Abstract
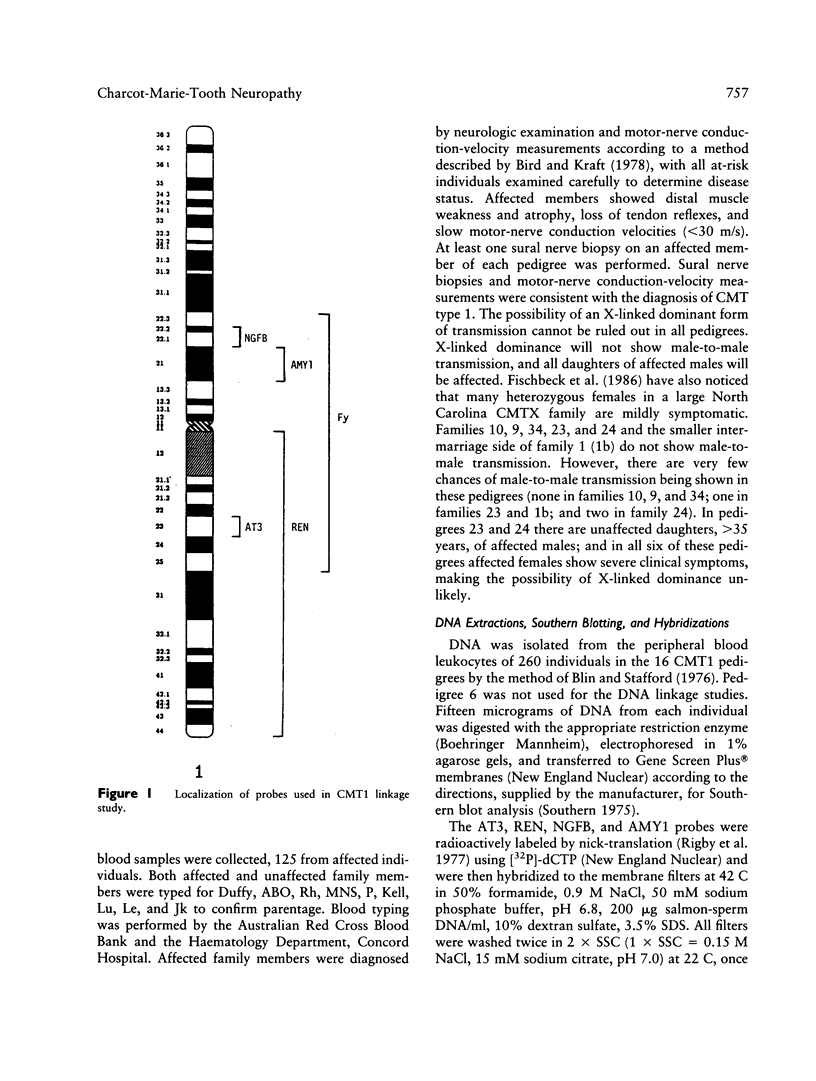
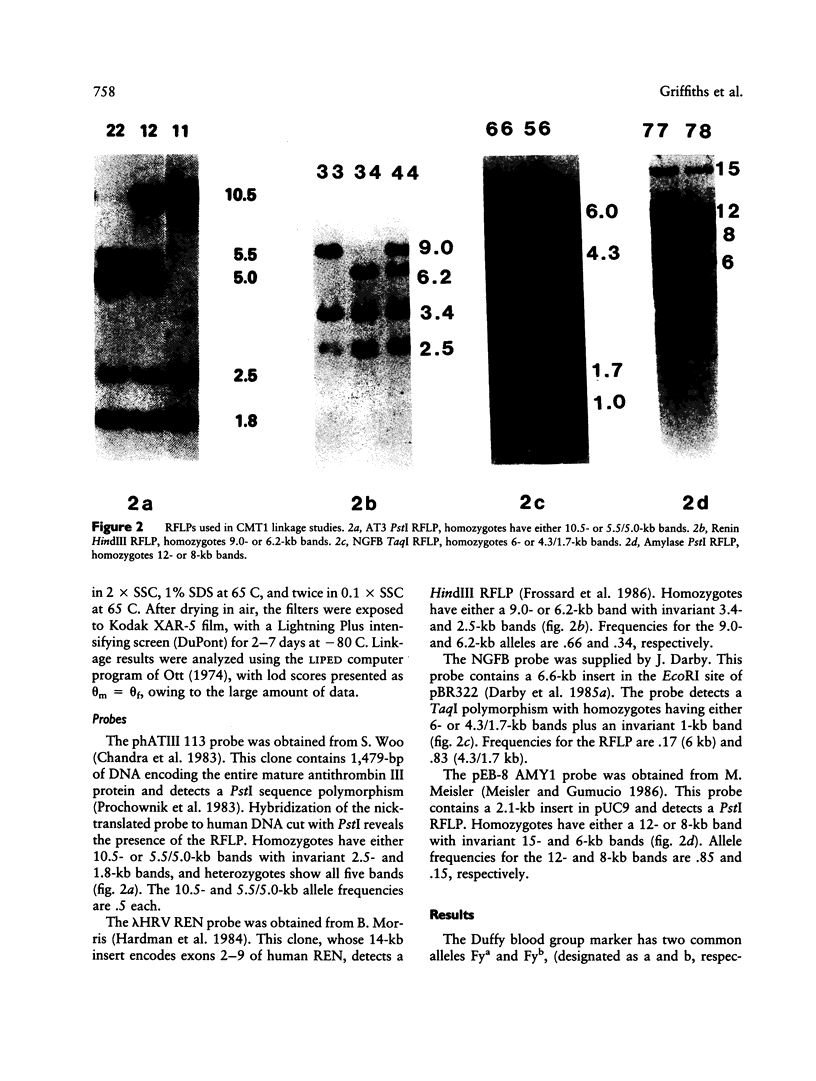
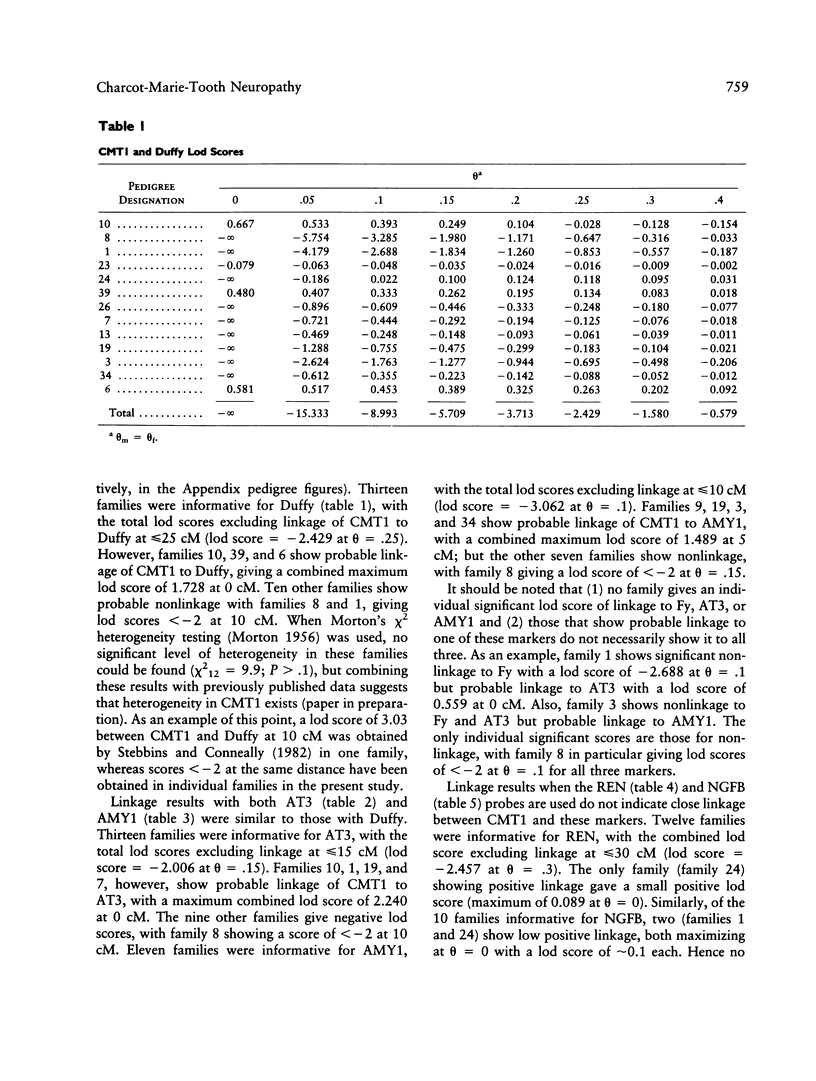
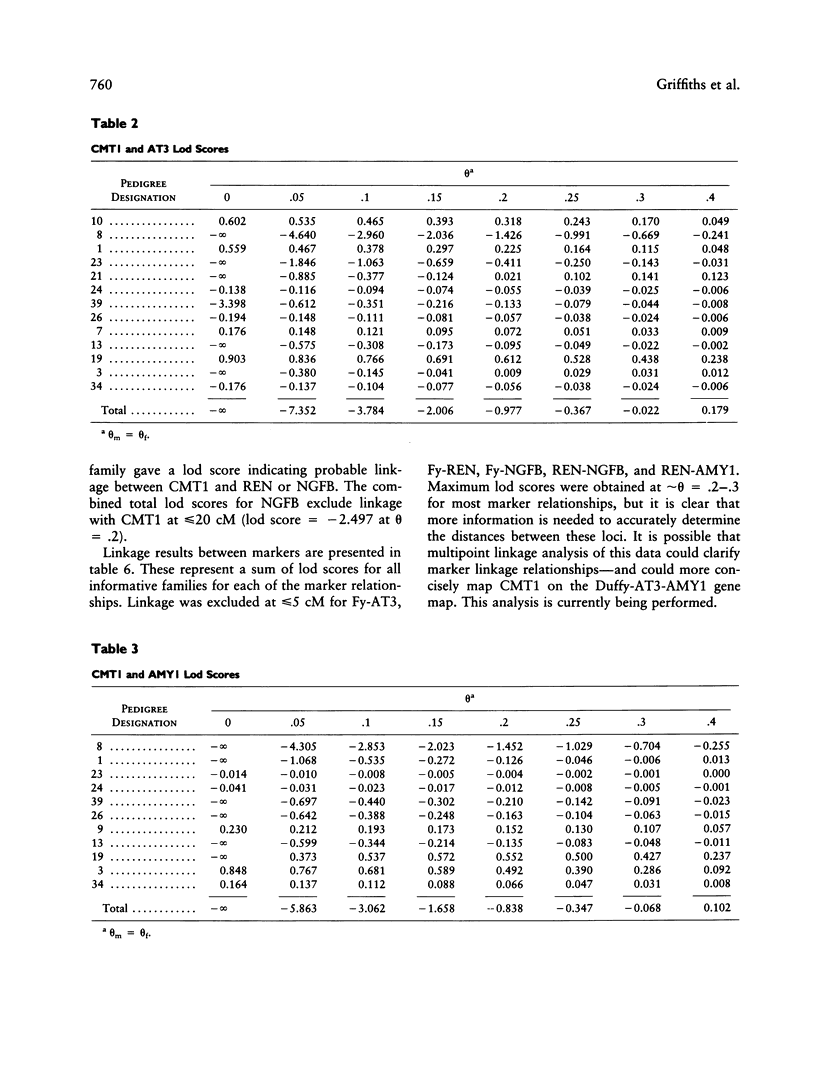
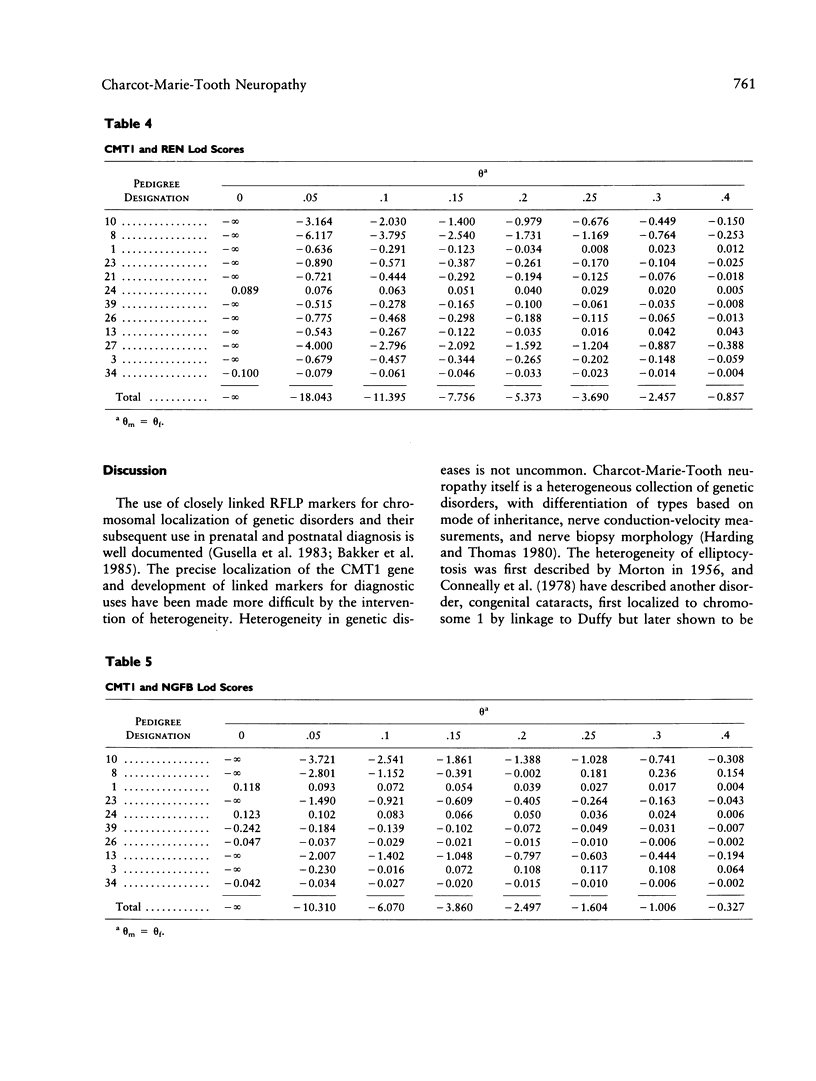
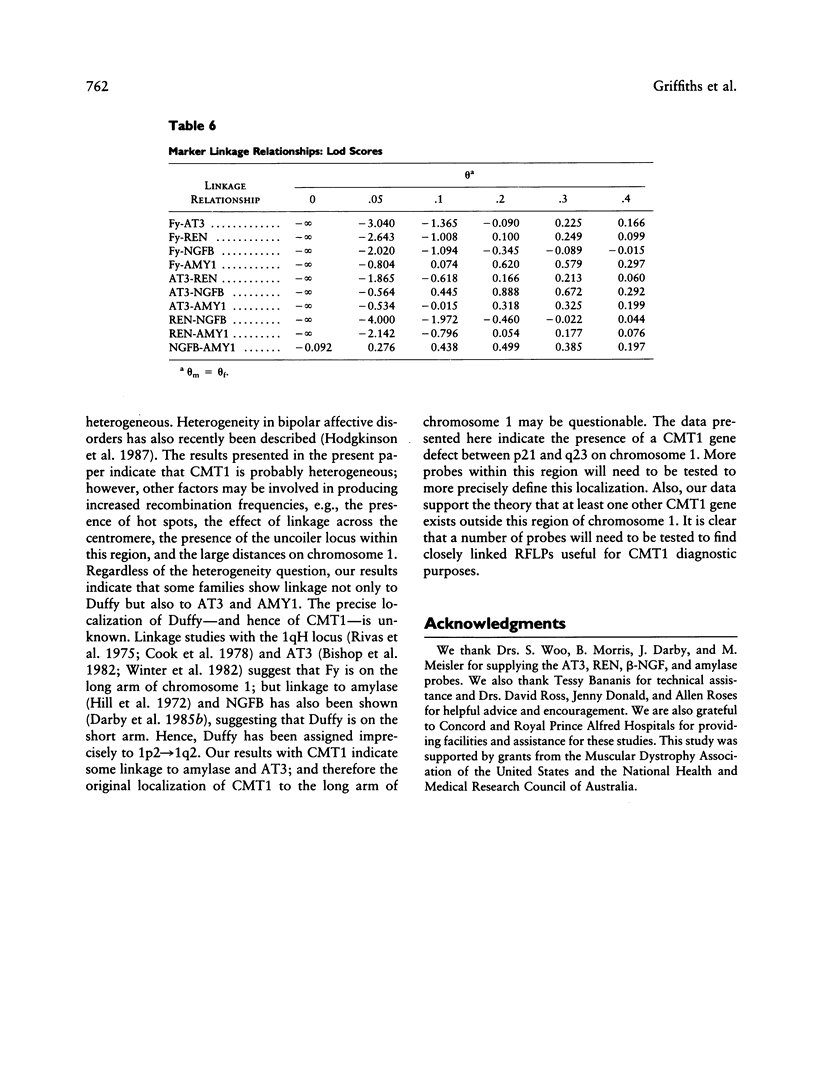
