Abstract
Mutants of Escherichia coli susceptible to vancomycin were isolated after mutagenesis with nitrosoguanidine. One such mutant was studied extensively. Multiple regression analysis of the relationship between physical properties of 20 glycopeptides and their in vitro activities against the vancomycin-susceptible mutant revealed a significant correlation with molecular mass (P = 0.007). pI, hydrophobicity, and affinity of the glycopeptide for the pentapeptide target were not as important for activity. This suggested that a block of access of the antibiotic to its target could be the major factor determining activity. Outer membrane proteins of the vancomycin-susceptible mutant, resistant parent, and revertant strains appeared normal. The mutant exhibited increased susceptibility to both erythromycin and fusidic acid which was lost in single-step revertants to vancomycin resistance. Polymyxin B nonapeptide was synergistic with erythromycin and fusidic acid against the parent and revertant but not against the susceptible mutant. Analysis of the susceptibilities of control strains of E. coli and Salmonella typhimurium with known defects in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) synthesis revealed that core LPS mutants (Re chemotype) were phenotypically similar to the E. coli mutant under study. However, the LPS core of the mutant migrated slightly less rapidly on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis than wild-type or revertant core LPS and did not resemble Re chemotype LPS core obtained from Salmonella rfaC and rfaD mutants. These data suggest that defects in LPS core structure other than loss of heptose moieties may also be important in loss of resistance to large, hydrophilic molecules such as glycopeptides.
Full text
PDF
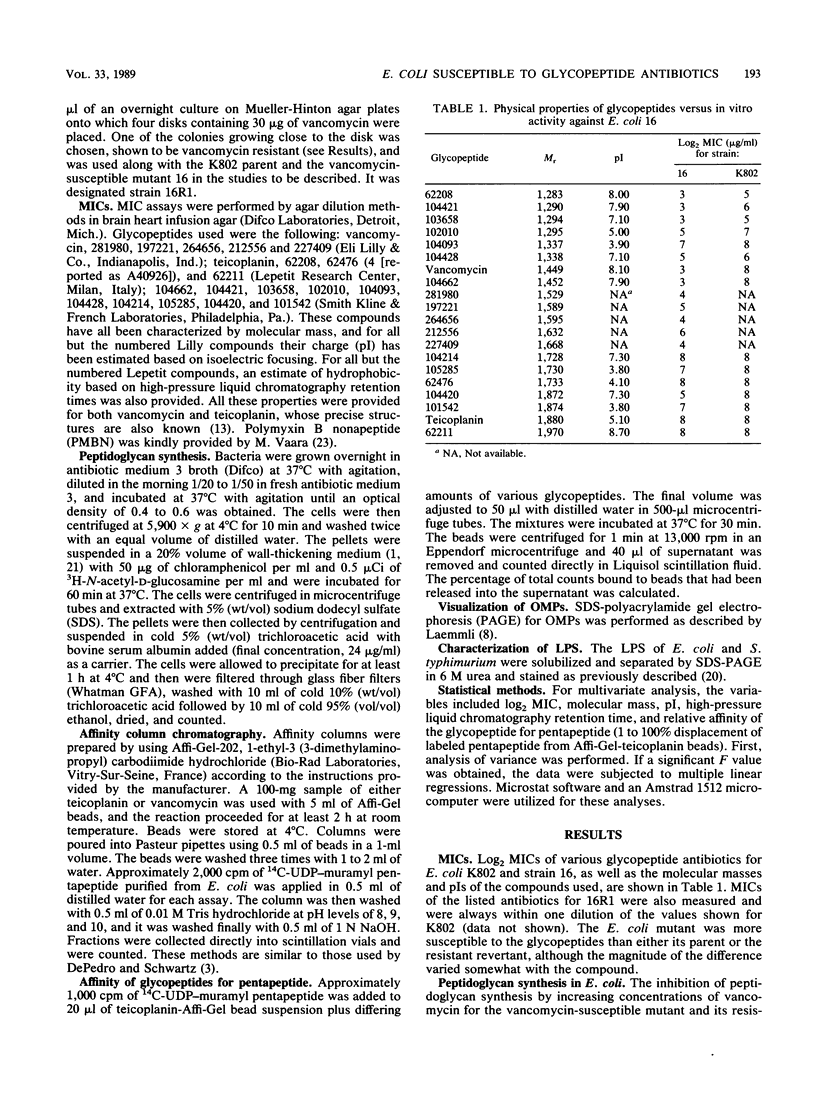
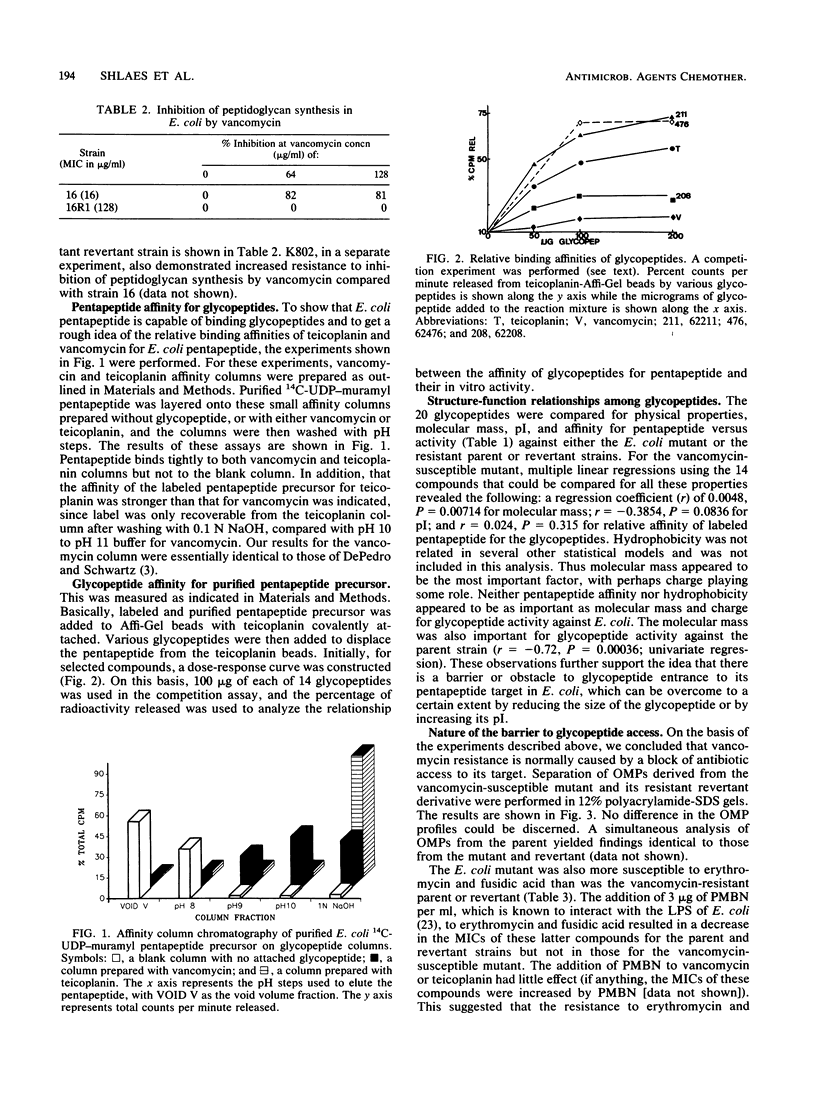



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett J. F., Schramm V. L., Shockman G. D. Hydrolysis of soluble, linear, un-cross-linked peptidoglycans by endogenous bacterial N-acetylmuramoylhydrolases. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):520–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.520-526.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. S., Georgopapadakou N. H. Routes of quinolone permeation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):438–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. P., Selva E., Gastaldo L., Berti M., Pallanza R., Ripamonti F., Ferrari P., Denaro M., Arioli V., Cassani G. A40926, a new glycopeptide antibiotic with anti-Neisseria activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1961–1966. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Leive L., Mäkelä P. H., Rietschel E. T., Strittmatter W., Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide nomenclature--past, present, and future. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):699–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.699-705.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. T., Koeltzow D. E., Stocker B. A. Genetic transfer of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide antigens to Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;111(3):758–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.3.758-770.