Abstract
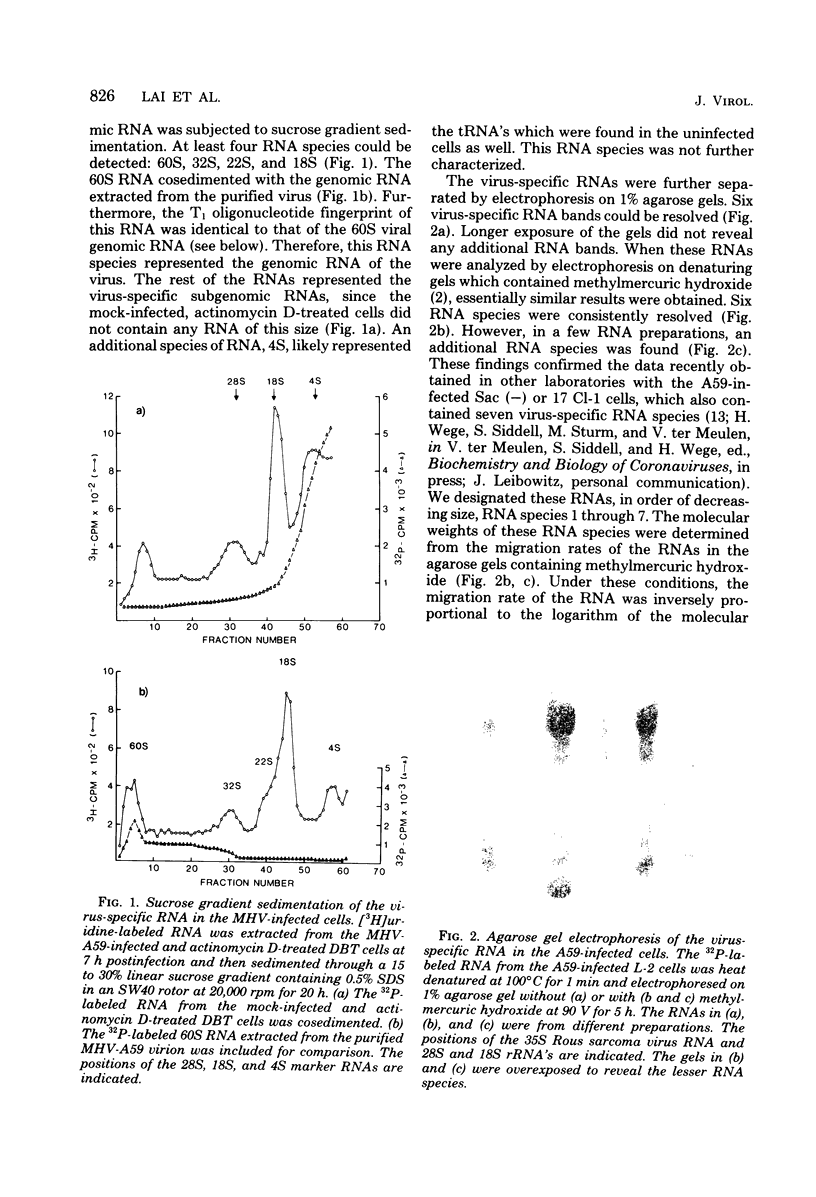
The composition and structure of the mouse hepatitis virus (MHV)-specific RNA in actinomycin D-treated, infected L-2 cells were studied. SEven virus-specific RNA species with molecular weights of 0.6 X 10(6), 0.9 X 10(6), 1.2 X 10(6), 1.5 X 10(6), 3.0 X 10(6), 4.0 X 10(6), and 5.4 X 10(6) (equivalent to the viral genome) were detected. T1 oligonucleotide fingerprinting studies suggested that the sequences of each RNA species were totally included within the next large RNa species. The oligonucleotides of each RNA species were mapped on the 60S RNA genome of the virus. Each RNA species contained the oligonucleotides starting from the 3' end of the genome and extending continuously for various lengths in the 3' leads to 5' direction. All of the viral RNA species contained a polyadenylate stretch of 100 to 130 nucleotides and probably identical sequences immediately next to the polyadenylate. These data suggested that the virus-specific RNAs are mRNA's and have a stairlike structure similar to that of infectious bronchitis virus, an avian coronavirus. A proposal is presented, based on the mRNA structure, for the designation of the genes on the MHV genome. Using this proposal, the sequence differences between A59, a weakly pathogenic strain, and MHV-3, a strongly hepatotropic strain, were localized primarily in mRNA's 1 and 3, corresponding t genes A and C.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy J. S., Brian D. A. Bovine coronavirus genome. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):293–300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.293-300.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S. Size and genetic content of viral RNAs in avian oncovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):47–63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.47-63.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Stohlman S. A. Comparative analysis of RNA genomes of mouse hepatitis viruses. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):661–670. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.661-670.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Stohlman S. A. RNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):236–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.236-242.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B., Kennedy I. Genome of infectious bronchitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.99-107.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnaughton M. R., Madge M. H. The genome of human coronavirus strain 229E. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jun;39(3):497–504. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-3-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A., Bond C. W. Pathogenic murine coronaviruses. I. Characterization of biological behavior in vitro and virus-specific intracellular RNA of strongly neurotropic JHMV and weakly neurotropic A59V viruses. Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):352–370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90467-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G., Wege H., Barthel A., ter Meulen V. Coronavirus JHM: cell-free synthesis of structural protein p60. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):10–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.10-17.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Isolation and identification of virus-specific mRNAs in cells infected with mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-A59). Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90449-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kennedy S. I. Coronavirus multiplication strategy. I. Identification and characterization of virus-specified RNA. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):665–674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.665-674.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kennedy S. I. Coronavirus multiplication strategy. II. Mapping the avian infectious bronchitis virus intracellular RNA species to the genome. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):440–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.440-449.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S. I. Structural proteins: effects of preparative conditions on the migration of protein in polyacrylamide gels. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):637–649. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90488-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. A., Almeida J. D., Cunningham C. H., Dowdle W. R., Hofstad M. S., McIntosh K., Tajima M., Zakstelskaya L. Y., Easterday B. C., Kapikian A. Coronaviridae. Intervirology. 1975;5(1-2):76–82. doi: 10.1159/000149883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Müller A., ter Meulen V. Genomic RNA of the murine coronavirus JHM. J Gen Virol. 1978 Nov;41(2):217–227. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The size and genetic composition of virus-specific RNAs in the cytoplasm of cells producing avian sarcoma-leukosis viruses. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Hirano N., Hino S., Shibuta H., Matumoto M. Polyadenylate in the virion RNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(4):1103–1108. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]