Abstract
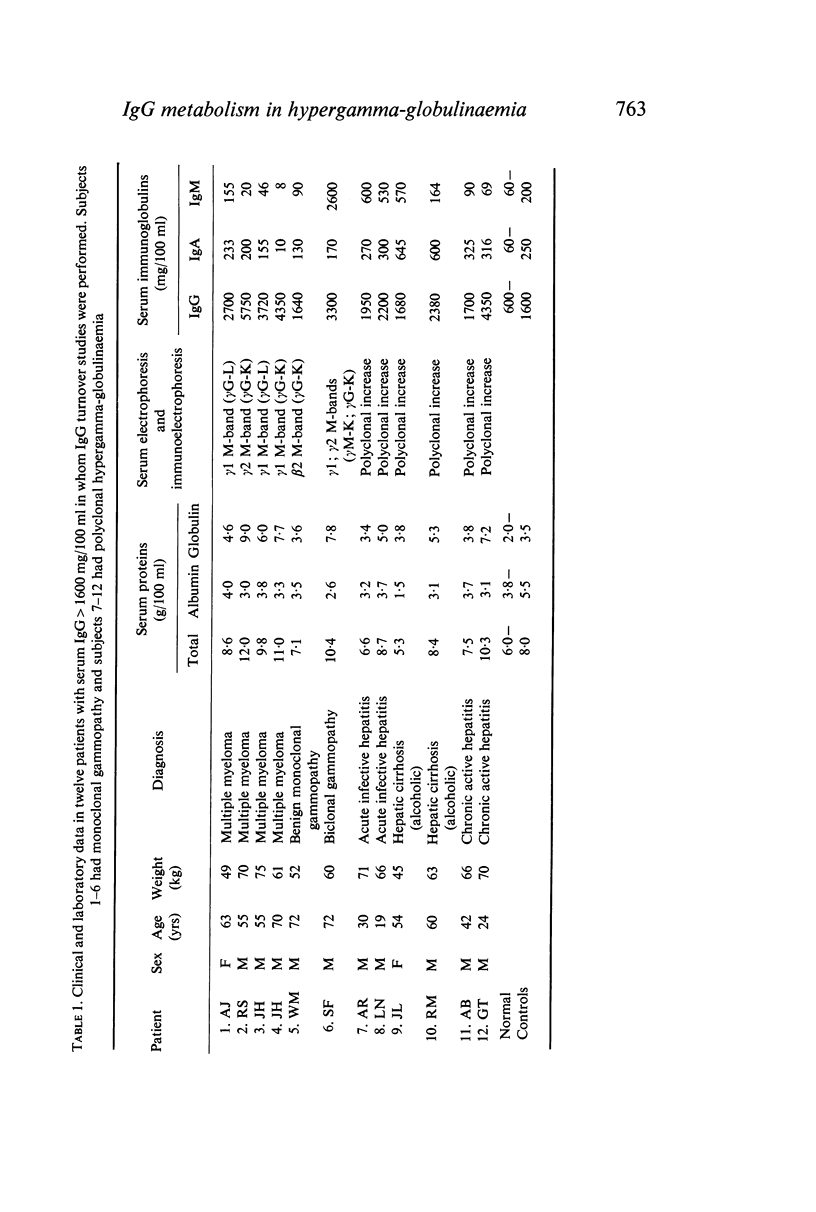
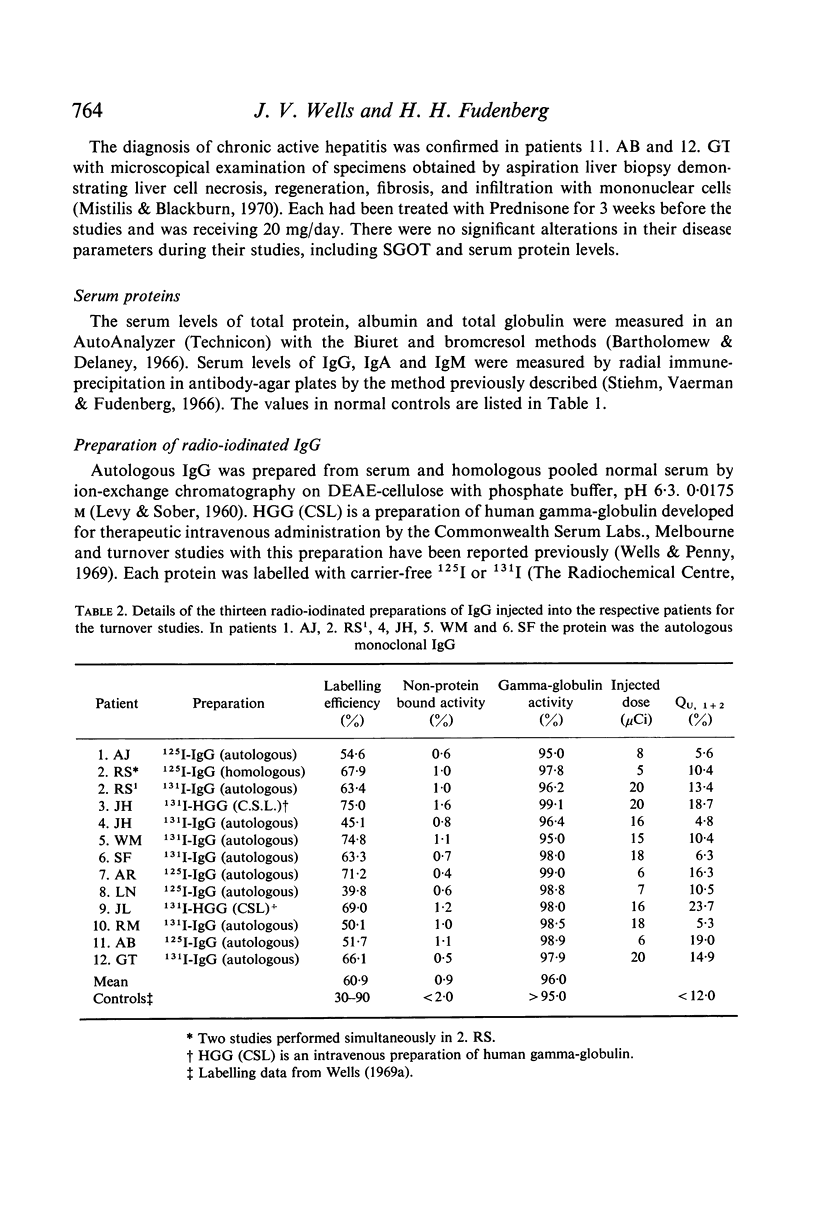
Metabolic turnover studies were performed with radio-iodinated IgG in twelve patients with a serum IgG level greater than 1600 mg/100 ml (six with monoclonal gammopathy and six with a polyclonal increase in IgG associated with liver disease). The six patients with an IgG monoclonal protein comprised four multiple myeloma, one benign monoclonal gammopathy and one biclonal gammopathy presenting as Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia. The six patients with liver disease comprised two patients with cirrhosis, two with infective hepatitis and two with chronic active hepatitis. The injected IgG was either autologous normal IgG (five cases), autologous monoclonal IgG (five cases), homologous normal IgG (one case) or therapeutic intravenous HGG (two cases).
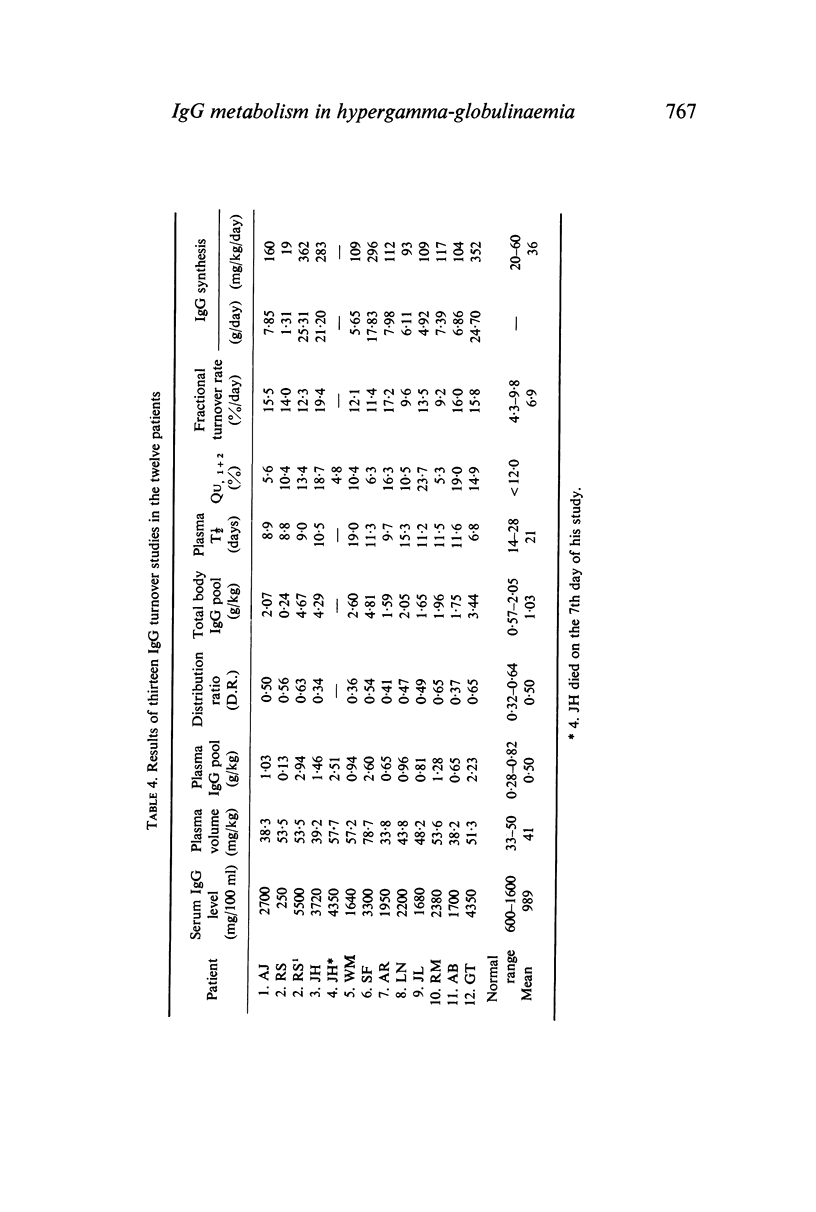
The plasma volume was increased in six patients; the plasma IgG pool in nine; and the total body IgG pool in seven. The plasma T½ was normal in one patient with monoclonal and one patient with polyclonal gammopathy but shortened in the other ten studies with mean values of 11·3 and 11·0 days in monoclonal and polyclonal gammopathy respectively. The fractional turnover rate was normal in two studies in polyclonal gammopathy and increased in the other ten with mean values of 13·6% per day in both groups of patients. The IgG synthesis rate was significantly increased in all studies except for a reduced synthesis of normal IgG in one patient with multiple myeloma. The mean synthesis rates in monoclonal and polyclonal gammopathy were respectively 6·7 and 4·1 times the mean synthesis rate in normal controls.
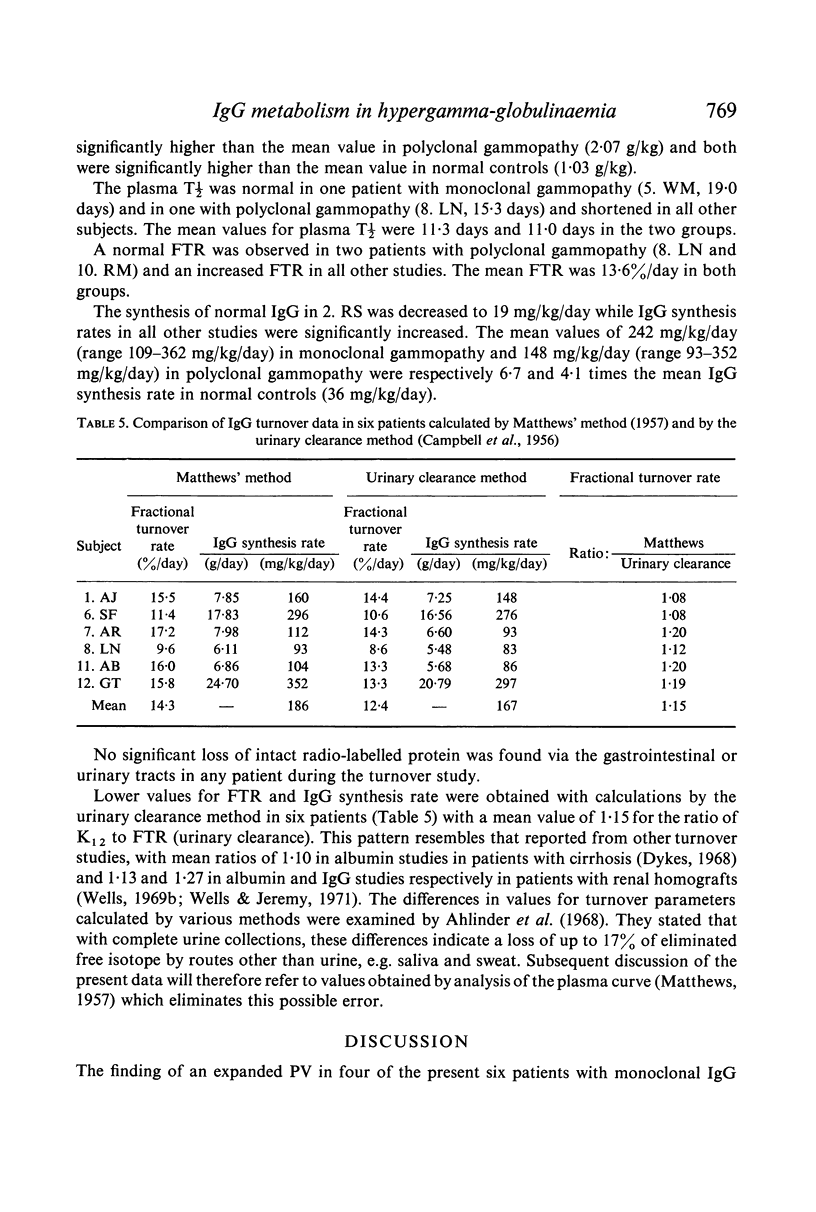
The pattern of increased synthesis and increased catabolism in such patients confirms published reports in some diseases and demonstrates a similar pattern in chronic active hepatitis. The findings are consistent with the `concentration-catabolism' effect.