Abstract
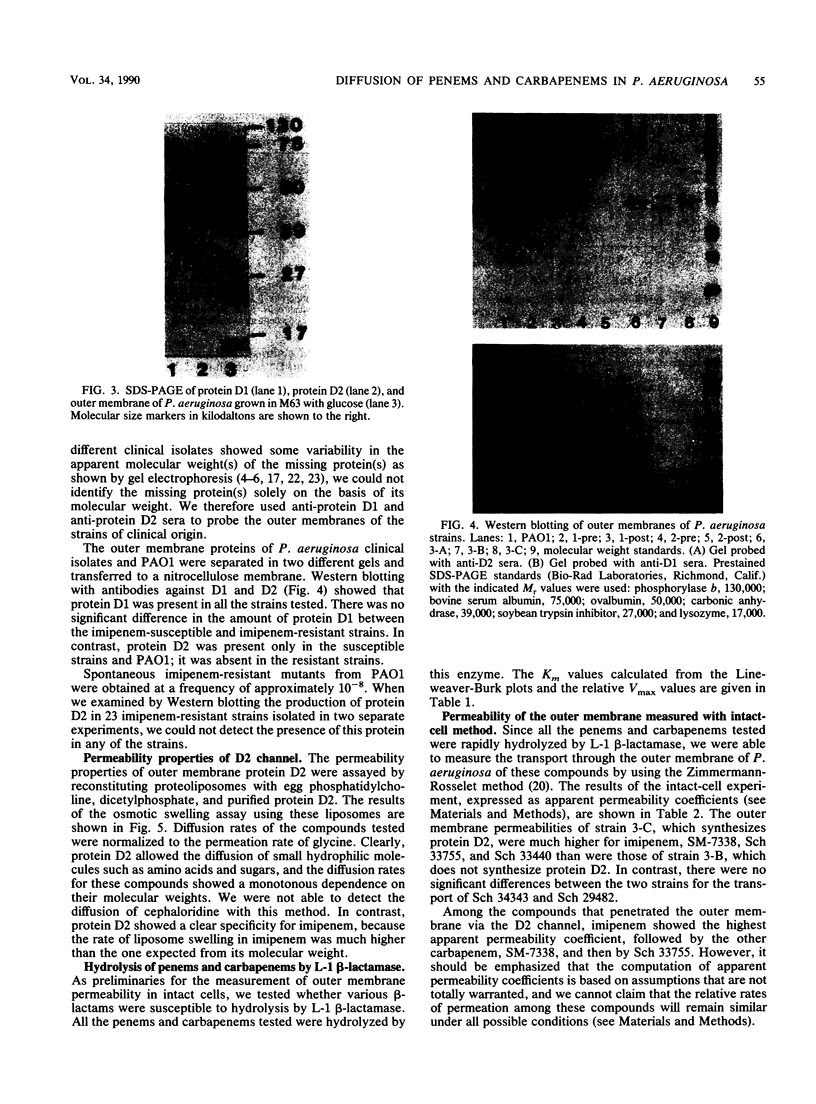
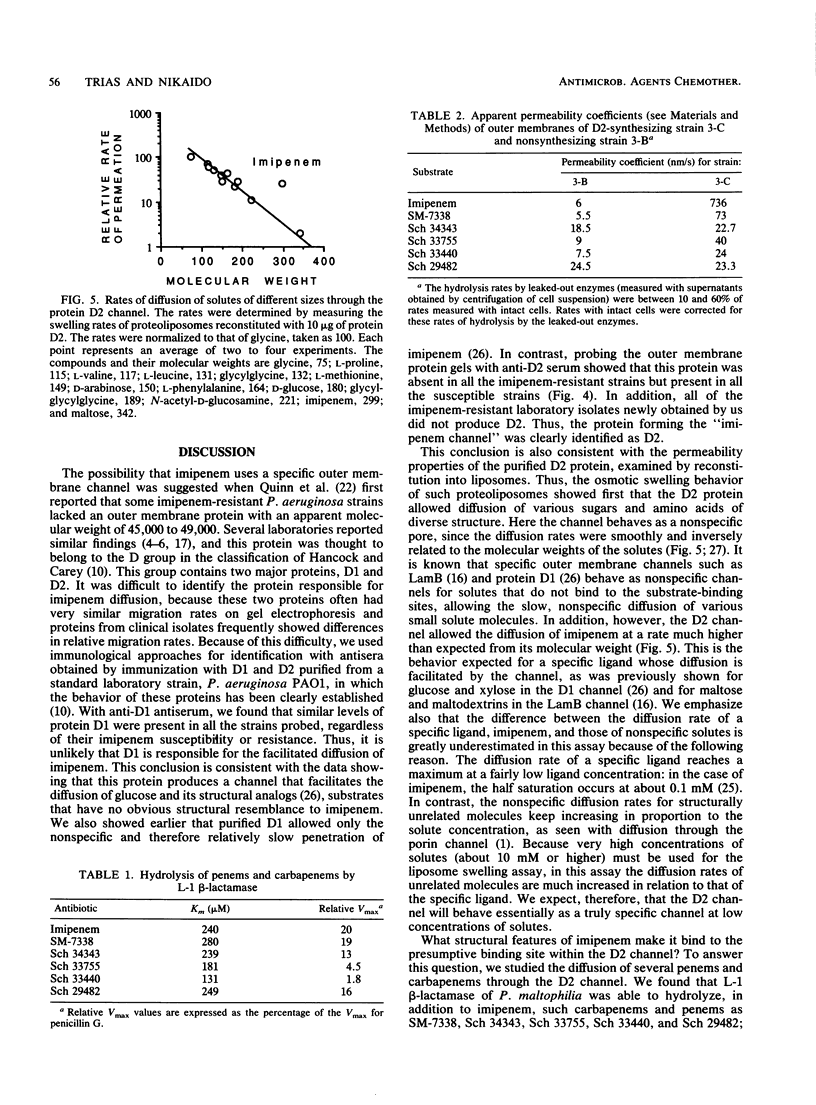
The outer membrane of imipenem-resistant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with decreased permeability to imipenem was shown by Western (immuno-) blotting to contain protein D1 and to lack protein D2. Protein D2 was purified and was shown to allow the permeation of imipenem at a rate higher than expected from its molecular weight. Spontaneous imipenem-resistant mutants of P. aeruginosa PAO1 appeared at a frequency of 10(-8) in the laboratory and did not synthesize protein D2. Experiments performed with intact cells carrying plasmid pHN4 containing the gene for L-1 beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas maltophilia showed that this channel could also be used by SM-7338, Sch 33755, and Sch 33440 but apparently not by Sch 34343 or Sch 29482.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benz R., Schmid A., Vos-Scheperkeuter G. H. Mechanism of sugar transport through the sugar-specific LamB channel of Escherichia coli outer membrane. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(1):21–29. doi: 10.1007/BF02209137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher K. H., Cullmann W., Dick W., Opferkuch W. Imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa resulting from diminished expression of an outer membrane protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):703–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher K. H., Cullmann W., Dick W., Wendt S., Opferkuch W. Imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is due to diminished expression of outer membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):681–684. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher K. H., Cullmann W., Opferkuch W. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to imipenem is independent of beta-lactamase production. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 May;19(5):700–701. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.5.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., Eisenstadt R. L., East S. J., Cornford R. J., Walker L. A., White A. J. Iron-regulated outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli K-12 and mechanism of action of catechol-substituted cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Dec;32(12):1879–1886. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.12.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufresne J., Vézina G., Levesque R. C. Cloning and expression of the imipenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase operon from Pseudomonas maltophilia in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):819–826. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heukeshoven J., Dernick R. Improved silver staining procedure for fast staining in PhastSystem Development Unit. I. Staining of sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Electrophoresis. 1988 Jan;9(1):28–32. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Aldridge K. E., Allen S. D., Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C., Gerlach E. H., Pfaller M. A. Multicenter in vitro evaluation of SM-7338, a new carbapenem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):562–565. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckey M., Nikaido H. Specificity of diffusion channels produced by lambda phage receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch M. J., Drusano G. L., Mobley H. L. Emergence of resistance to imipenem in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1892–1896. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier C., Bremer E., Schmid A., Benz R. Pore-forming activity of the Tsx protein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Demonstration of a nucleoside-specific binding site. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2493–2499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki H., Yamada H., Oikawa Y., Murakami K., Ishiguro J., Kosuzume H., Aizawa N., Mochida E. Bactericidal activity of M14659 enhanced in low-iron environments. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1648–1654. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y., Foulds J. Porin channels in Escherichia coli: studies with beta-lactams in intact cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):232–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.232-240.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Dudek E. J., DiVincenzo C. A., Lucks D. A., Lerner S. A. Emergence of resistance to imipenem during therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):289–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Studemeister A. E., DiVincenzo C. A., Lerner S. A. Resistance to imipenem in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: clinical experience and biochemical mechanisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):892–898. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Cromie K. D. Penicillin-binding proteins of gram-negative bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):699–711. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias J., Dufresne J., Levesque R. C., Nikaido H. Decreased outer membrane permeability in imipenem-resistant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1202–1206. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias J., Rosenberg E. Y., Nikaido H. Specificity of the glucose channel formed by protein D1 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 3;938(3):493–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara E., Nakae T. Identification of porins in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that form small diffusion pores. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6297–6301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through the porin channels of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):84–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Permeability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane to hydrophilic solutes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):636–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.636-642.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]