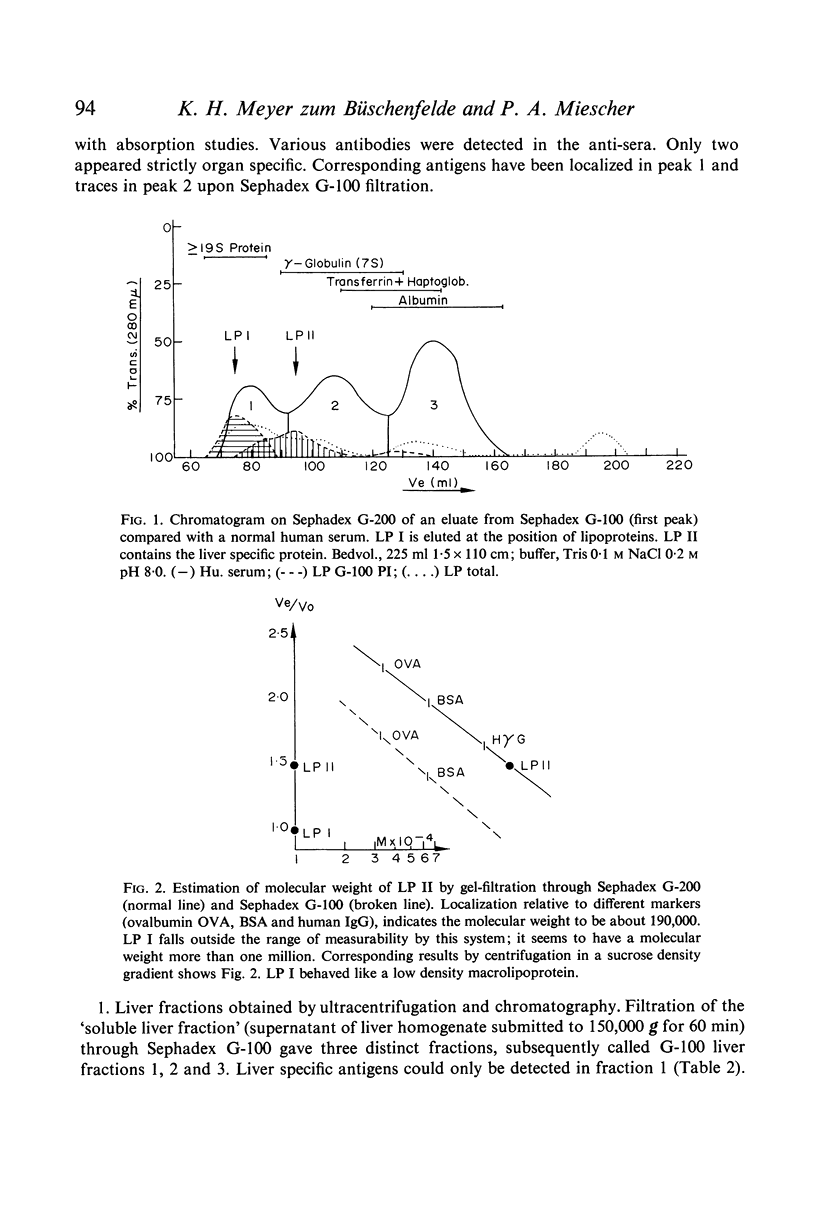
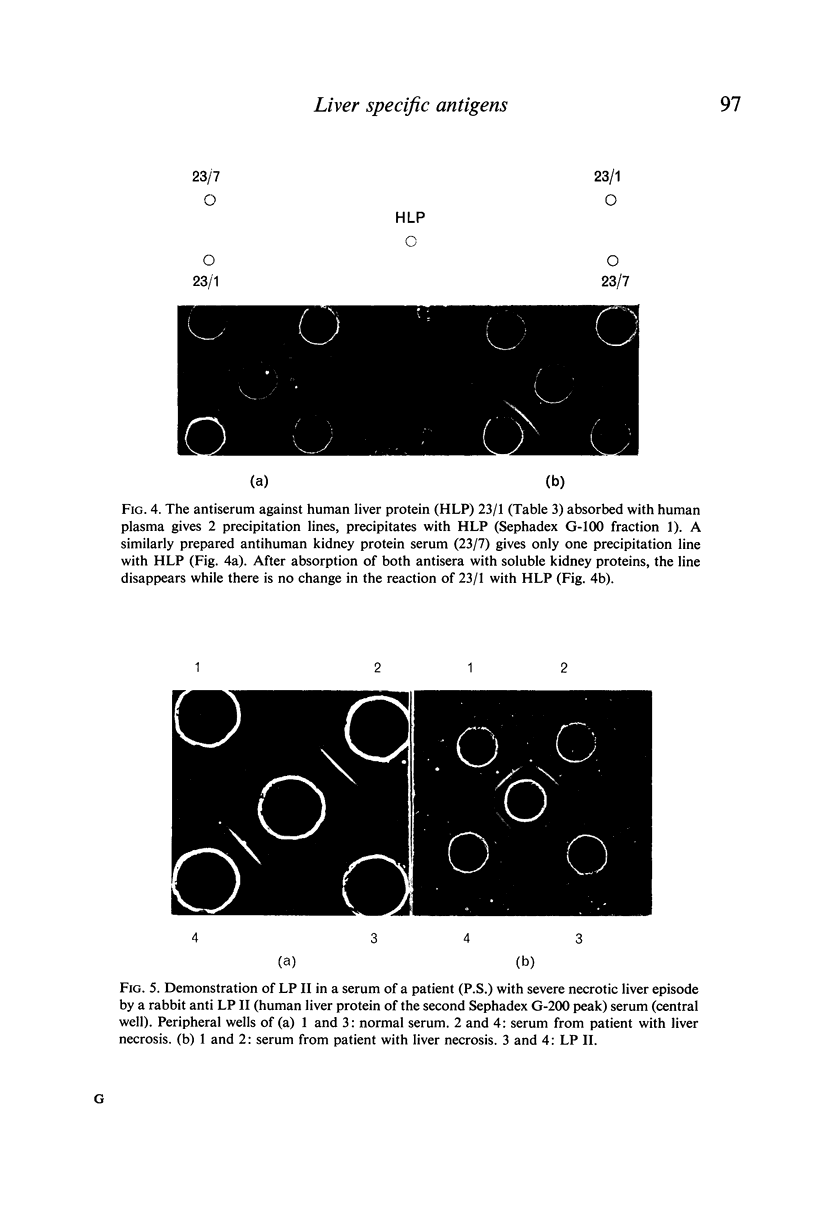
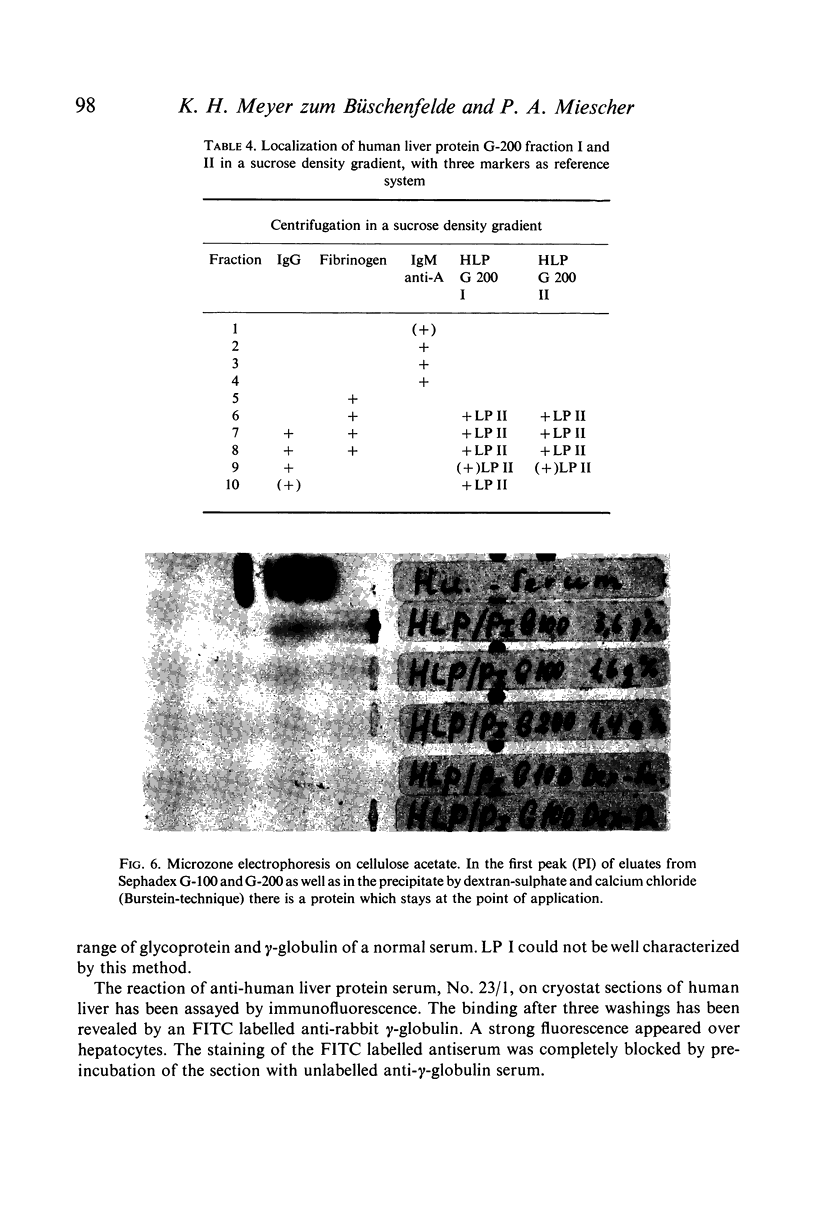
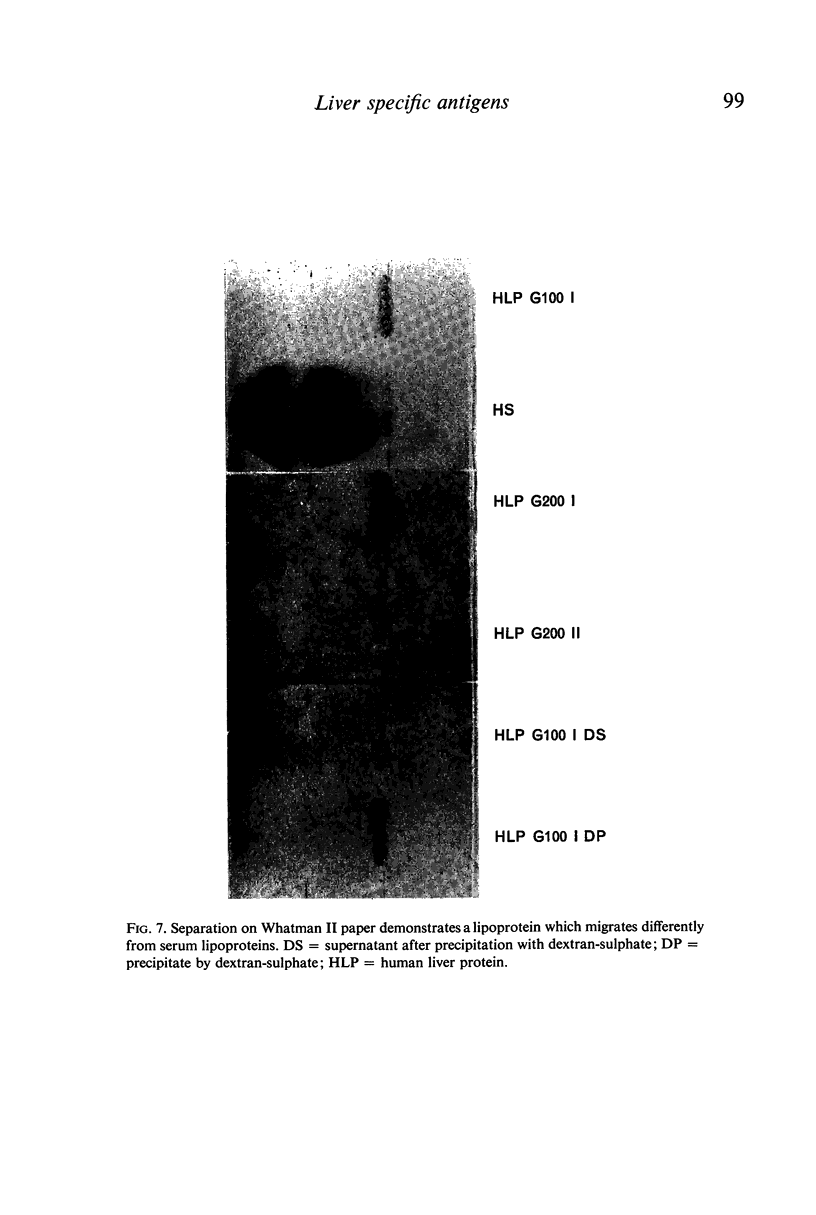
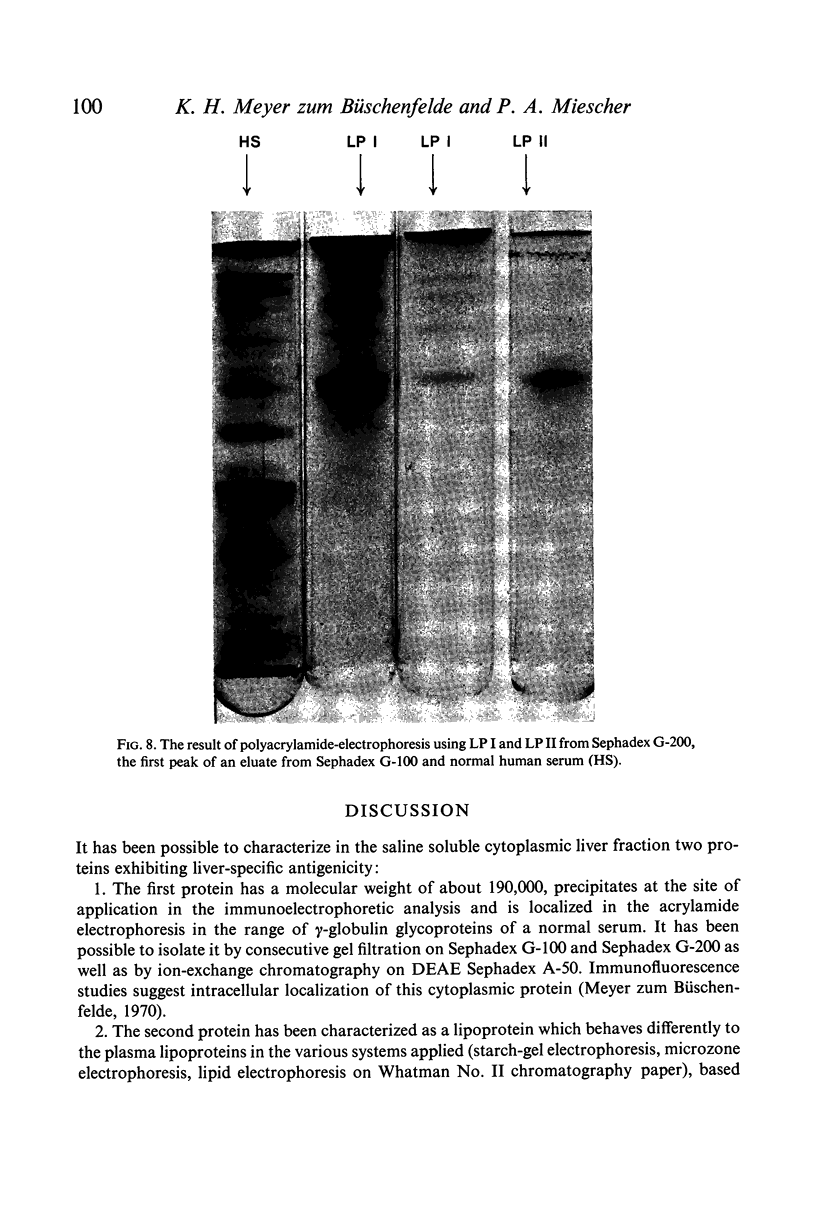
Human liver has been homogenated and submitted to 150,000 g in order to investigate the supernatant for the presence of liver specific antigens. Gel-filtration on Sephadex G-100 revealed liver specific antigenicity in the first peak. Gel-filtration of the first peak on Sephadex G-200 revealed two peaks each exhibiting liver specific antigenicity. Immunochemical and physicochemical analysis made it possible to define the liver-specific antigen present in the first peak as a lipoprotein with the characteristics of a high molecular weight, low density protein. It is partly located in the membrane of liver cells. The liver specific protein of the second Sephadex G-200 peak has a molecular weight of about 190,000. It is located