Abstract
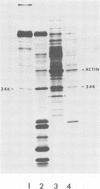
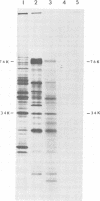
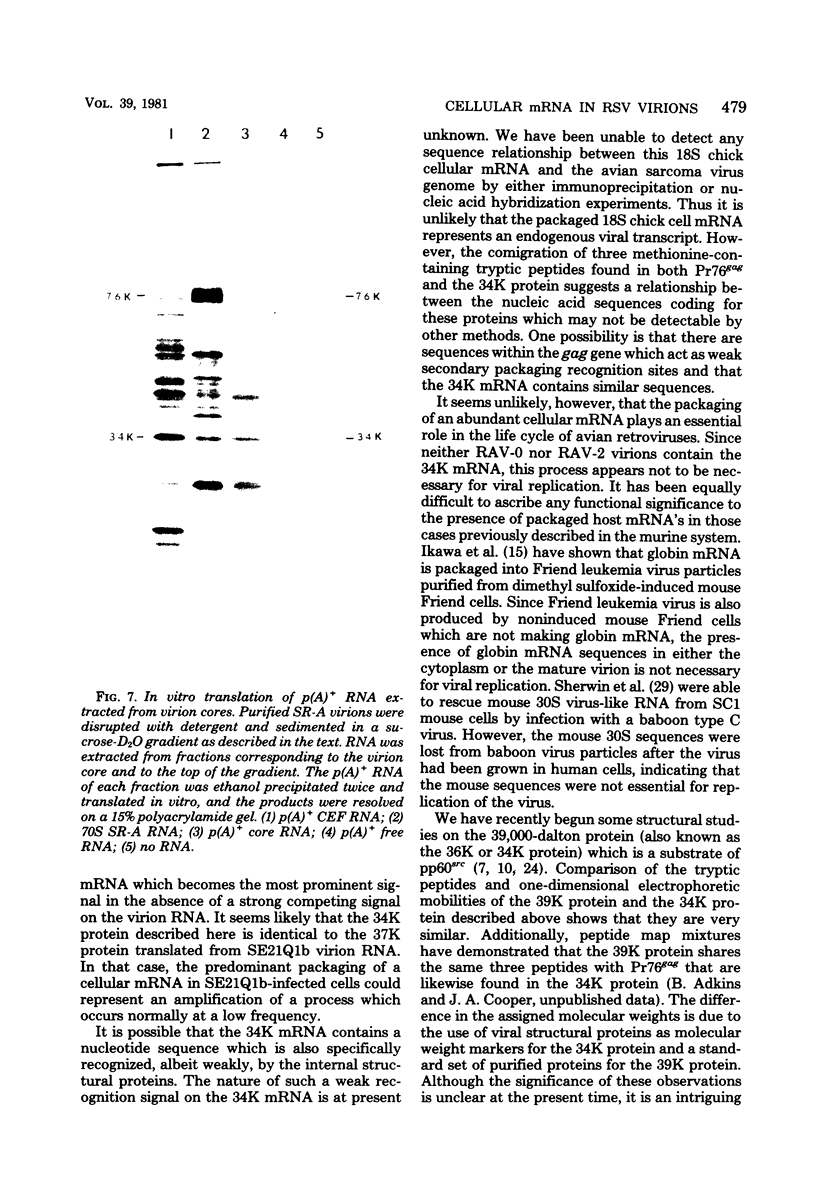
A novel messenger activity has been identified by in vitro translation of the 70S virion RNAs of a variety of avian leukosis and avian sarcoma viruses. When the 70S virion RNA complex was heat dissociated and the polyadenylated RNA was fractionated on neutral sucrose gradients, a polypeptide of 34,000 daltons (34K) was observed in the translation products of 18S polyadenylic acid-containing virion RNA. Aside from the p60src-related subgenomic messenger activities, this was the only prominent messenger activity that sedimented at <20S. It was determined that the 34K protein was not virally coded because (i) messenger activity for the 34K protein was not generated by mild alkaline hydrolysis of 35S genomic RNA, (ii) the 34K proteins synthesized in response to different virion RNAs had identical tryptic peptide maps, and (iii) the tryptic peptide map of the 34K protein coded for by virion RNA was identical to that of a major in vitro translation product of 34,000 daltons made from 18S uninfected chick cell polyadenylated RNA. The 18S RNA was shown to be contained within virion particles, rather than part of a cellular structure copurifying with virus preparations, by demonstrating the presence of 34K messenger activity in virion cores made from detergent-disrupted virus. This cellular mRNA, however, was not observed in the virion RNAs of Rous-associated virus types 0 and 2 avian leukosis viruses and therefore is not packaged by all avian retroviruses. Since no other cellular message has been detected by this assay, it seems likely that the 34K mRNA found in 70S virion RNA is the result of selective packaging of an abundant host cell mRNA by certain avian retroviruses.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beemon K., Hunter T. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus src gene products synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):551–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.551-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K., Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Polymorphism of avian sarcoma virus src proteins. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):190–200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.190-200.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P., Olshevsky U., Baltimore D., Dolberg D., Fan H. Virus-like 30S RNA in mouse cells. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1168–1176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1168-1176.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi D. P., Montelaro R. C., Frank H., Schäfer W. Assembly of type C oncornaviruses: a model. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):183–186. doi: 10.1126/science.202022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Stedman J. D. Efficient fluorography of 3H and 14C on thin layers. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90747-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Temin H. M. Comparison of Rous sarcoma virus-specific deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases in virions of Rous sarcoma virus and in Rous sarcoma virus-infected chicken cells. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):625–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.625-634.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Four different classes of retroviruses induce phosphorylation of tyrosines present in similar cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 May;1(5):394–407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.5.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., DeLorbe W., Swanstrom R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Tischer E., Goodman H. M. The nucleotide sequence of an untranslated but conserved domain at the 3' end of the avian sarcoma virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2967–2984. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. L., Rueckert R. R. Properties of a ribonucleoprotein particle isolated from Nonidet P-40-treated Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1010–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1010-1020.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk W. R., Faras A. J. Initiation of DNA synthesis by the avian oncornavirus RNA-directed DNA polymerase: tryptophan tRNA as the major species of primer RNA. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):1049–1051. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.1049-1051.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallis B., Linial M., Eisenman R. An avian oncovirus mutant deficient in genomic RNA: characterization of the packaged RNA as cellular messenger RNA. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):146–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90445-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S. Size and genetic content of viral RNAs in avian oncovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):47–63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.47-63.