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L., Telesetsky S., Coleman W. G., Jr, Carr D. Tetracyclines of various hydrophobicities as a probe for permeability of Escherichia coli outer membranes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):539–544. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Transmembrane diffusion of some hydrophobic substances. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 16;433(1):118–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parenti F. Glycopeptide antibiotics. J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;28(2):136–140. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb05737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins H. R., Nieto M. The chemical basis for the action of the vancomycin group of antibiotics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):348–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Fesik S. W., McGroarty E. J. Decreased binding of antibiotics to lipopolysaccharides from polymyxin-resistant strains of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):230–237. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Clark D. C., Wotton S. Indirect method for assessing the penetration of beta-lactamase-nonsusceptible penicillins and cephalosporins in Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):215–218. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M., Hancock R. E., Sawyer J. G., Haug A., McGroarty E. J. Enhanced binding of polycationic antibiotics to lipopolysaccharide from an aminoglycoside-supersusceptible, tolA mutant strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):649–655. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J., Kuo T. T., MacPhee D. G. The effect of defined lipopolysaccharide core defects upon antibiotic resistances of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):223–234. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocque W. J., Fesik S. W., Haug A., McGroarty E. J. Polycation binding to isolated lipopolysaccharide from antibiotic-hypersusceptible mutant strains of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Mar;32(3):308–313. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.3.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tynecka Z., Ward J. B. Peptidoglycan synthesis in Bacillus licheniformis. The inhibition of cross-linking by benzylpenicillin and cephaloridine in vivo accompanied by the formation of soluble peptidoglycan. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):253–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1460253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Sarvas M. Decreased binding of polymyxin by polymyxin-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):664–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.664-667.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljanen P., Vaara M. Susceptibility of gram-negative bacteria to polymyxin B nonapeptide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):701–705. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. O., Lee J. C. Integration of synthetic globin genes into an E. coli plasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Aug;3(8):1961–1971. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.8.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]