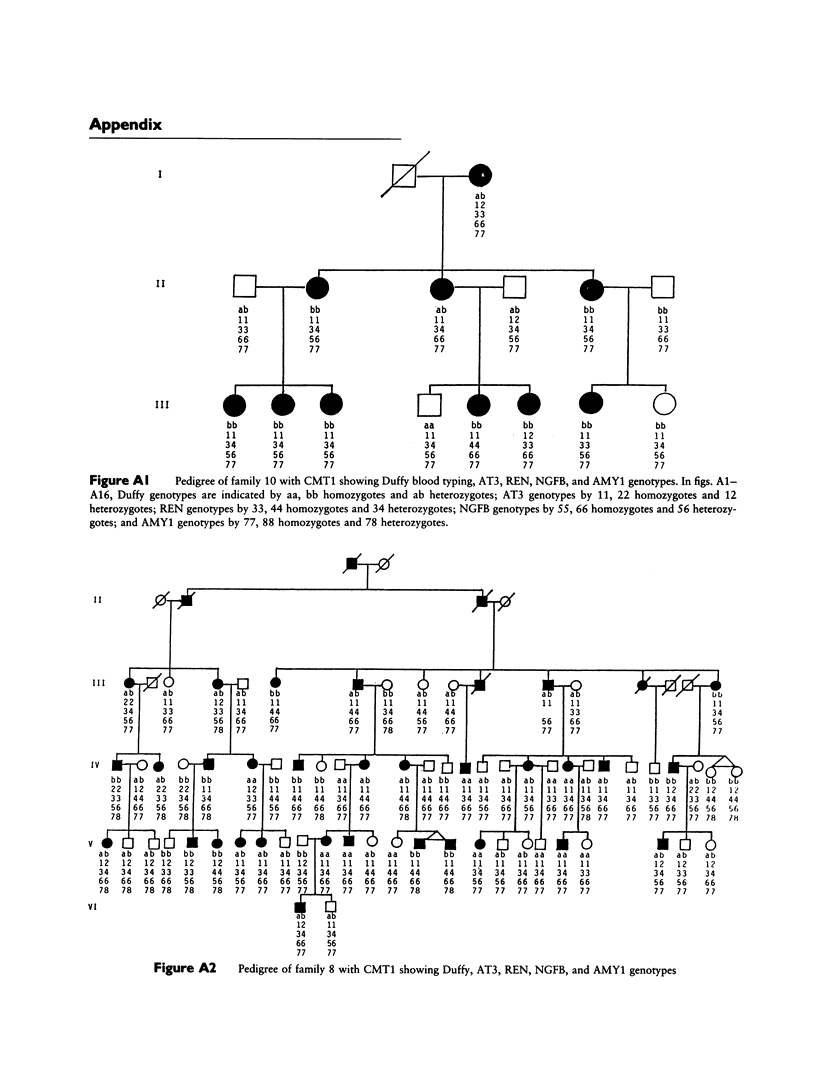
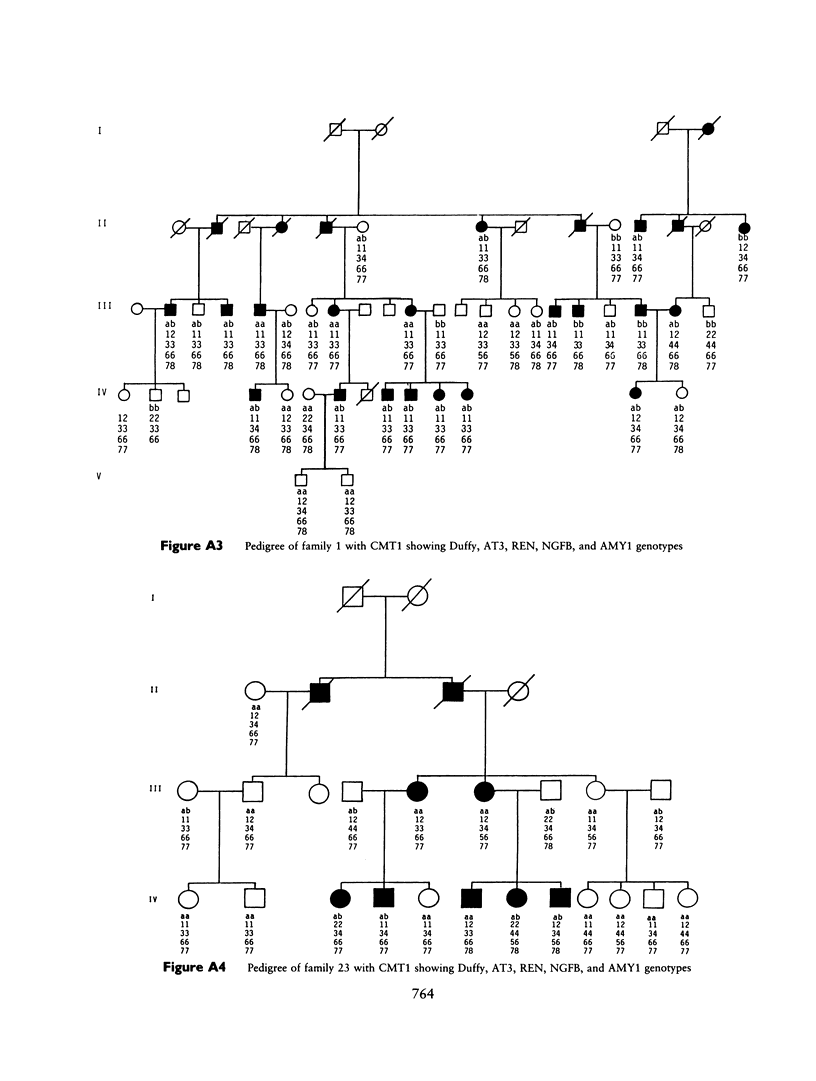
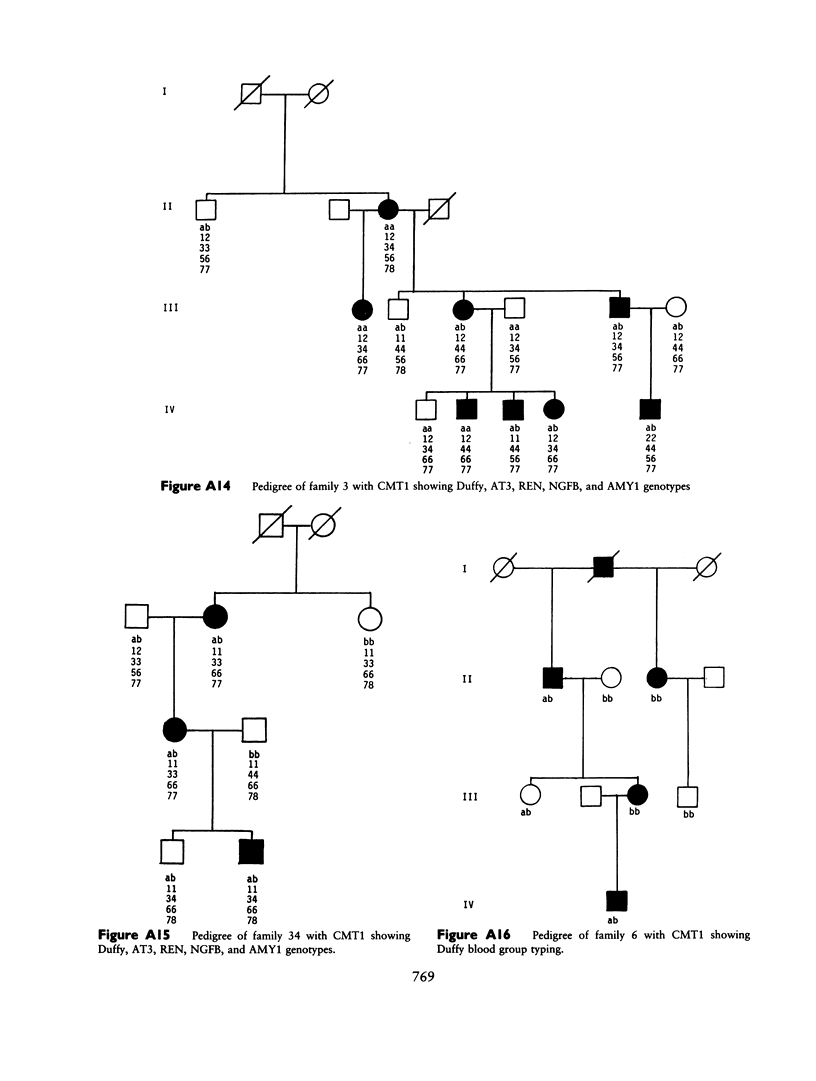
Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1 (CMT1) is an autosomal dominant disorder of peripheral nerve. The gene for CMT1 was originally localized to chromosome 1 by linkage to the Duffy blood group, but it has since been shown that not all CMT1 pedigrees show this linkage. We report here the results of linkage studies using five chromosome 1 markers--Duffy (Fy), antithrombin III (AT3), renin (REN), beta-nerve growth factor (NGFB), and salivary amylase (AMY1)--in 16 CMT1 pedigrees. The total lod scores exclude close linkage of CMT1 to any of these markers. However, individual families show probable linkage of CMT1 to Duffy, AT3, and/or AMY1. No linkage was indicated with REN or NGFB. These results indicate the possible location of a CMT1 gene between the AMY1 and AT3 loci at p21 and q23, respectively, on chromosome 1 and support the theory that there is at least one other CMT1 gene.