within the cytoplasm of hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGGLUTINATION-INHIBITION test proposed as a standard of reference in influenza diagnostic studies; Committee on Standard Serological Procedures in Influenza Studies. J Immunol. 1950 Sep;65(3):347–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg P. A., Doniach D., Roitt I. M. Immunologische Phänomene bei Leberkrankheiten: Die Bedeutung mitochondrialer Antikörper. Klin Wochenschr. 1969 Dec 15;47(24):1297–1307. doi: 10.1007/BF01484292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'AMELIO V., PERLMANN P. The distribution of soluble antigens in cellular structures of rat liver. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Mar;19:383–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumonde D. C. Tissue-specific antigens. Adv Immunol. 1966;5:245–412. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60275-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F., BORGSTROM B. Physico-chemical state of lipids in intestinal content during their digestion and absorption. Fed Proc. 1962 Jan-Feb;21:43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kössling F. K., Meyer zum Büschenfelde Untersuchungen zur Pathogenese der aktiven chronischen Hepatitis. Z Gesamte Exp Med. 1970;153(2):150–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kössling F. K., Meyer zum Büschenfelde Zur Induktion einer aktiven chronischen Hepatitis durch heterologe lösliche Leberproteine. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1968;345(4):365–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht W. Zur Frage leberspezifischer Antigene beim Menschen. Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Jul 15;44(14):833–837. doi: 10.1007/BF01711502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer Zum Büschenfelde Untersuchungen über die immunbiologische Bedeutung