Abstract
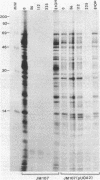
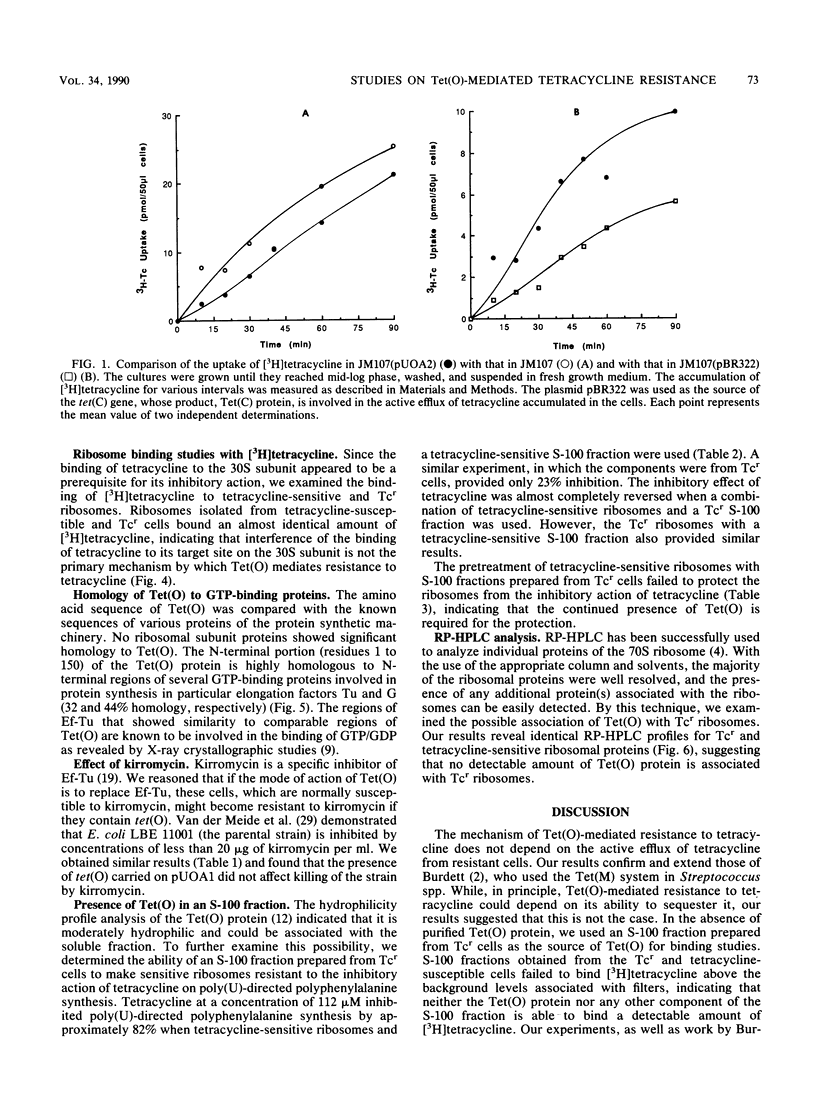
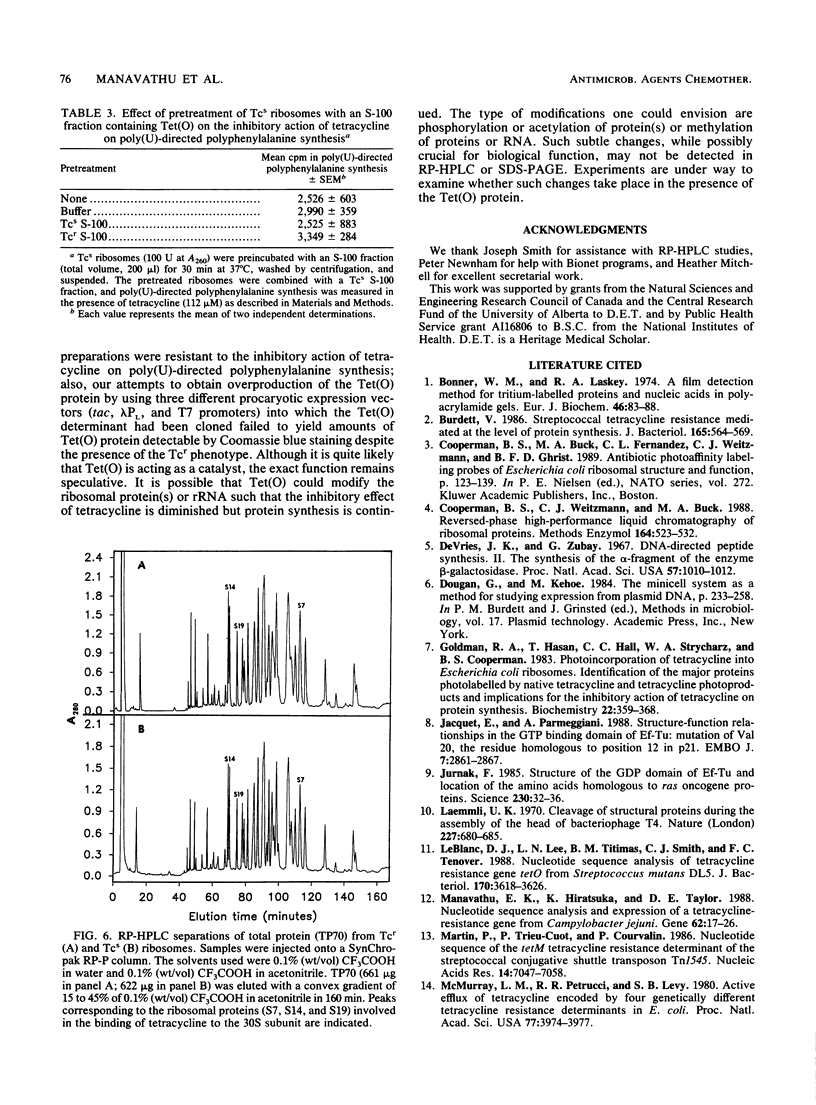
The mechanism of resistance to tetracycline in Escherichia coli mediated by the Campylobacter jejuni-derived resistance determinant Tet(O) was investigated. The cloned Tet(O) protein had no detectable effect on the intracellular accumulation of tetracycline. The presence of Tet(O) markedly diminished the inhibitory effect of tetracycline on protein synthesis both in vivo and in vitro. Ribosomes prepared from tetracycline-resistant and susceptible E. coli cells bound almost identical amounts of radiolabeled tetracycline. Thus, a reduction in the binding of the antibiotic to its target site on the ribosome is not the primary mechanism of resistance. Poly(U)-directed polyphenylalanine synthesis revealed that an S-100 fraction prepared from tetracycline-resistant cells made the ribosomes prepared from susceptible cells considerably more resistant to the inhibitory action of tetracycline. The N-terminal portion (1 to 150 residues) of Tet(O) is highly homologous to the GTP-binding domain of elongation factor Tu and to elongation factor G, indicating that the Tet(O) protein has the potential to bind GTP. These data suggest that the Tet(O) protein could function either as a tetracycline-resistant analog of this elongation factor(s) or by modifying the target sites on the ribosomes in a catalytic fashion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett V. Streptococcal tetracycline resistance mediated at the level of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):564–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.564-569.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperman B. S., Weitzmann C. J., Buck M. A. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of ribosomal proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:523–532. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVries J. K., Zubay G. DNA-directed peptide synthesis. II. The synthesis of the alpha-fragment of the enzyme beta-galactosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1010–1012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. A., Hasan T., Hall C. C., Strycharz W. A., Cooperman B. S. Photoincorporation of tetracycline into Escherichia coli ribosomes. Identification of the major proteins photolabeled by native tetracycline and tetracycline photoproducts and implications for the inhibitory action of tetracycline on protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):359–368. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet E., Parmeggiani A. Structure-function relationships in the GTP binding domain of EF-Tu: mutation of Val20, the residue homologous to position 12 in p21. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2861–2867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurnak F. Structure of the GDP domain of EF-Tu and location of the amino acids homologous to ras oncogene proteins. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):32–36. doi: 10.1126/science.3898365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Lee L. N., Titmas B. M., Smith C. J., Tenover F. C. Nucleotide sequence analysis of tetracycline resistance gene tetO from Streptococcus mutans DL5. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3618–3626. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3618-3626.