Abstract
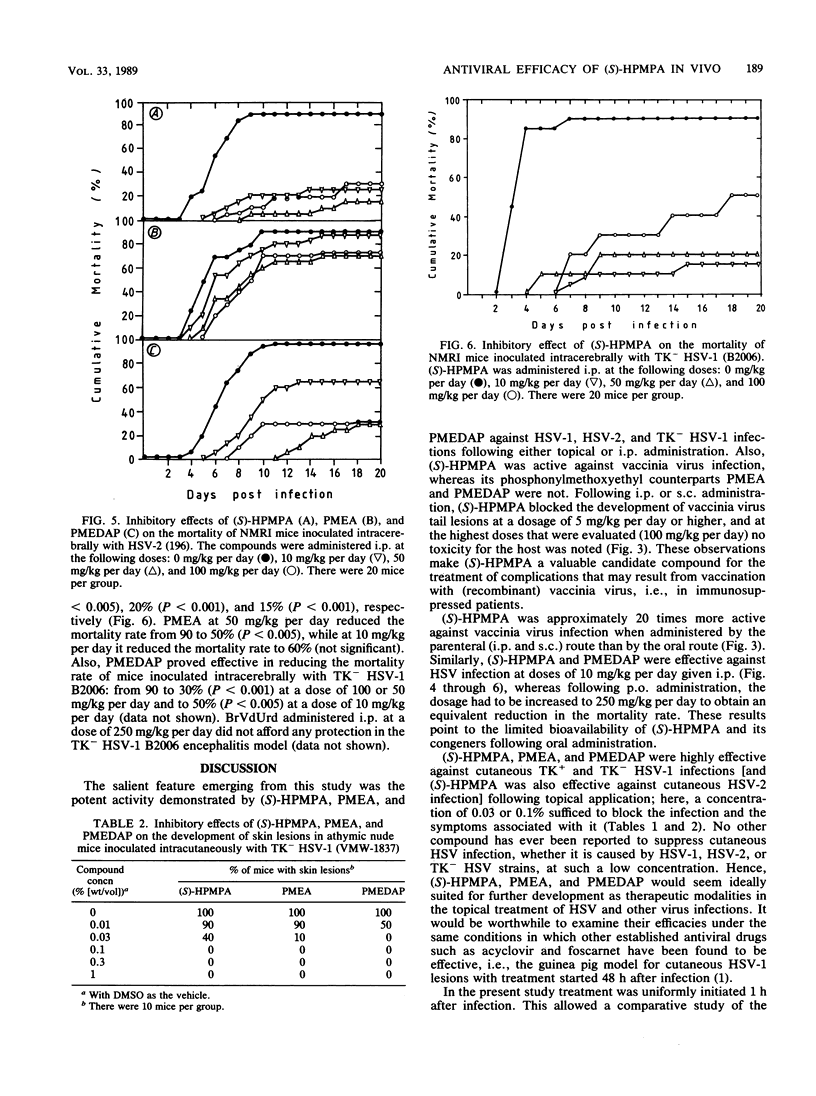
The phosphonylmethoxyalkyl derivatives (S)-9-(3-hydroxy-2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine [(S)-HPMPA], 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine (PMEA), and 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)-2,6-diaminopurine (PMEDAP) were evaluated for their in vivo efficacies in several animal model infections, i.e., mice infected intravenously with vaccinia virus and mice infected intracutaneously, intraperitoneally, or intracerebrally with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) or type 2 (HSV-2) or thymidine kinase-deficient (TK-) HSV-1. (S)-HPMPA inhibited the development of tail lesions caused by vaccinia virus if it was administered intraperitoneally or subcutaneously at a dosage as low as 5 mg/kg per day. All three compounds completely suppressed the development of skin lesions and the mortality associated therewith in hairless or athymic nude mice inoculated intracutaneously with HSV-1 or TK- HSV-1, if they were administered topically at a concentration as low as 0.1%; when (S)-HPMPA was applied topically at a concentration of greater than or equal to 0.3%, it completely abrogated mortality resulting from intracutaneous HSV-2 infection. Most dramatic were the effects shown by the compounds in mice inoculated intracerebrally with HSV-1, HSV-2, or TK- HSV-1, in which all three compounds given intraperitoneally at a dose of 50 or 100 mg/kg per day effected a significant reduction in the mortality rate of HSV-1-infected mice. The mortality of mice infected intracerebrally with HSV-2 or TK- HSV-1 was significantly reduced even when (S)-HPMPA was given at doses as low as 10 mg/kg per day. These data point to the great potential of the phosphonylmethoxyalkylpurines for both topical and parenteral treatment of HSV-1, HSV-2, and TK- HSV-1 infections.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alenius S., Berg M., Broberg F., Eklind K., Lindborg B., Oberg B. Therapeutic effects of foscarnet sodium and acyclovir on cutaneous infections due to herpes simplex virus type 1 in guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):569–573. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arzuza O., García-Villalón D., Tabarés E., Gil-Fernández C., De Clercq E. Inhibition of African swine fever virus DNA synthesis by (S)-9-(3-hydroxy-2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90644-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba M., Konno K., Shigeta S., De Clercq E. In vitro activity of (S)-9-(3-hydroxy-2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine against newly isolated clinical varicella-zoster virus strains. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;6(2):158–160. doi: 10.1007/BF02018198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba M., Mori S., Shigeta S., De Clercq E. Selective inhibitory effect of (S)-9-(3-hydroxy-2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine and 2'-nor-cyclic GMP on adenovirus replication in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):337–339. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Descamps J., Verhelst G., Walker R. T., Jones A. S., Torrence P. F., Shugar D. Comparative efficacy of antiherpes drugs against different strains of herpes simplex virus. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):563–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Holý A., Rosenberg I., Sakuma T., Balzarini J., Maudgal P. C. A novel selective broad-spectrum anti-DNA virus agent. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):464–467. doi: 10.1038/323464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Luczak M., Shugar D., Torrence P. F., Waters J. A., Witkop B. Effect of cytosine, arabinoside, iododeoxyuridine, ethyldeoxyuridine, thiocyanatodeoxyuridine, and ribavirin on tail lesion formation in mice infected with vaccinia virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Mar;151(3):487–490. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Rosenwirth B. Selective in vitro and in vivo activities of 5-(2-haloalkyl)pyrimidine nucleoside analogs, particularly 5-(2-chloroethyl)-2'-deoxyuridine, against herpes simplex virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):246–251. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Sakuma T., Baba M., Pauwels R., Balzarini J., Rosenberg I., Holý A. Antiviral activity of phosphonylmethoxyalkyl derivatives of purine and pyrimidines. Antiviral Res. 1987 Dec;8(5-6):261–272. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(87)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Fernández C., De Clercq E. Comparative efficacy of broad-spectrum antiviral agents as inhibitors of African swine fever virus replication in vitro. Antiviral Res. 1987 Mar;7(3):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Fernández C., García-Villalón D., De Clercq E., Rosenberg I., Holý A. Phosphonylmethoxyalkylpurines and -pyrimidines as inhibitors of African swine fever virus replication in vitro. Antiviral Res. 1987 Dec;8(5-6):273–281. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(87)80005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanella B. C., Stehlin J. S. Heterotransplantation of human malignant tumors in "nude" thymusless mice. I. Breeding and maintenance of "nude" mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Aug;51(2):615–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., DeClercq E., Pagano J. S. Novel acyclic adenosine analogs inhibit Epstein-Barr virus replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1431–1433. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudgal P. C., De Clercq E., Huyghe P. Efficacy of (S)-HPMPA against thymidine kinase-deficient herpes simplex virus-keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Feb;28(2):243–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterhaus A. D., Groen J., De Clercq E. Selective inhibitory effects of (S)-9-(3-hydroxy-2-phosphonyl-methoxypropyl) adenine and 1-(2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-iodouracil on seal herpesvirus (phocid herpesvirus 1) infection in vitro. Antiviral Res. 1987 May;7(4):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels R., Balzarini J., Schols D., Baba M., Desmyter J., Rosenberg I., Holy A., De Clercq E. Phosphonylmethoxyethyl purine derivatives, a new class of anti-human immunodeficiency virus agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):1025–1030. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinckier F., Boogaerts M., De Clerck D., De Clercq E. Chronic herpetic infection in an immunocompromised patient: report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1987 Aug;45(8):723–728. doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(87)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Votruba I., Bernaerts R., Sakuma T., De Clercq E., Merta A., Rosenberg I., Holý A. Intracellular phosphorylation of broad-spectrum anti-DNA virus agent (S)-9-(3-hydroxy-2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine and inhibition of viral DNA synthesis. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;32(4):524–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Clercq E. Topical treatment of cutaneous herpes simplex virus infection in hairless mice with (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine and related compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):155–159. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Clercq E. Virus-drug resistance: thymidine kinase-deficient (TK-) mutants of herpes simplex virus. Therapeutic approaches. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 1987;23(4):841–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]