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALPER C. A., FREEMAN T., WALDENSTROEM J. THE METABOLISM OF GAMMA GLOBULINS IN MYELOMA AND ALLIED CONDITIONS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Dec;42:1858–1868. doi: 10.1172/JCI104870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN S. B., GLENERT J., WALLEVIK K. GAMMA GLOBULIN TURNOVER AND INTESTINAL DEGRADATION OF GAMMA GLOBULIN IN THE DOG. J Clin Invest. 1963 Dec;42:1873–1881. doi: 10.1172/JCI104872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlinder S., Birke G., Norberg R., Olhagen B., Plantin L. O., Reizenstein P. The normal metabolism of gammaG-globulin. Acta Med Scand. 1968 Jul-Aug;184(1-2):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1968.tb02419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., HALPERN B. N., STIFFEL C., CRUCHAUD S., BIOZZI G. Phagocytose d'une fraction du sérum chauffé et iodé par le système réticulo-endothélial et comportement consécutif de ses cellules a l'égard d'autres colloïdes. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1955 Dec;89(6):601–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S. Serum protein turnover in multiple myeloma. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Mar;49(3):386–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKE G., LILJEDAHL S. O., OLHAGEN B., PLANTIN L. O., AHLINDER S. Catabolism and distribution of gamma-globulin. A preliminary study with 131 I-labelled gammaglobulin. Acta Med Scand. 1963 May;173:589–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAMBELL F. W., HEMMINGS W. A., MORRIS I. G. A THEORETICAL MODEL OF GAMMA-GLOBULIN CATABOLISM. Nature. 1964 Sep 26;203:1352–1354. doi: 10.1038/2031352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin H., Malet F. The metabolism of different immunoglobulin classes in irradiated mice. Immunology. 1969 Sep;17(3):345–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL R. M., CUTHBERTSON D. P., MATTHEWS C. M., MCFARLANE A. S. Behaviour of 14C- and 131I-labelled plasma proteins in the rat. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1956 Jul;1(1-2):66–84. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(56)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S., FREEMAN T. Metabolic heterogeneity of human gamma-globulin. Biochem J. 1960 Sep;76:475–487. doi: 10.1042/bj0760475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRIVSHOLM A. Turnover rate of myeloma proteins in serum and urine determined after intravital labelling with glycine--1--C--14. Acta Med Scand. 