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manavathu E. K., Hiratsuka K., Taylor D. E. Nucleotide sequence analysis and expression of a tetracycline-resistance gene from Campylobacter jejuni. Gene. 1988;62(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90576-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Trieu-Cuot P., Courvalin P. Nucleotide sequence of the tetM tetracycline resistance determinant of the streptococcal conjugative shuttle transposon Tn1545. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7047–7058. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry L., Petrucci R. E., Jr, Levy S. B. Active efflux of tetracycline encoded by four genetically different tetracycline resistance determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3974–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnuki T., Katoh T., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Molecular cloning of tetracycline resistance genes from Streptomyces rimosus in Streptomyces griseus and characterization of the cloned genes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1010–1016. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1010-1016.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. H., Levy S. B. The cryptic tetracycline resistance determinant on Tn4400 mediates tetracycline degradation as well as tetracycline efflux. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Dec;32(12):1797–1800. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.12.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador R., Brown J. T., Roberts M., Urdea M. S. Homology of the TetM with translational elongation factors: implications for potential modes of tetM-conferred tetracycline resistance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1218–1218. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer B. S., Salyers A. A. Characterization of a novel tetracycline resistance that functions only in aerobically grown Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1423–1429. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1423-1429.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer B. S., Salyers A. A. Novel aerobic tetracycline resistance gene that chemically modifies tetracycline. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):148–153. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.148-153.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Courvalin P. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1107–1112. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., De Grandis S. A., Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Transmissible plasmids from Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):831–835. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Garner R. S., Allan B. J. Characterization of tetracycline resistance plasmids from Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Dec;24(6):930–935. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.6.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Hiratsuka K., Ray H., Manavathu E. K. Characterization and expression of a cloned tetracycline resistance determinant from Campylobacter jejuni plasmid pUA466. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2984–2989. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2984-2989.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener L., Brimacombe R. Protein binding sites on Escherichia coli 16S RNA; RNA regions that are protected by proteins S7, S14 and S19 in the presence or absence of protein S9. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3653–3670. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Kastelein R. A., Vijgenboom E., Bosch L. tuf gene dosage effects on the intracellular concentration of EF-TuB. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;130(2):409–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]