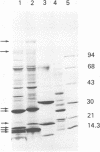
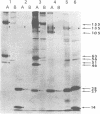
Abstract
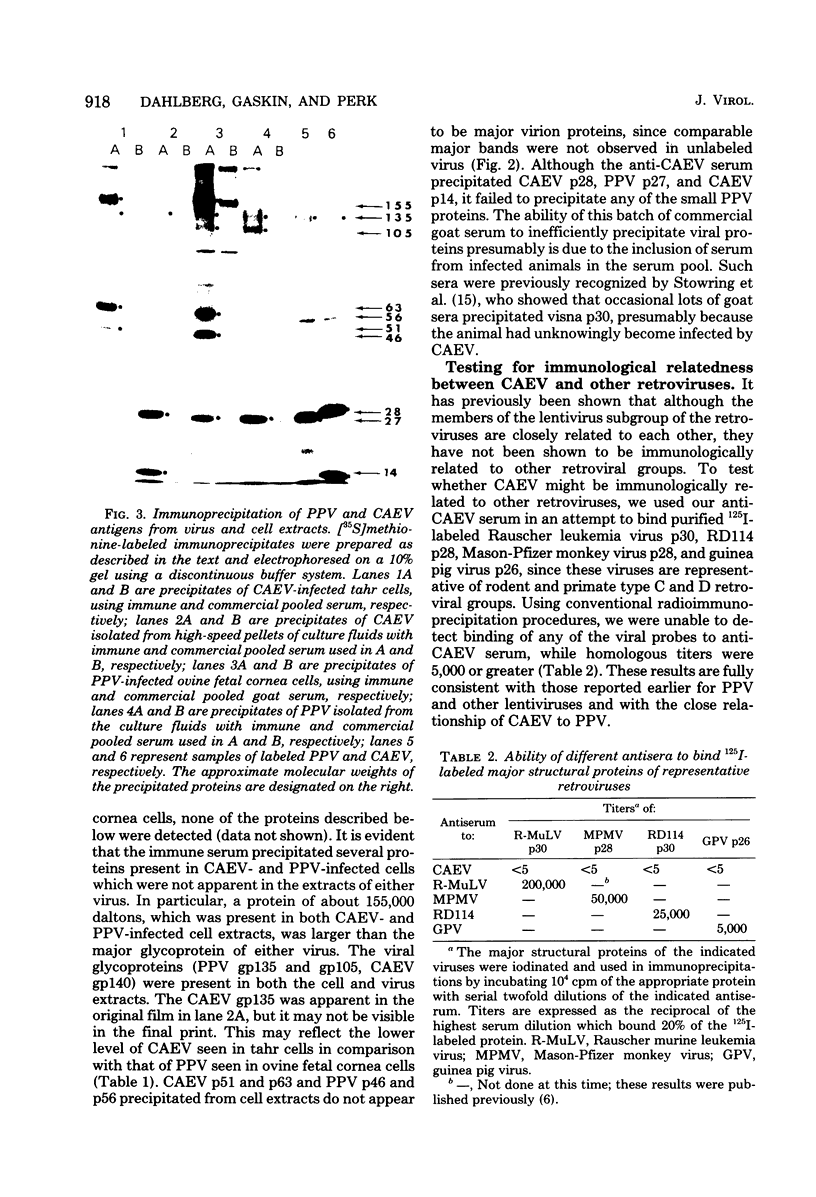
Caprine arthritis encephalitis virus (CAEV) causes a variety of pathological conditions ranging from mild to very severe and from acute to chronic, depending upon the age of initial infection and other variables. Although the virus has been reported to have properties of characteristic of retroviruses and to be related to maedi-visna virus (also called progressive pneumonia virus [PPV]), relatively little information about its morphological and immunological characteristics has been reported. We describe the morphological features of CAEV replicating in cultured caprine cells. Although the virus replicates slowly and very little virus is released from productively infected cells, it is apparent that the morphogenesis of CAEV is strikingly similar to that of maedi-visna. After the transmission of CAEV to a more permissive permanent cell line derived from Himalayan tahr ovary, it was possible to grow and purify enough virus to initiate biochemical characterization. The structural proteins of CAEV are generally very similar to those of PPV, suggesting that the two viruses are closely related but not identical. This was substantiated by showing that serum from a CAEV-infected goat immunoprecipitated both CAEV and PPV virion structural antigens from extracts of radiolabeled virus and also precipitated putative nonstructural viral antigens from extracts of both CAEV- and PPV-infected cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cork L. C., Davis W. C. Ultrastructural features of viral leukoencephalomyelitis of goats. Lab Invest. 1975 Mar;32(3):359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cork L. C., Hadlow W. J., Gorham J. R., Piper R. C., Crawford T. B. Pathology of viral leukoencephalomyelitis of goats. Acta Neuropathol. 1974;29(4):281–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00685482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cork L. C., Narayan O. The pathogenesis of viral leukoencephalomyelitis-arthritis of goats. I. Persistent viral infection with progressive pathologic changes. Lab Invest. 1980 Jun;42(6):596–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coward J. E., Harter D. H., Morgan C. Electron microscopic observations of Visna virus-infected cell cultures. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):1030–1038. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90149-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford T. B., Adams D. S., Cheevers W. P., Cork L. C. Chronic arthritis in goats caused by a retrovirus. Science. 1980 Feb 29;207(4434):997–999. doi: 10.1126/science.6153243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Immunological relationships of an endogenous guinea pig retrovirus with prototype mammalian type B and type D retroviruses. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):522–530. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.522-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Baringer J. R. The structural polypeptides of RNA slow viruses. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):238–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T. The slow infection caused by visna virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;72:101–156. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66289-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter D. H., Axel R., Burny A., Gulati S., Schlom J., Spiegelman S. The relationship of visna, maedi and RNA tumor viruses as studied by molecular hybridization. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90418-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino S., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Radiommunoassays for the 70,000-molecular-weight glycoproteins of endogenous mouse type C viruses: viral antigen expression in normal mouse tissues and sera. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):933–941. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.933-941.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle W. E., Harter D. H., Choppin P. W. The proteins of visna virus. Virology. 1972 Feb;47(2):542–545. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90299-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. M. Viral leukoencephalomyelitis in two Minnesota goats. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1978 Nov;73(11):1439–1440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowring L., Haase A. T., Charman H. P. Serological definition of the lentivirus group of retroviruses. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):523–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.523-528.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORMAR H. An electron microscope study of tissue cultures infected with visna virus. Virology. 1961 Aug;14:463–475. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90339-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Mattern C. F., Stone L. B., Coe J. E., Lavelle G. Antigenic and morphological similarities of progressive pneumonia virus, a recently isolated "slow virus" of sheep, to visna and maedi viruses. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):301–308. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.301-308.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]