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howk R. S., Troxler D. H., Lowy D., Duesberg P. H., Scolnick E. M. Identification of a 30S RNA with properties of a defective type C virus in murine cells. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):115–123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.115-123.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa Y., Ross J., Leder P. An association between globin messenger RNA and 60S RNA derived from Friend leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1154–1158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J. P., McGinnis J., Green R. W. Rous sarcoma virus p19 binds to specific double-stranded regions of viral RNA: effect of p19 on cleavage of viral RNA by RNase III. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):87–98. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. G., Seidman J. G. Selective packaging of host tRNA's by murine leukemia virus particles does not require genomic RNA. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):328–335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.328-335.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Medeiros E., Hayward W. S. An avian oncovirus mutant (SE 21Q1b) deficient in genomic RNA: biological and biochemical characterization. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1371–1381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Harvey R., Smith A. E. The size of Rous sarcoma virus mRNAs active in cell-free translation. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):416–420. doi: 10.1038/268416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Dahlberg J. E. RNA-directed DNA synthesis in Moloney murine leukemia virus: interaction between the primer tRNA and the genome RNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):398–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.398-407.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a polypeptide encoded by the avian sarcoma virus src gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1567–1571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: effects of src gene expression on the synthesis and phosphorylation of cellular polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. C., Dahlberg J. E. Small RNAs of Rous sarcoma virus: characterization by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and fingerprint analysis. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1226–1237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1226-1237.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. C., Hanafusa H. Comparison of the small RNAs of polymerase-deficient and polymerase-positive Rous sarcoma virus and another species of avian retrovirus. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):863–871. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.863-871.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Todaro G. J. The genome-associated, specific RNA binding proteins of avian and mammalian type C viruses. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Linial M. Avian oncovirus mutant (SE21Q1b) deficient in genomic RNA: characterization of a deletion in the provirus. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):450–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.450-456.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin S. A., Rapp U. R., Benveniste R. E., Sen A., Todaro G. J. Rescue of endogenous 30S retroviral sequences from mouse cells by baboon type C virus. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):257–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.257-264.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P., Beemon K., Vogt P. K. Mapping RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of avian tumor virus RNAs: sarcoma-specific oligonucleotides are near the poly(A) end and oligonucleotides common to sarcoma and transformation-defective viruses are at the poly(A) end. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1051–1070. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1051-1070.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Baltimore D. Relationship of retrovirus polyprotein cleavages to virion maturation studied with temperature-sensitive murine leukemia virus mutants. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):750–761. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.750-761.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. C., Lewis R. B., Bose H. R., Jr, Kang C. Y. Assembly of avian reticuloendotheliosis virus: association of the core precursor polypeptide with the intracellular ribonucleoprotein complex. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):484–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.484-489.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeger H., Kalnins V. I., Stephenson J. R. Type-C retrovirus maturation and assembly: post-translational cleavage of the gag-gene coded precursor polypeptide occurs at the cell membrane. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):34–44. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]