Abstract
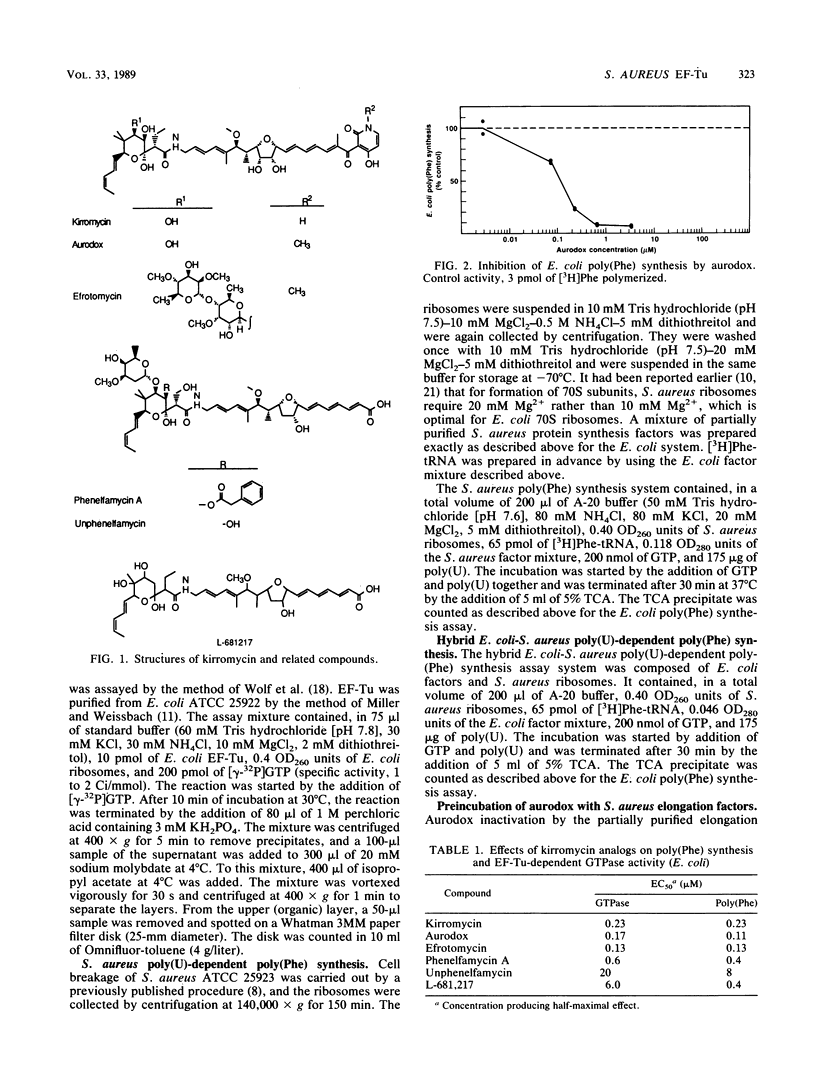
Six kirromycin analogs (elfamycins) were compared on the basis of their inhibition of Escherichia coli poly(U)-directed poly(Phe) synthesis and stimulation of elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu)-associated GTPase activity. The elfamycins tested were kirromycin, aurodox, efrotomycin, phenelfamycin A, unphenelfamycin, and L-681,217. The last three lack the pyridone ring present in the other elfamycins. All the elfamycins inhibited poly(U)-dependent poly(Phe) synthesis and stimulated EF-Tu-associated GTPase activity, suggesting that the pyridone ring is not essential for activity. The six elfamycins were also examined in a poly(U)-directed, poly(Phe)-synthesizing system derived from Staphylococcus aureus and had 50% inhibitory concentrations of greater than or equal to 1 mM. When S. aureus ribosomes and E. coli elongation factors were combined in a hybrid poly(Phe)-synthesizing system, aurodox produced essentially complete inhibition of poly(Phe) synthesis with a 50% inhibitory concentration of 0.13 microM. This suggests that the observed high MICs of kirromycin and its congeners in S. aureus reflect a kirromycin-resistant EF-Tu rather than permeability constraints.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber J., Carver J. A., Leberman R., Tebb G. M. The molecular basis of kirromycin (mocimycin) action; a 1H NMR study using deuterated elongation factor Tu. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1988 Feb;41(2):202–206. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.41.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinali G. Synthetic analogs of aurodox and kirromycin active on elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1981 Aug;34(8):1039–1045. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.34.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinali G., Wolf H., Parmeggiani A. Effect of kirromycin on elongation factor Tu. Location of the catalytic center for ribosome-elongation-factor-Tu GTPase activity on the elongation factor. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):55–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Blumenthal T. Conformational transition of protein synthesis elongation factor Tu induced by guanine nucleotides. Modulation by kirromycin and elongation factor Ts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5383–5387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duisterwinkel F. J., De Graaf J. M., Schretlen P. J., Kraal B., Bosch L. A mutant elongation factor Tu which does not immobilize the ribosome upon binding of kirromycin. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):7–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duisterwinkel F. J., de Graaf J. M., Kraal B., Bosch L. A kirromycin resistant elongation factor EF-Tu from Escherichia coli contains a threonine instead of an alanine residue in position 375. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 17;131(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80894-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E., Wolf H., Hantke K., Parmeggiani A. Elongation factor Tu resistant to kirromycin in an Escherichia coli mutant altered in both tuf genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4341–4345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Smith S. A., Bonner D. P. Penicillin-binding proteins in a Staphylococcus aureus strain resistant to specific beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):172–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempf A. J., Wilson K. E., Hensens O. D., Monaghan R. L., Zimmerman S. B., Dulaney E. L. L-681,217, a new and novel member of the efrotomycin family of antibiotics. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1986 Oct;39(10):1361–1367. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.39.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C. Protein synthesis in a cell-free extract from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):80–86. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.80-86.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Weissbach H. Studies on the purification and properties of factor Tu from E. coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):26–37. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmeggiani A., Swart G. W. Mechanism of action of kirromycin-like antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:557–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swart G. W., Parmeggiani A., Kraal B., Bosch L. Effects of the mutation glycine-222----aspartic acid on the functions of elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):2047–2054. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meide P. H., Duisterwinkel F. J., De Graaf J. M., Kraal B., Bosch L., Douglass J., Blumenthal T. Molecular properties of two mutant species of the elongation factor Tu. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Kirromycin, an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis that acts on elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Mechanism of the inhibition of protein synthesis by kirromycin. Role of elongation factor Tu and ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wörner W., Wolf H. Kirromycin-resistant elongation factor Tu from wild-type of Lactobacillus brevis. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 20;146(2):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80944-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


