Abstract
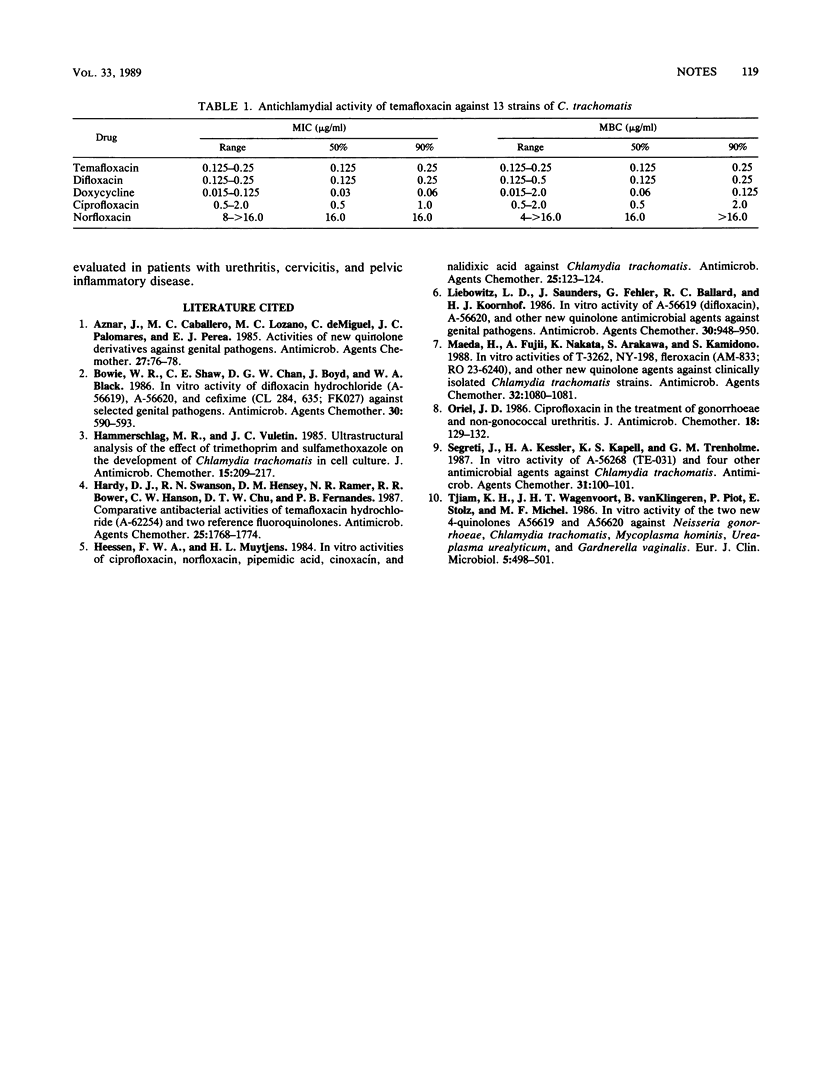
The in vitro activity of temafloxacin (A-62254), a new quinolone antibiotic, against 13 strains of Chlamydia trachomatis was determined and compared with those of doxycycline, norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and difloxacin. Temafloxacin and difloxacin were the most active quinolones tested, with bactericidal activity comparable to that of doxycycline.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aznar J., Caballero M. C., Lozano M. C., de Miguel C., Palomares J. C., Perea E. J. Activities of new quinoline derivatives against genital pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):76–78. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowie W. R., Shaw C. E., Chan D. G., Boyd J., Black W. A. In vitro activity of difloxacin hydrochloride (A-56619), A-56620, and cefixime (CL 284,635; FK 027) against selected genital pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):590–593. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschlag M. R., Vuletin J. C. Ultrastructural analysis of the effect of trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole on the development of Chlamydia trachomatis in cell culture. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Feb;15(2):209–217. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy D. J., Swanson R. N., Hensey D. M., Ramer N. R., Bower R. R., Hanson C. W., Chu D. T., Fernandes P. B. Comparative antibacterial activities of temafloxacin hydrochloride (A-62254) and two reference fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1768–1774. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heessen F. W., Muytjens H. L. In vitro activities of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, pipemidic acid, cinoxacin, and nalidixic acid against Chlamydia trachomatis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):123–124. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz L. D., Saunders J., Fehler G., Ballard R. C., Koornhof H. J. In vitro activity of A-56619 (difloxacin), A-56620, and other new quinolone antimicrobial agents against genital pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):948–950. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Fujii A., Nakata K., Arakawa S., Kamidono S. In vitro activities of T-3262, NY-198, fleroxacin (AM-833; RO 23-6240), and other new quinolone agents against clinically isolated Chlamydia trachomatis strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):1080–1081. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriel J. D. Ciprofloxacin in the treatment of gonorrhoea and non-gonococcal urethritis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):129–132. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segreti J., Kessler H. A., Kapell K. S., Trenholme G. M. In vitro activity of A-56268 (TE-031) and four other antimicrobial agents against Chlamydia trachomatis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jan;31(1):100–101. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjiam K. H., Wagenvoort J. H., van Klingeren B., Piot P., Stolz E., Michel M. F. In vitro activity of the two new 4-quinolones A56619 and A56620 against Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma hominis, Ureaplasma urealyticum and Gardnerella vaginalis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;5(5):498–501. doi: 10.1007/BF02017690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


