Abstract
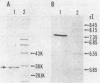
The chromosomally encoded beta-lactamase gene of Klebsiella oxytoca E23004, a strain resistant to cefoperazone and aztreonam, was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli HB101. The molecular mass and pI of this enzyme were 28 kilodaltons and 7.4, respectively. Although the beta-lactamase of K. oxytoca hydrolyzed many cephalosporins, including broad-spectrum drugs, the nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid sequence lacked homology with chromosomal class C beta-lactamase genes (ampC) of E. coli or Citrobacter freundii. Rather, about 45% nucleotide sequence homology and 40% deduced amino acid sequence homology were observed between the K. oxytoca beta-lactamase and TEM-1, a class A beta-lactamase which does not efficiently hydrolyze cephalosporins. Values of Km, relative Vmax, and relative Vmax/Km for the K. oxytoca beta-lactamase indicated that the enzyme is a penicillinase but that it can hydrolyze cefoperazone effectively and other broad-spectrum cephems weakly. Hence, the chromosomal beta-lactamase of K. oxytoca E23004 belongs to class A but differences in its amino acid sequence provide a broader spectrum of activity.
Full text
PDF


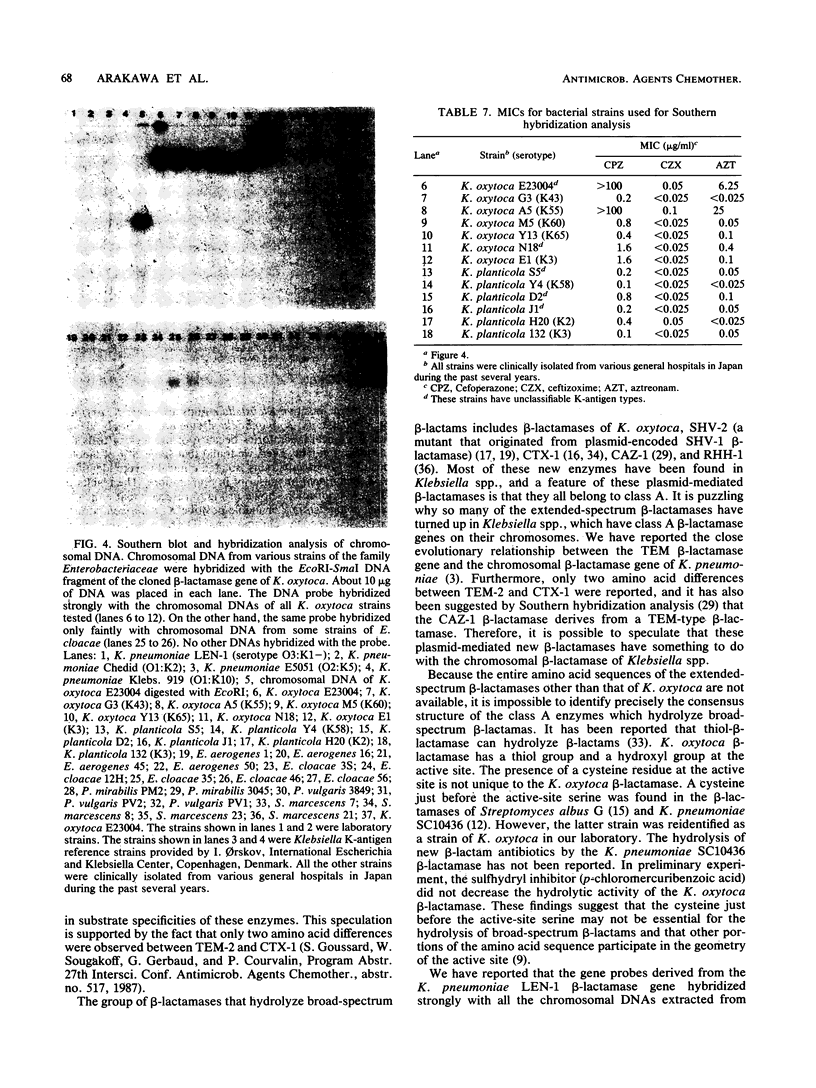


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Scott G. K. Partial amino acid sequence of penicillinase coded by Escherichia coli plasmid R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3732–3736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P. The amino acid sequence of Staphylococcus aureus penicillinase. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):197–218. doi: 10.1042/bj1510197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa Y., Ohta M., Kido N., Fujii Y., Komatsu T., Kato N. Close evolutionary relationship between the chromosomally encoded beta-lactamase gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae and the TEM beta-lactamase gene mediated by R plasmids. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome-Smith J. K., Edelman A., Yousif S., Spratt B. G. The nucleotide sequences of the ponA and ponB genes encoding penicillin-binding protein 1A and 1B of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 1;147(2):437–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Sykes R. B. Methodology for the study of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):6–10. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Tanaka S. K., Bonner D. P., Sykes R. B. Resistance caused by decreased penetration of beta-lactam antibiotics into Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):555–560. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel E. L., Gagnon J., Waley S. G. Structural and kinetic studies on beta-lactamase K1 from Klebsiella aerogenes. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):343–347. doi: 10.1042/bj2340343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., McCarthy B. J., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. DNA sequence analysis of the transposon Tn3: three genes and three sites involved in transposition of Tn3. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., Moult J. Bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics: crystal structure of beta-lactamase from Staphylococcus aureus PC1 at 2.5 A resolution. Science. 1987 May 8;236(4802):694–701. doi: 10.1126/science.3107125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Grundström T. ampC cephalosporinase of Escherichia coli K-12 has a different evolutionary origin from that of beta-lactamases of the penicillinase type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris B., De Meester F., Galleni M., Frère J. M., Van Beeumen J. The K1 beta-lactamase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):561–567. doi: 10.1042/bj2430561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris B., De Meester F., Galleni M., Reckinger G., Coyette J., Frere J. M., Van Beeumen J. The beta-lactamase of Enterobacter cloacae P99. Chemical properties, N-terminal sequence and interaction with 6 beta-halogenopenicillanates. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):241–248. doi: 10.1042/bj2280241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris B., Dusart J., Frere J. M., van Beeumen J., Emanuel E. L., Petursson S., Gagnon J., Waley S. G. The active site of the P99 beta-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):271–274. doi: 10.1042/bj2230271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris B., Ghuysen J. M., Dive G., Renard A., Dideberg O., Charlier P., Frère J. M., Kelly J. A., Boyington J. C., Moews P. C. The active-site-serine penicillin-recognizing enzymes as members of the Streptomyces R61 DD-peptidase family. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2500313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F. W., Williamson R., Tran Van Nhieu G., Carlet J., Acar J. F., Gutmann L. Dissemination of the novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase CTX-1, which confers resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins, and its inhibition by beta-lactamase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliebe C., Nies B. A., Meyer J. F., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Evolution of plasmid-coded resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott-Hunziker V., Petursson S., Jayatilake G. S., Waley S. G., Jaurin B., Grundström T. Active sites of beta-lactamases. The chromosomal beta-lactamases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1982 Mar 1;201(3):621–627. doi: 10.1042/bj2010621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korfmann G., Kliebe C., Wiedemann B. Beta-lactam antibiotics and selection of resistance: speculation on the evolution of R-plasmids. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Oct;18 (Suppl 100):113–121. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_c.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Morand A., Guionie M., Heitz M., Pitton J. S. Bêtalactamases de Klebsiella oxytoca: étude de leur action sur les céphalosporines de troisième génération. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1986 Jun;34(5 Pt 2):611–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Lindquist S., Normark S. Inactivation of the ampD gene causes semiconstitutive overproduction of the inducible Citrobacter freundii beta-lactamase. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1923–1928. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1923-1928.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Normark S. Sequence of the Citrobacter freundii OS60 chromosomal ampC beta-lactamase gene. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 2;156(3):441–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Westman L., Normark S. Regulatory components in Citrobacter freundii ampC beta-lactamase induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Sawai T., Tazaki T., Yamagishi S., Mitsuhashi S. Characterization of the chromosomally mediated penicillinase in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Jpn J Microbiol. 1972 May;16(3):169–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1972.tb00645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Maruyama I. N., Soma M., Kato J., Suzuki H., Horota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: nucleotide sequence of the gene for penicillin-binding protein 3. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00330881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit A., Sirot D. L., Chanal C. M., Sirot J. L., Labia R., Gerbaud G., Cluzel R. A. Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae more resistant to ceftazidime than to other broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):626–630. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Yamagishi S., Mitsuhashi S. Penicillinases of Klebsiella pneumoniae and their phylogenetic relationship to penicillinases mediated by R factors. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1045–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1045-1054.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Harwood B. G., Arentzen R. Thiol-beta-lactamase: replacement of the active-site serine of RTEM beta-lactamase by a cysteine residue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7157–7160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot D., Sirot J., Labia R., Morand A., Courvalin P., Darfeuille-Michaud A., Perroux R., Cluzel R. Transferable resistance to third-generation cephalosporins in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae: identification of CTX-1, a novel beta-lactamase. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Sep;20(3):323–334. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloma A., Gross M. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the type I beta-lactamase gene from Bacillus cereus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4997–5004. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. C., Wheat P. F., Winstanley T. G., Cox D. M., Plested S. J. Novel beta-lactamase in a clinical isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae conferring unusual resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Dec;20(6):919–921. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer G. V., Plamann M. D., Stauffer L. T. Construction and expression of hybrid plasmids containing the Escherichia coli glyA genes. Gene. 1981 Jun-Jul;14(1-2):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of the ampicillin resistance gene of Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3737–3741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Then R. L., Glauser M. P., Angehrn P., Arisawa M. Cephalosporin resistance in strains of Klebsiella oxytoca isolated during antibiotic therapy. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Jul;254(4):469–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsui Y., Yokota T. Role of an altered penicillin-binding protein in methicillin- and cephem-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):397–403. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu H., Nikaido H. Role of beta-lactam hydrolysis in the mechanism of resistance of a beta-lactamase-constitutive Enterobacter cloacae strain to expanded-spectrum beta-lactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):393–398. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Sequence of active site peptides from the penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidase of Bacillus subtilis. Mechanism of penicillin action and sequence homology to beta-lactamases. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3964–3976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]