1961 May;169:503–507. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1961.tb07860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykes P. W. The rates of distribution and catabolism of albumin in normal subjects and in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Clin Sci. 1968 Feb;34(1):161–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman L. L., Pachas W. N., Pinals R. S., Bloch K. J. M-components in patients with chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1969 Aug;57(2):138–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englisová M., Englis M., Hoenig V., Hoenigová J. Incidence of paraproteins in chronic liver diseases. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1968;3(4):413–416. doi: 10.3109/00365526809180138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., SELL S. THE IMMUNOGLOBULINS OF MICE. V. THE METABOLIC (CATABOLIC) PROPERTIES OF FIVE IMMUNOGLOBULIN CLASSES. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:41–58. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN T. The biological behaviour of normal and denatured human plasma albumin. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 Nov;4:788–792. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T. Immunoglobulins in chronic liver disease. Gut. 1968 Apr;9(2):193–198. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.2.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GABUZDA T. G. The turnover and distribution of I-131-labeled myeloma and macroglobulin proteins. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Jan;59:65–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVENS W. P., Jr, DICKENSHEETS J., BIERLY J. N., EBERHARD T. P. The half-life of I131 labeled normal human gamma globulin in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. J Immunol. 1954 Oct;73(4):256–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON A., DAY E. D., PRESSMAN D. The effect of iodination on antibody activity. J Immunol. 