Abstract
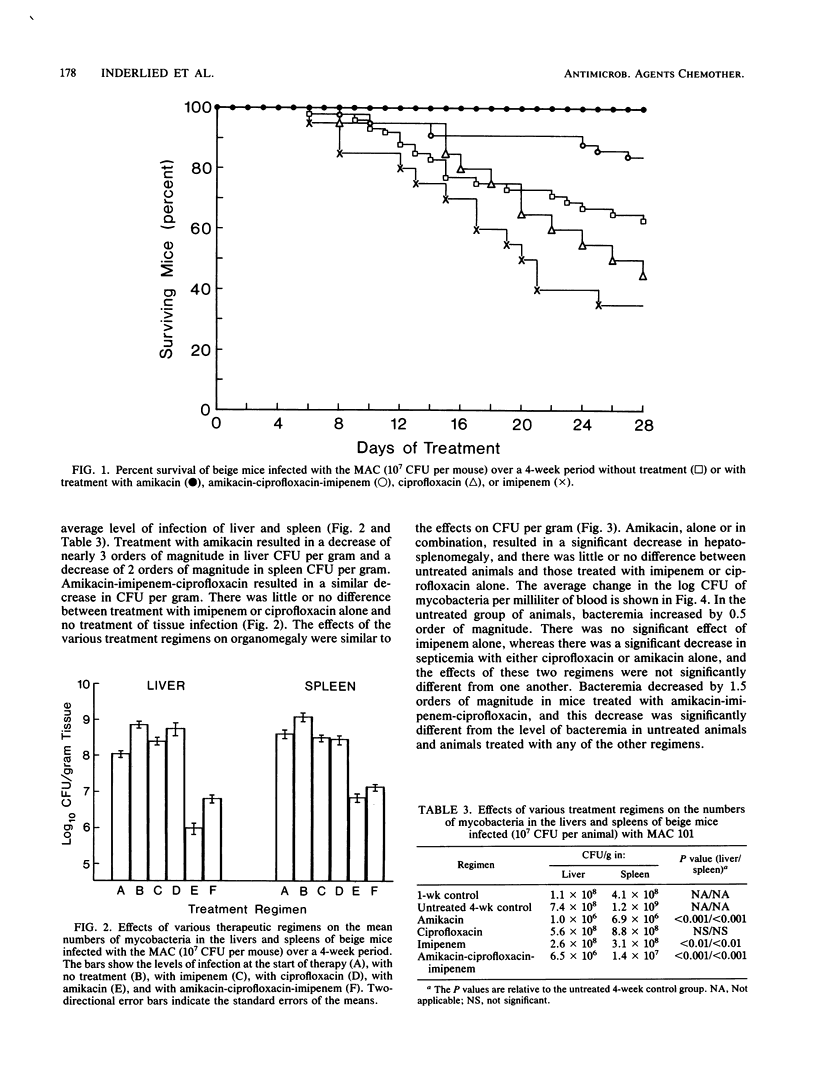
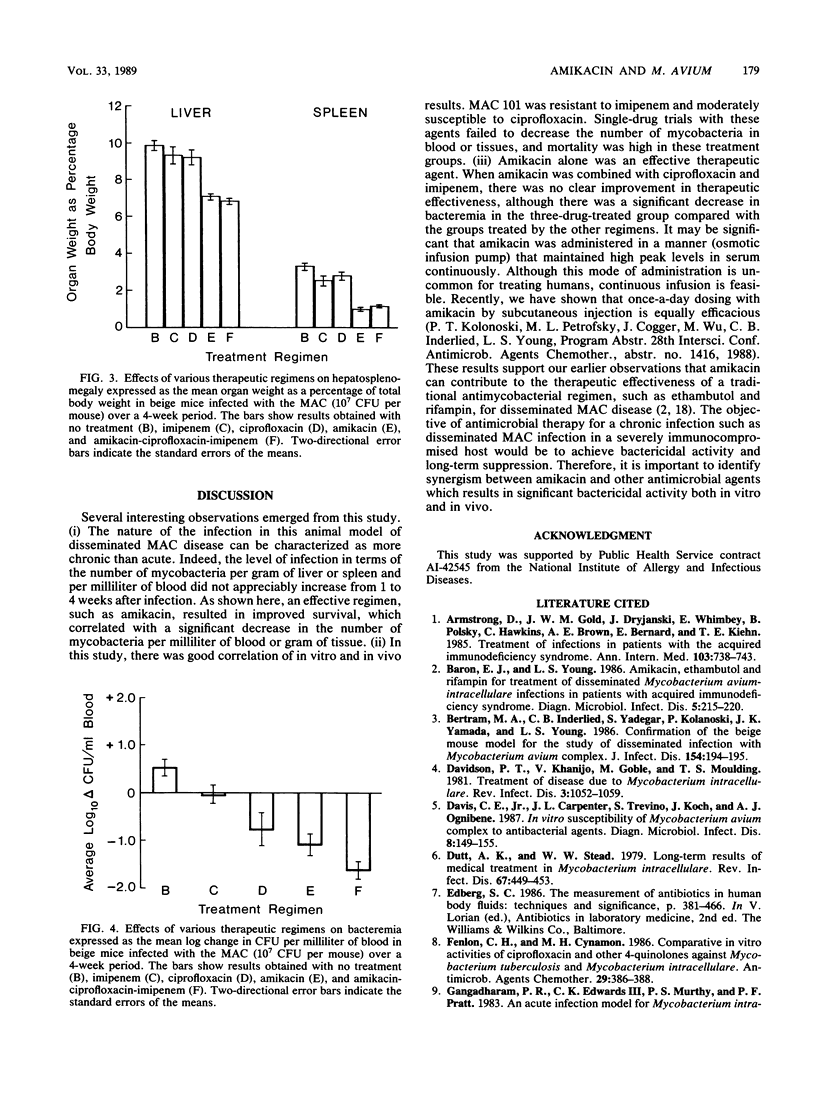
The Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) is a common cause of disseminated infection in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and is increasingly seen as a cause of infection in other immunocompromised patients. Traditional antimycobacterial therapy often is ineffective, and there is a clear need for antibiotics with proven activity against the MAC. Three agents, amikacin, ciprofloxacin, and imipenem, were tested in vitro for activity against MAC strain 101. Amikacin was bacteriostatic, with an MIC of 4.8 micrograms/ml, which is significantly lower than the concentration in serum obtained with standard dosing. Imipenem and ciprofloxacin had little or no activity alone (MICs, greater than 16 and 4.7 micrograms/ml, respectively), but when they were combined with amikacin there was bactericidal activity. Each agent was tested individually and in combination by using the beige mouse model of disseminated MAC infection. There was no mortality in a group of animals infected with MAC 101 and treated with amikacin alone; also, there was a significant decrease in the infection of the blood, liver, and spleen. There was no apparent improvement in therapeutic effectiveness when amikacin was combined with the other agents. Neither ciprofloxacin nor imipenem was active as a single agent, which was consistent with the in vitro activities of these agents. Amikacin in combination with traditional antimycobacterial agents warrants further study as potential therapy for disseminated MAC infections.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D., Gold J. W., Dryjanski J., Whimbey E., Polsky B., Hawkins C., Brown A. E., Bernard E., Kiehn T. E. Treatment of infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):738–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron E. J., Young L. S. Amikacin, ethambutol, and rifampin for treatment of disseminated Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infections in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;5(3):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram M. A., Inderlied C. B., Yadegar S., Kolanoski P., Yamada J. K., Young L. S. Confirmation of the beige mouse model for study of disseminated infection with Mycobacterium avium complex. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):194–195. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson P. T., Khanijo V., Goble M., Moulding T. S. Treatment of disease due to Mycobacterium intracellulare. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):1052–1059. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.5.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. E., Jr, Carpenter J. L., Trevino S., Koch J., Ognibene A. J. In vitro susceptibility of Mycobacterium avium complex to antibacterial agents. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;8(3):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutt A. K., Stead W. W. Long-term results of medical treatment in Mycobacterium intracellulare infection. Am J Med. 1979 Sep;67(3):449–453. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90792-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenlon C. H., Cynamon M. H. Comparative in vitro activities of ciprofloxacin and other 4-quinolones against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium intracellulare. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):386–388. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good R. C., Snider D. E., Jr Isolation of nontuberculous mycobacteria in the United States, 1980. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):829–833. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifets L. B., Lindholm-Levy P. J. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activity of ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex. Tubercle. 1987 Dec;68(4):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(87)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr, Mason U. G., 3rd, Farhi D. C., Iseman M. D. Disseminated infection with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. A report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1985 Jan;64(1):36–48. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198501000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inderlied C. B., Young L. S., Yamada J. K. Determination of in vitro susceptibility of Mycobacterium avium complex isolates to antimycobacterial agents by various methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1697–1702. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Roberts G. D. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin against the Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 May;7(1):89–91. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders W. E., Jr, Hartwig C., Schneider N., Cacciatore R., Valdez H. Activity of amikacin against Mycobacteria in vitro and in murine tuberculosis. Tubercle. 1982 Sep;63(3):201–208. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(82)80031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky E. Nontuberculous mycobacteria and associated diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jan;119(1):107–159. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajko D. M., Nassos P. S., Hadley W. K. Broth microdilution testing of susceptibilities to 30 antimicrobial agents of Mycobacterium avium strains from patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1579–1584. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Berlin O. G., Inderlied C. B. Activity of ciprofloxacin and other fluorinated quinolones against mycobacteria. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Inderlied C. B., Berlin O. G., Gottlieb M. S. Mycobacterial infections in AIDS patients, with an emphasis on the Mycobacterium avium complex. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1024–1033. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Mycobacterium avium complex infection. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):863–867. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., DeYoung D. R., Roberts G. D. In vitro synergistic activity of ethambutol, isoniazid, kanamycin, rifampin, and streptomycin against Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):148–150. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