Full text
PDF
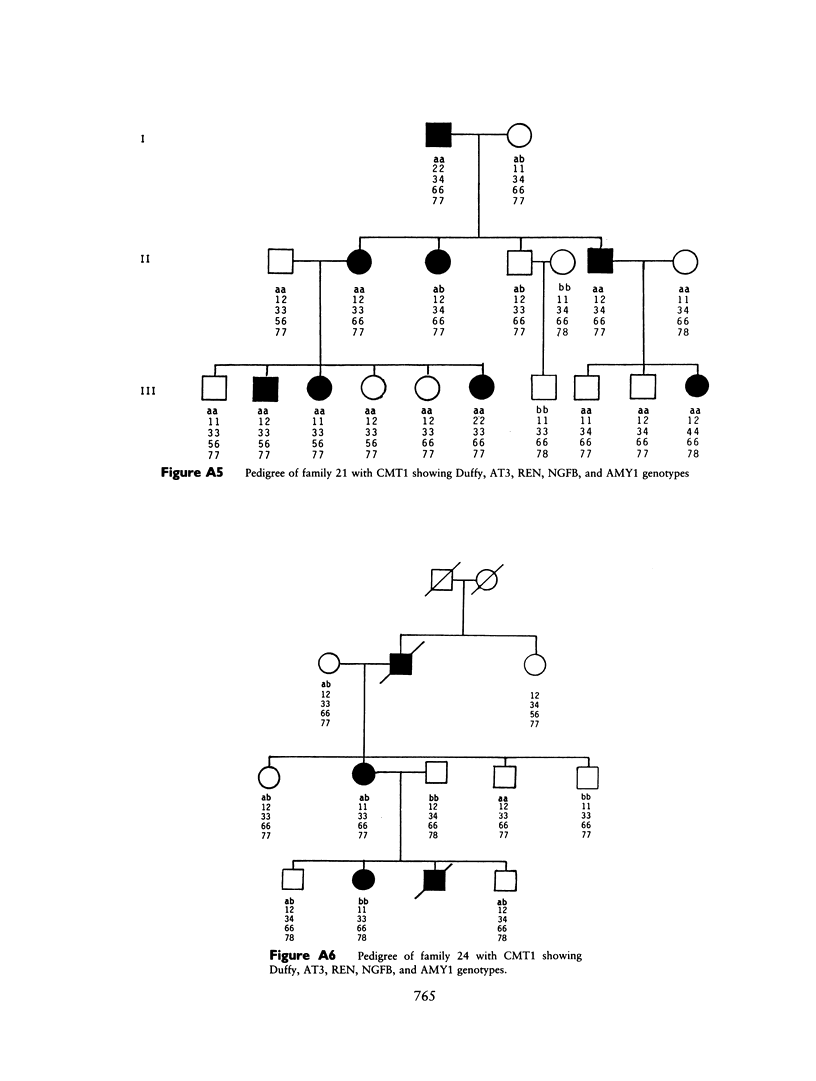
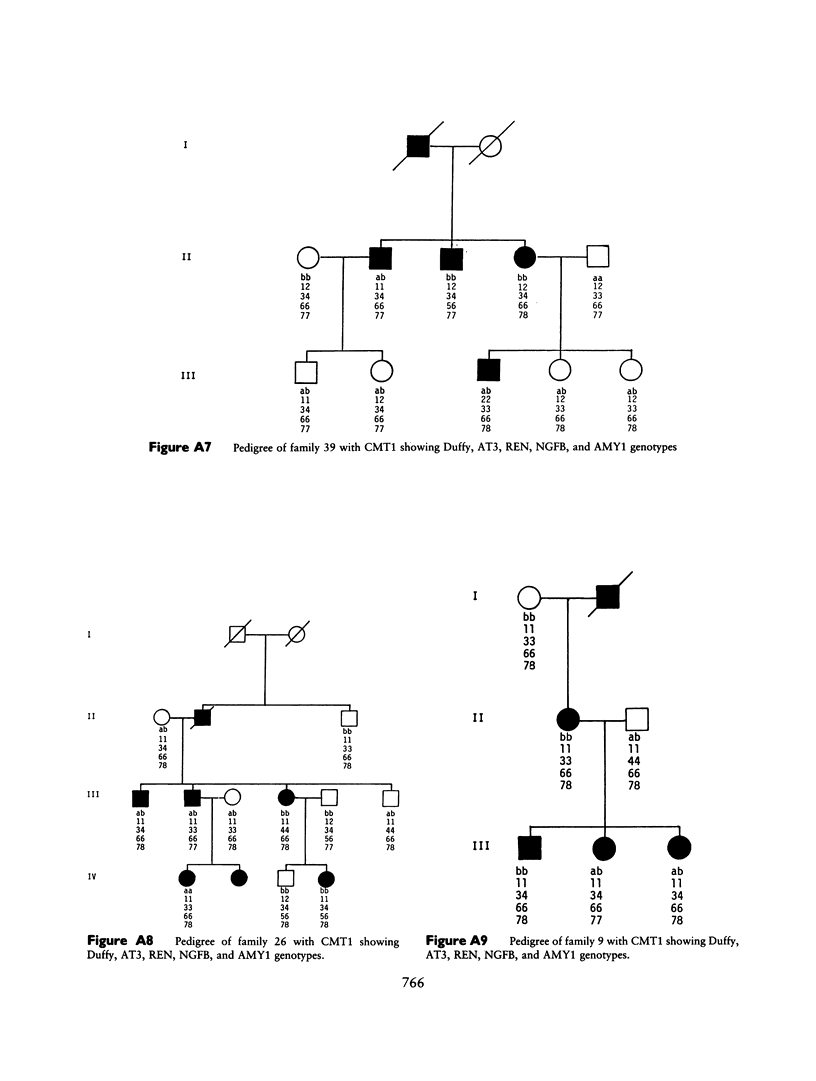
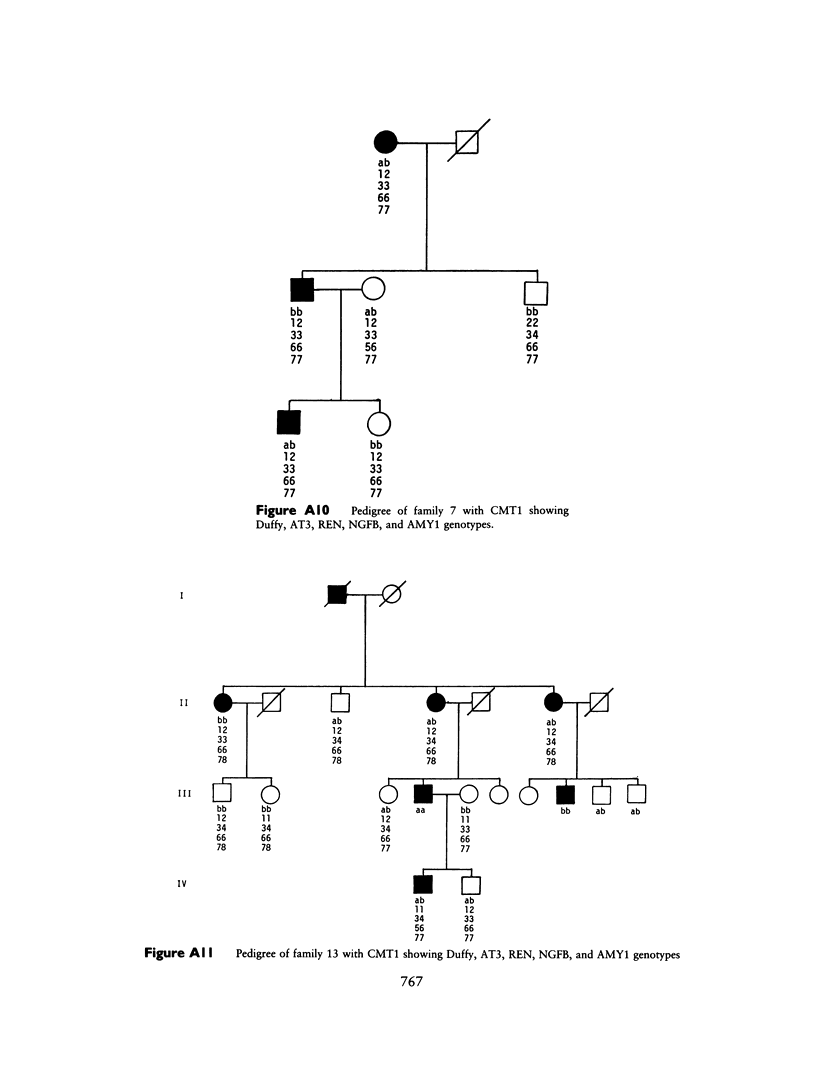
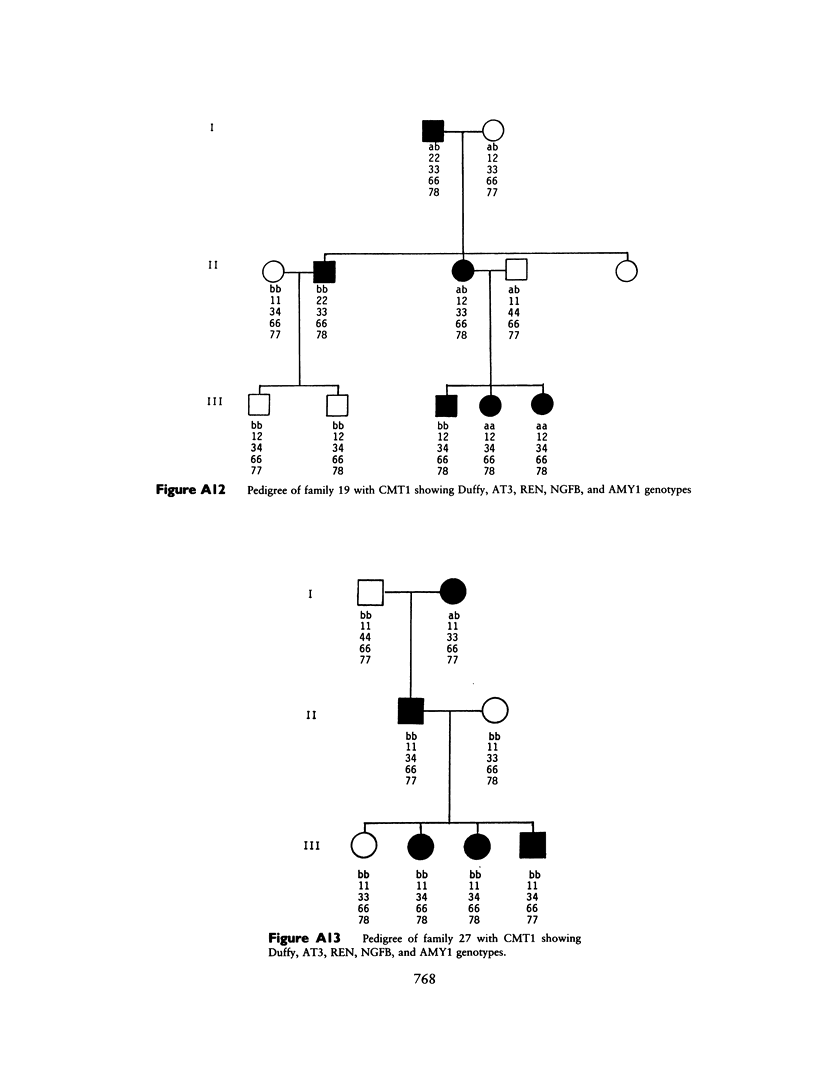


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E., Hofker M. H., Goor N., Mandel J. L., Wrogemann K., Davies K. E., Kunkel L. M., Willard H. F., Fenton W. A., Sandkuyl L. Prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection of Duchenne muscular dystrophy with closely linked RFLPs. Lancet. 1985 Mar 23;1(8430):655–658. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91325-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. D., Kraft G. H. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: data for genetic counseling relating age to risk. Clin Genet. 1978 Jul;14(1):43–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1978.tb02059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. D., Ott J., Giblett E. R., Chance P. F., Sumi S. M., Kraft G. H. Genetic linkage evidence for heterogeneity in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy (HMSN type I). Ann Neurol. 1983 Dec;14(6):679–684. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. D., Ott J., Giblett E. R. Evidence for linkage of Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy to the Duffy locus on chromosome 1. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 May;34(3):388–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock S. C., Harris J. F., Balazs I., Trent J. M. Assignment of the human antithrombin III structural gene to chromosome 1q23-25. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39(1):67–69. doi: 10.1159/000132105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance P. F., Murray J. C., Bird T. D., Kochin R. S. Genetic linkage relationships of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (HMSN-Ib) to chromosome 1 markers. Neurology. 1987 Feb;37(2):325–329. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.2.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra T., Stackhouse R., Kidd V. J., Woo S. L. Isolation and sequence characterization of a cDNA clone of human antithrombin III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1845–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Wilson A. F., Merritt A. D., Helveston E. M., Palmer C. G., Wang L. Y. Confirmation of genetic heterogeneity in autosomal dominant forms of congenital cataracts from linkage studies. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):295–297. doi: 10.1159/000130957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. J., Page B. M., Johnston A. W., Stanford W. K., Gavin J. Four further families informative for 1q and the Duffy blood group. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):378–380. doi: 10.1159/000130976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby J. K., Feder J., Selby M., Riccardi V., Ferrell R., Siao D., Goslin K., Rutter W., Shooter E. M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. A discordant sibship analysis between beta-NGF and neurofibromatosis. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jan;37(1):52–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby J. K., Kidd J. R., Pakstis A. J., Sparkes R. S., Cann H. M., Ferrell R. E., Gerhard D. G., Riccardi V., Egeland J. A., Shooter E. M. Linkage relationships of the gene for the beta subunit of nerve growth factor (NGFB) with other chromosome 1 marker loci. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39(2):158–160. doi: 10.1159/000132127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue R. P., Bias W. B., Renwick J. H., McKusick V. A. Probable assignment of the Duffy blood group locus to chromosome 1 in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):949–955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Ott J., Moore S. B., Swanson C. J., Lambert E. H. Linkage evidence for genetic heterogeneity among kinships with hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy, type I. Mayo Clin Proc. 1983 Jul;58(7):430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbeck K. H., ar-Rushdi N., Pericak-Vance M., Rozear M., Roses A. D., Fryns J. P. X-linked neuropathy: gene localization with DNA probes. Ann Neurol. 1986 Oct;20(4):527–532. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frossard P. M., Gonzalez P. A., Fritz L. C., Ponte P. A., Fiddes J. C., Atlas S. A. Two RFLPs at the human renin (ren) gene locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4380–4380. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths L. R., Nicholson G. A., Ross D. A., Zwi M. B., McLeod J. G., Mohandas T., Morris B. J. Regional chromosomal assignment of human renin gene to 1q12----qter and use in linkage studies in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;45(3-4):231–233. doi: 10.1159/000132459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiloff R. J., Thomas P. K., Contreras M., Armitage S., Schwarz G., Sedgwick E. M. Linkage of autosomal dominant type I hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy to the Duffy locus on chromosome 1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Aug;45(8):669–674. