Abstract
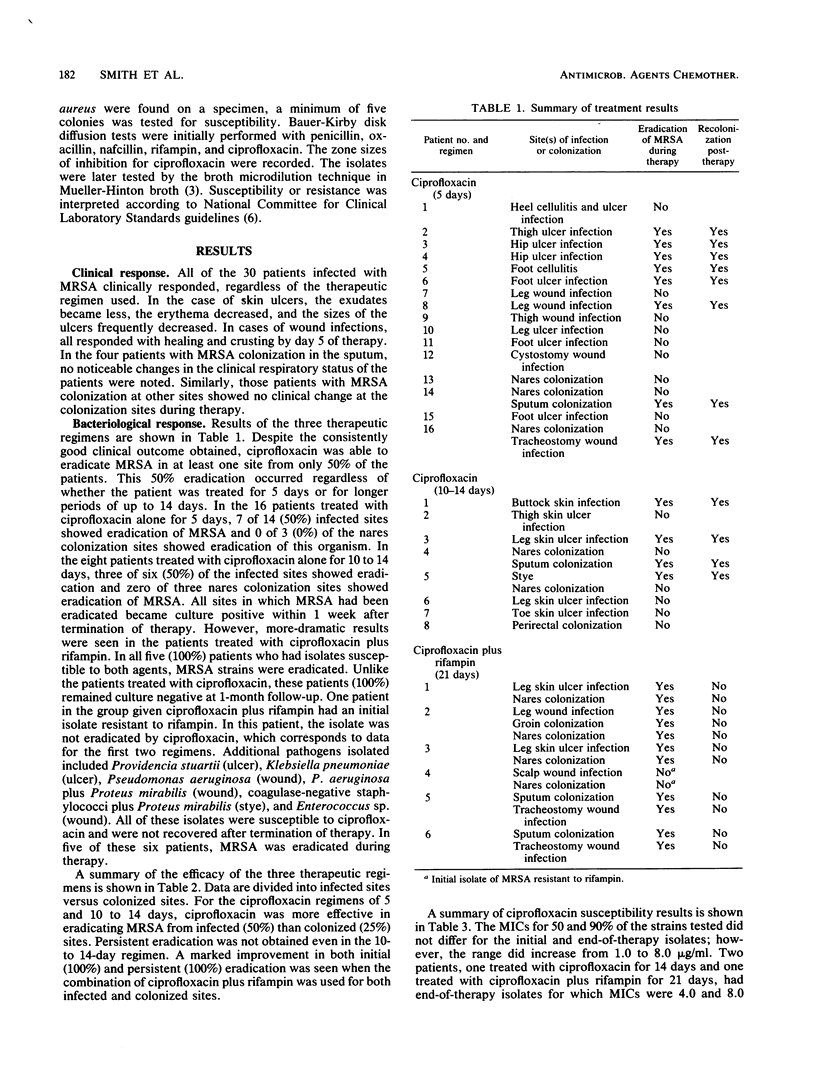
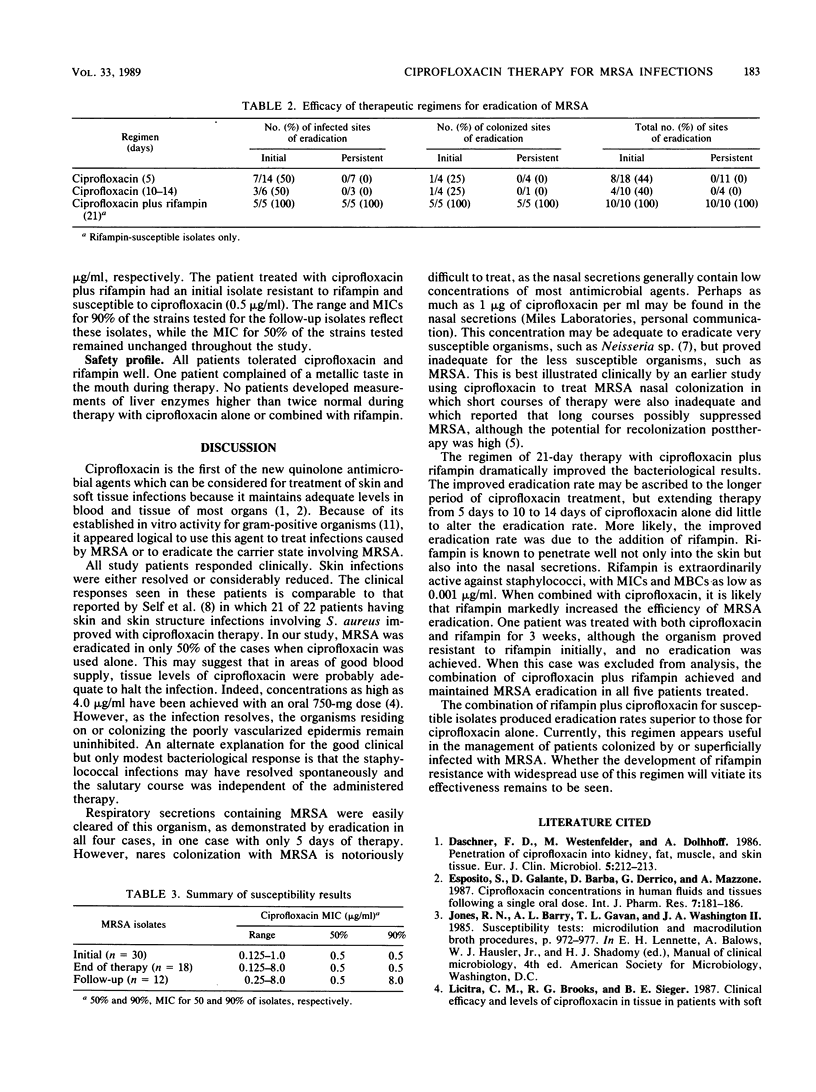
Thirty patients were treated for colonization or for skin and soft tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Three treatment regimens were evaluated, each progressively more aggressive. Our regimen was 750 mg of ciprofloxacin twice daily for 5 days, the second regimen was 750 mg of ciprofloxacin twice daily for 10 to 14 days, and the final regimen was 750 mg of ciprofloxacin twice daily plus 300 mg of rifampin twice daily for 21 days. It appears that ciprofloxacin alone produced an initial eradication rate in at least one site in 50% of the patients, regardless of whether the treatment was for 5 or up to 14 days. All of the patients with eradication became recolonized within 1 week posttherapy. When rifampin was combined with ciprofloxacin, the eradication rate was 100% when the isolates were susceptible to both agents, and these patients remained free of methicillin-resistant S. aureus at 1-week and 1-month follow-ups.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crawford J., Eye-Boland M. K., Cohen H. J. Clinical utility of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and plasma protein analysis in the elderly. Am J Med. 1987 Feb;82(2):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daschner F. D., Westenfelder M., Dalhoff A. Penetration of ciprofloxacin into kidney, fat, muscle and skin tissue. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;5(2):212–213. doi: 10.1007/BF02013992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito S., Galante D., Barba D., D'Errico G., Mazzone A., Montanaro S. Ciprofloxacin concentrations in human fluids and tissues following a single oral dose. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 1987;7(3):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Ruane P. J., Johnston L., Wong P., Wheelock J. P., MacDonald K., Reinhardt J. F., Johnson C. C., Statner B., Blomquist I. Ciprofloxacin for eradication of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley M. P., Dworzack D. L., Horowitz E. A., Cuevas T. A., Sanders W. E., Jr, Sanders C. C. Efficacy of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carriers of Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):211–213. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Eng R. H. Activity of ciprofloxacin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):688–691. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Eng R. H., Berman E. The effect of ciprofloxacin on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Mar;17(3):287–295. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.3.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M. In vitro comparison of A-56619, A-56620, amifloxacin, ciprofloxacin, enoxacin, norfloxacin, and ofloxacin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):325–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


