Abstract
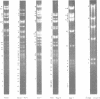
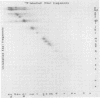
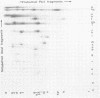
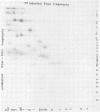
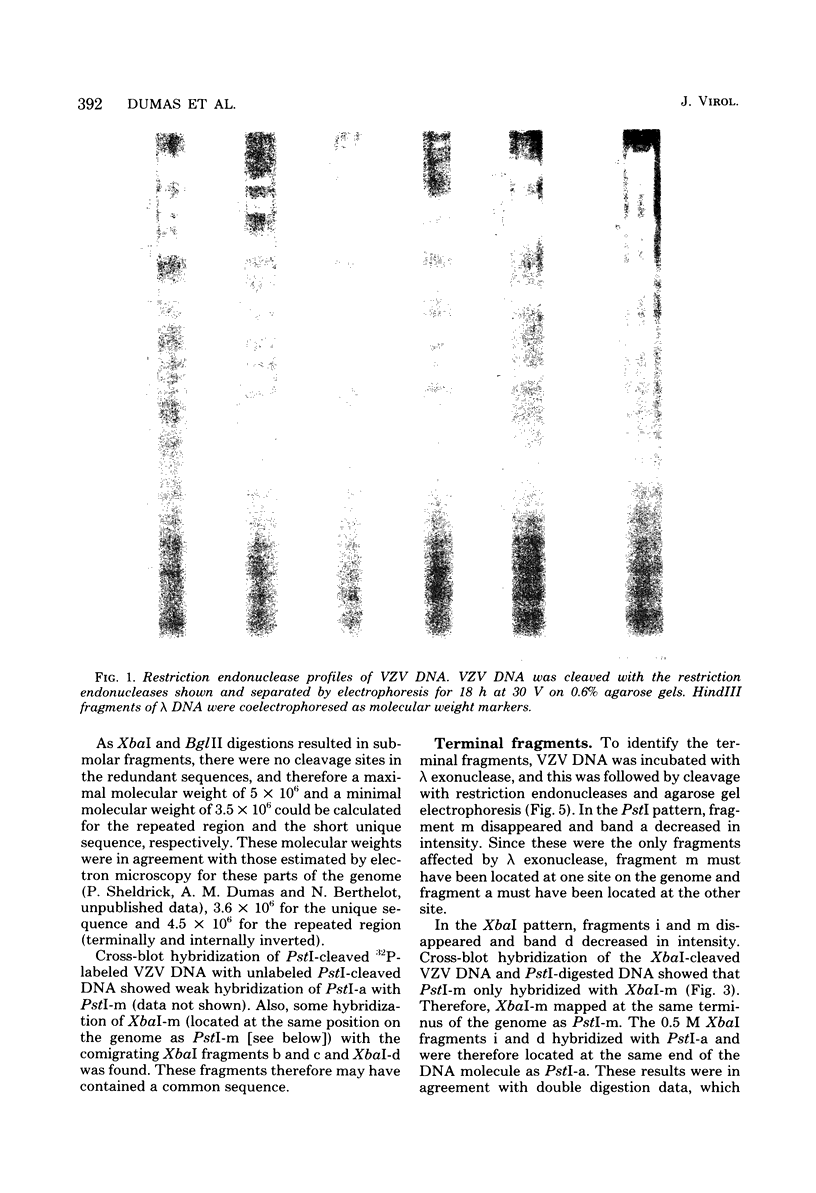
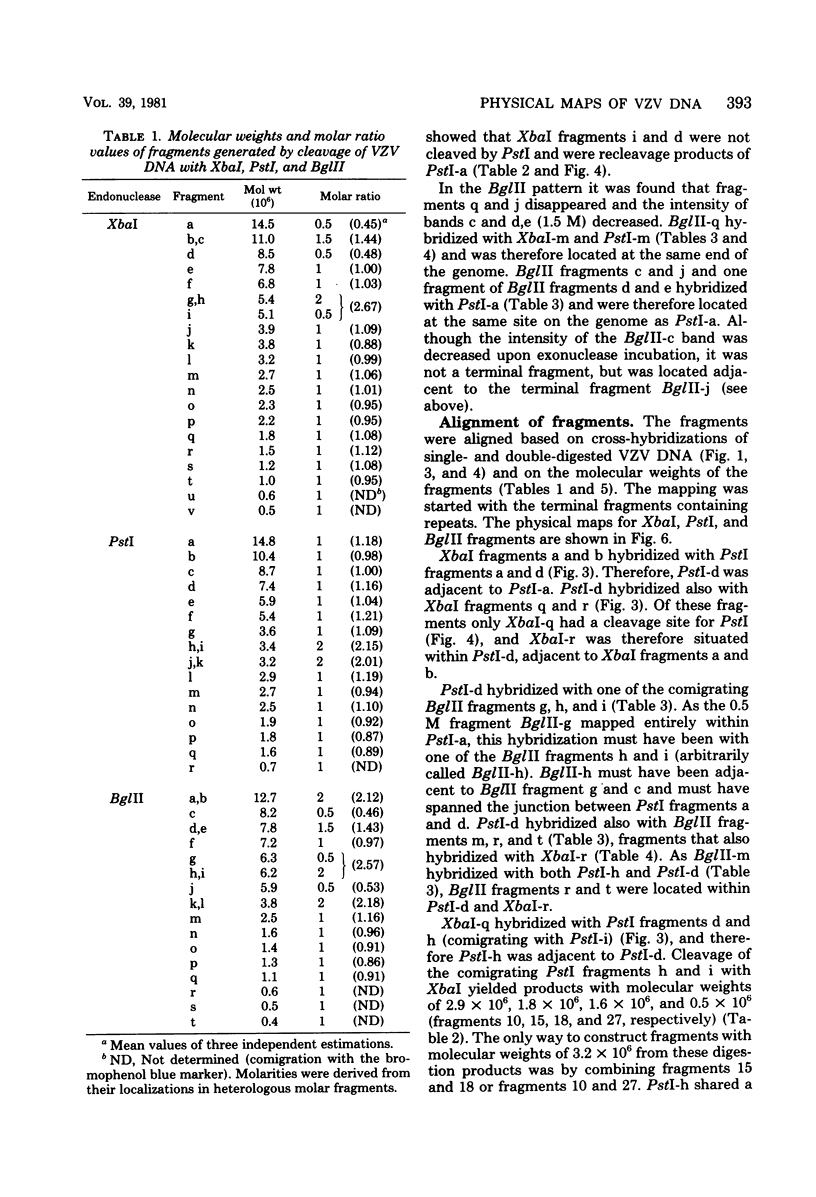
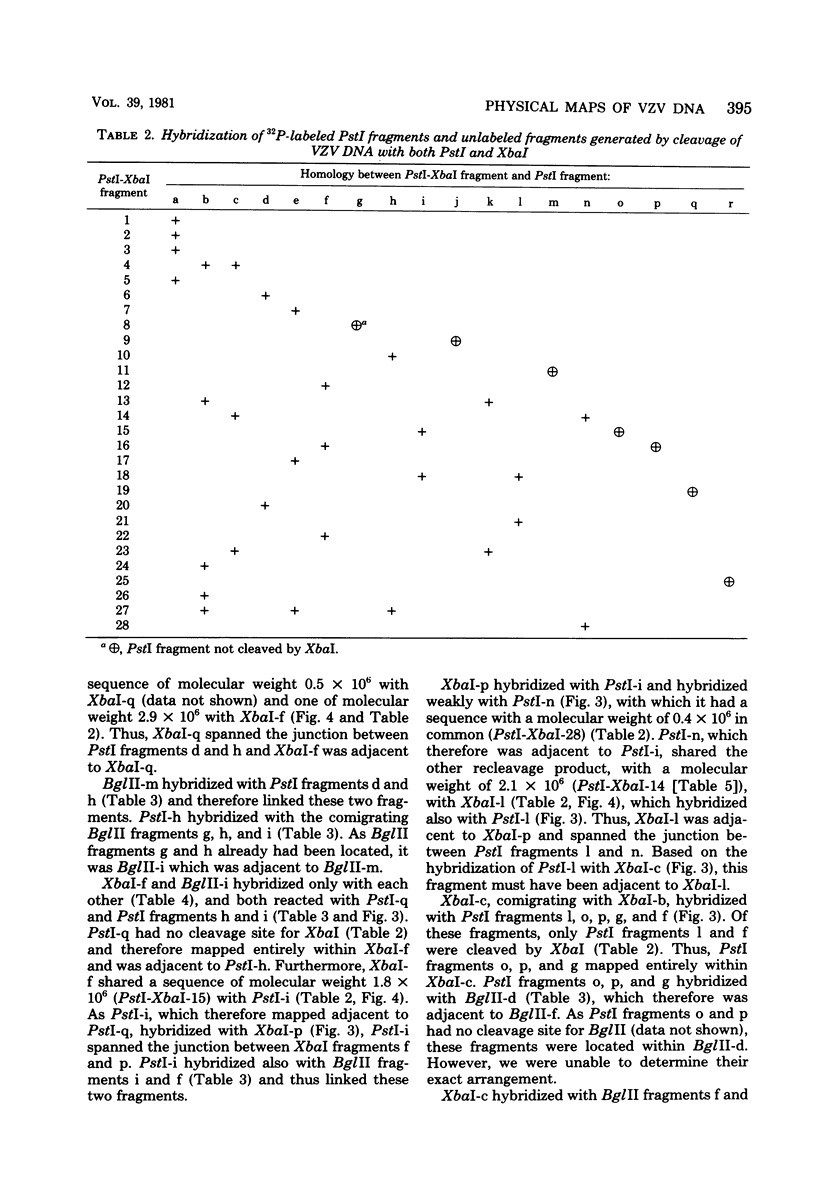
Cleavage of varicella-zoster virus DNA with the restriction endonucleases PstI, XbaI, and BglII resulted in 18, 22, and 20 fragments, respectively. Based on the molecular weights and molarities of these fragments, a molecular weight of 84 x 10(6) could be calculated for the varicella-zoster virus genome. In both the XbaI and the BglII patterns, four 0.5 M fragments were identified. The arrangement of the fragments was determined by molecular hybridization techniques, and the terminal fragments were identified by lambda exonuclease digestion. The 0.5 M fragments, of which two were located at the same terminus of the genome, contained repeated sequences: one terminally and one inverted internally. These results were in agreement with the existence of two equimolar subpopulations of the varicella-zoster virus genome, differing in the relative orientation of a short region of unique sequences. This region was bounded by the repeated sequences. From the molecular weights of the submolar fragments, a maximal molecular weight of 5 x 10(6) for the repeated region and a minimal molecular weight of 3.5 x 10(6) for the short unique sequence could be calculated.