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.8.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Thomas P. K. Genetic aspects of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy (types I and II). J Med Genet. 1980 Oct;17(5):329–336. doi: 10.1136/jmg.17.5.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman J. A., Hort Y. J., Catanzaro D. F., Tellam J. T., Baxter J. D., Morris B. J., Shine J. Primary structure of the human renin gene. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):457–468. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. J., Rowe S. I., Lovrien E. W. Probable genetic linkage between human serum amylase (Amy 2 ) and Duffy blood group. Nature. 1972 Jan 21;235(5334):162–163. doi: 10.1038/235162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkinson S., Sherrington R., Gurling H., Marchbanks R., Reeders S., Mallet J., McInnis M., Petursson H., Brynjolfsson J. Molecular genetic evidence for heterogeneity in manic depression. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):805–806. doi: 10.1038/325805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. The detection and estimation of linkage between the genes for elliptocytosis and the Rh blood type. Am J Hum Genet. 1956 Jun;8(2):80–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Markham A. F., Orkin S. H. Isolation of a cDNA clone for human antithrombin III. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8389–8394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivas M. L., Conneally P. M., Lovrien E. W., Magenis R. E., Merritt A. D., Meyers D. A., Palmer C. G., Parks M., Wang L., Yu P. L. The linkage and mapping relationships of 1 qh. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;16(1-5):347–350. doi: 10.1159/000130629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter J. H., Bennett B., Watt J. L., Brown T., San Román C., Schinzel A., King J., Cook P. J. Confirmation of linkage between antithrombin III and Duffy blood group and assignment of AT3 to 1q22 lead to q25. Ann Hum Genet. 1982 Jan 1;46(Pt 1):29–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1982.tb00692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