löslicher Leberproteine. Z Gesamte Exp Med. 1968;148(2):131–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer zum Büschenfelde Immunosuppressive Therapie der chronischen Hepatitis. Dtsch Med J. 1969 Aug;20(16):522–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer zum Büschenfelde Klinische Untersuchungen zur immunologischen Spezifität des Leberparenchyms. Arch Klin Med. 1968;215(2):107–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer zum Büschenfelde, Kössling F. K. Untersuchungen über die immunbiologische Bedeutung löslicher Leberproteine. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1968;74:529–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer zum Büschenfelde, Schrank C. Untersuchungen zur Frage organspezifischer Antigene der Leber. Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Jun 1;44(11):654–656. doi: 10.1007/BF01745901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMANN P., D'AMELIO V. Soluble antigens in microsomes and other cell-fractions of rat liver. Nature. 1958 Feb 15;181(4607):491–492. doi: 10.1038/181491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher K., Koch W. Nachweis zirkulierender Auto-Antikörper bei chronisch-progressiver Hepatitis. Klin Wochenschr. 1968 Sep 1;46(17):925–929. doi: 10.1007/BF01747156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON J. F., MIKUTA E. T. Enzymatic activity of cytoplasmic particulates of rat liver isolated by gradient centrifugation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Aug;51(2):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90504-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT P. K. [The immunology of liver microsomes. III. The localization of tissue-specific antigens within the structural components of endoplastic reticulum]. Z Naturforsch B. 1960 Apr;15B:221–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]