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaij C., Borst P. The gel electrophoresis of DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 10;269(2):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allet B., Bukhari A. I. Analysis of bacteriophage mu and lambda-mu hybrid DNAs by specific endonucleases. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 15;92(4):529–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Rixon F. J., Blankenship M. L. Analysis of the structure of the genome of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90484-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Robbins A. K. The cleavage of polyoma virus DNA by restriction enzymes KpnI and PstI. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):315–321. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Unity and diversity in the herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):15–37. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iltis J. P., Oakes J. E., Hyman R. W., Rapp F. Comparison of the DNAs of varicella-zoster viruses isolated from clinical cases of varicella and herpes zoster. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):345–352. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig H., Haines H. G., Biswal N., Benyesh-Melnick M. The characterization of Varicella-zoster virus DNA. J Gen Virol. 1972 Jan;14(1):111–114. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E., Iltis J. P., Hyman R. W., Rapp F. Analysis by restriction enzyme cleavage of human varicella-zoster virus DNAs. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):353–361. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp F., Iltis J. P., Oakes J. E., Hyman R. W. A novel approach to study the DNA of herpes zoster virus. Intervirology. 1977;8(5):272–280. doi: 10.1159/000148902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Summers W. C. Structure and function of herpesvirus genomes. II. EcoRl, Sbal, and HindIII endonuclease cleavage sites on herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):581–595. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevely W. S. Inverted repetition in the chromosome of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):232–234. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.232-234.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie N. M., Davison A., Chartrand P., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C. Recombination in herpes simplex virus: mapping of mutations and analysis of intertypic recombinants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):827–840. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Padmanabhan R., Bambara R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of bacteriophage DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:231–253. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]