1960 Feb;84:213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp W. L., MacKinney A. A., Jr, Wasson G. Blood volume and hematocrit value in macroglobulinemia and myeloma. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Apr;123(4):394–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. B., SOBER H. A. A simple chromatographic method for preparation of gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jan;103:250–252. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPPINCOTT S. W., KORMAN S., FONG C., STICKLEY E., WOLINS W., HUGHES W. L. Turnover of labeled normal gamma globulin in multiple myeloma. J Clin Invest. 1960 Apr;39:565–572. doi: 10.1172/JCI104069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie M. R., Fudenberg H. H., O'Reilly R. A. The hyperviscosity syndrome. I. In IgG myeloma. The role of protein concentration and molecular shape. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jan;49(1):15–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI106213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mistilis S. P., Blackburn C. R. Active chronic hepatitis. Am J Med. 1970 Apr;48(4):484–495. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Terry W. D., Waldmann T. A. Metabolic properties of IgG subclasses in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI106279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasma cell dyscrasias. Current clinical and biochemical concepts. Am J Med. 1968 Feb;44(2):256–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. S. Theory and use of tracers in determining transfer rates in biological systems. Physiol Rev. 1957 Apr;37(2):133–154. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1957.37.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH E., KOCHWA S., WASSERMAN L. R. AGGREGATION OF IGG GLOBULIN IN VIVO. I. THE HYPERVISCOSITY SYNDROME IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA. Am J Med. 1965 Jul;39:35–48. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L. Clinical and experimental metabolism of normal 6.6s gamma-globulin in normal subjects and in patients with macroglobulinemia and multiple myeloma. