Abstract
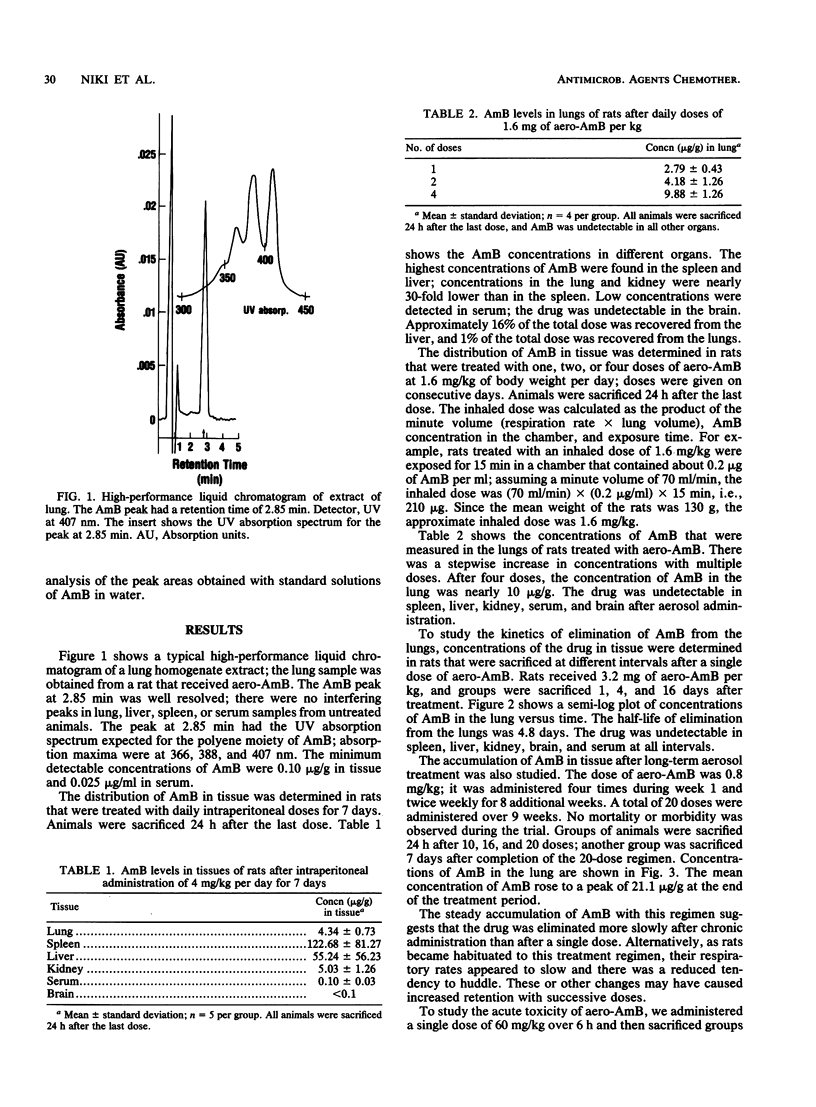
The distributions of amphotericin B (AmB) in tissue were compared after intraperitoneal or aerosol administration. Rats were sacrificed 24 h after receiving single or repeated daily doses; AmB concentrations in tissues were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. After intraperitoneal doses of 4 mg/kg of body weight per day for 7 days, mean concentrations of AmB were 122.7, 55.2, and 4.31 micrograms/g in the spleen, liver, and lung, respectively. After aerosol doses (aero-AmB) of 1.6 mg/kg per day, the mean concentrations of AmB in the lung were 2.79 micrograms/g after a single dose and 9.88 micrograms/g after four doses, while the drug was undetectable (less than 0.1 micrograms/g) in serum, spleen, liver, kidney, and brain. The half-life of elimination of AmB from the lungs was 4.8 days according to serial sacrifices done after a single dose of 3.2 mg of aero-AmB per kg. Treatment with 60 mg of aero-AmB per kg was well tolerated and produced no histopathologic changes in the lungs. The aerosol route was much more efficient than the systemic route in delivering AmB to the lungs, and it limited the accumulation of AmB in other organs. Because AmB is eliminated slowly, infrequent dosing schedules can be used. These pharmacokinetic characteristics and its proven effectiveness in an animal model make aero-AmB a highly promising new method for the prevention of pulmonary aspergillosis. Aero-AmB should also be considered for use as an adjunct to intravenous AmB for treatment of fungal pneumonias.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christiansen K. J., Bernard E. M., Gold J. W., Armstrong D. Distribution and activity of amphotericin B in humans. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):1037–1043. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collette N., van der Auwera P., Lopez A. P., Heymans C., Meunier F. Tissue concentrations and bioactivity of amphotericin B in cancer patients treated with amphotericin B-deoxycholate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):362–368. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouhet E., Dupont B. Evolution of antifungal agents: past, present, and future. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9 (Suppl 1):S4–14. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_1.s4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerson S. L., Talbot G. H., Hurwitz S., Strom B. L., Lusk E. J., Cassileth P. A. Prolonged granulocytopenia: the major risk factor for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Mar;100(3):345–351. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-3-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara M., Seth V. K., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of six clinical isolates of Aspergillus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):908–914. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Young L. S., Armstrong D., Yu B. Aspergillosis complicating neoplastic disease. Am J Med. 1973 Jan;54(1):6–15. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. J., Bernard E. M., Häuser M., Armstrong D. Aerosol amphotericin B is effective for prophylaxis and therapy in a rat model of pulmonary aspergillosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1676–1679. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherertz R. J., Belani A., Kramer B. S., Elfenbein G. J., Weiner R. S., Sullivan M. L., Thomas R. G., Samsa G. P. Impact of air filtration on nosocomial Aspergillus infections. Unique risk of bone marrow transplant recipients. Am J Med. 1987 Oct;83(4):709–718. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90902-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