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jul;62:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Fishkin B. G., Grey H. M. Catabolism of human gammaG-immunoglobulins of different heavy chain subclasses. I. Catabolism of gammaG-myeloma proteins in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Oct;47(10):2323–2330. doi: 10.1172/JCI105917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Vaerman J. P., Fudenberg H. H. Plasma infusions in immunologic deficiency states: metabolic and therapeutic studies. Blood. 1966 Dec;28(6):918–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALDMANN T. A., SCHWAB P. J. IGG (7 S GAMMA GLOBULIN) METABOLISM IN HYPOGAMMAGLOBULINEMIA: STUDIES IN PATIENTS WITH DEFECTIVE GAMMA GLOBULIN SYNTHESIS, GASTROINTESTINAL PROTEIN LOSS, OR BOTH. J Clin Invest. 1965 Sep;44:1523–1533. doi: 10.1172/JCI105259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Metabolism of immunoglobulins. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:1–110. doi: 10.1159/000385919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Wang I. Y., McCormick J. N., Fudenberg H. H. The identity of light chains of monoclonal IgG and monoclonal IgM in one patient. Immunochemistry. 1969 May;6(3):451–459. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. V., Jeremy D. Metabolism of autologous 131-I-labelled IgG in patients after renal homo-transplantation. Clin Sci. 1971 May;40(5):393–401. doi: 10.1042/cs0400393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. V., Penny R. Survival studies on a commercial preparation of intravenous human gammaglobulin labelled with 131-I. Australas Ann Med. 1969 Aug;18(3):271–276. doi: 10.1111/imj.1969.18.3.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D. Hypercatabolism of normal IgG; an unexplained immunoglobulin abnormality in the connective tissue diseases. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):454–464. doi: 10.1172/JCI106254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim F. A. Immunoglobulins in the course of viral hepatitis and in cholestatic and obstructive jaundice. Acta Med Scand. 1968 May;183(5):473–479. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1968.tb10510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


